|
Pakuan Pajajaran
Pakuan Pajajaran ( Sundanese: ᮕᮊᮥᮝᮔ᮪ᮕᮏᮏᮛᮔ᮪; known as Dayeuh Pakuan/Pakwan or Pajajaran) was the fortified capital city of Sunda Kingdom. The location roughly corresponds to modern Bogor city in West Java, Indonesia, approximately around the site of Batu Tulis. The site is revered as the spiritual home of Sundanese people as it contains much of the shared identity and history of Sundanese people. The city was settled in at least the 10th century but did not gain major political importance until Sri Baduga Maharaja established it as the royal capital of the Sunda kingdom in the 15th century. In 1513, the city was visited by its first European visitor, Tomé Pires, the Portuguese envoy. According to his report, the city of ''Daio'' (''Dayeuh'' is a Sundanese term for "capital city") was a great city, with a population of around 50,000 inhabitants. After the reign of King Jayadewata (Sri Baduga Maharaja), Pakuan Pajajaran served as the royal capital for sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Kingdom
The Sunda Kingdom ( , ) was a Sundanese people, Sundanese Hindu kingdom located in the western portion of the island of Java from 669 to around 1579, covering the area of present-day Banten, Jakarta, West Java, Lampung, and the western part of Central Java. The capital of the Sunda Kingdom moved several times during its history, shifting between the Galuh (Kawali) area in the east and Pakuan Pajajaran in the west. The Sunda Kingdom reached its peak during the reign of King Sri Baduga Maharaja, whose reign from 1482 to 1521 is traditionally remembered as an age of peace and prosperity among Sundanese people. According to primary historical records such as the ''Bujangga Manik'' manuscript, the eastern border of the kingdom was the Pemali River (Ci Pamali; the present-day Brebes River) and the Serayu River (Ci Sarayu) in Central Java. Most accounts of the Sunda Kingdom come from primary historical records from the 16th century. The kingdom's inhabitants were primarily the eponymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingam
A lingam ( , lit. "sign, symbol or mark"), sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or Aniconism, aniconic representation of the Hinduism, Hindu Hindu deities, god Shiva in Shaivism. The word ''lingam'' is found in the Upanishads and Indian epic poetry, epic literature, where it means a "mark, sign, emblem, characteristic", the "evidence, proof, symptom" of Shiva and Shiva's power. The lingam of the Shaivism tradition is a short cylindrical pillar-like symbol of Shiva, made of stone, metal, gem, wood, clay or precious stones. It is often represented within a disc-shaped platform, the ''yoni'' – its feminine counterpart, consisting of a flat element, horizontal compared to the vertical lingam, and designed to allow liquid offerings to drain away for collection. The ''lingam'' is an emblem of generative and destructive power. While rooted in representations of the male sexual organ, the ''lingam'' is regarded as the "outward symbol" of the "formless reali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babad
Javanese literature has a very large historical component. In all sorts of texts, such as laudatory poems, chronicles, and travelogues, writers have interpreted the how and why of certain circumstances. These texts are important for the knowledge of Javanese perspectives on the past. Scholars of Javanese history have paid much attention to theoretical questions, aiming at a balanced evaluation of Javanese historiography next to Western historiography. In doing so they focused on Old and Modern Javanese sources, drawing both on written sources and archaeological and epigraphic material. The debate continues up to the present. Babads ''Babads'' as a genre belong to the traditional literature. A characteristic of this kind of literature is that it is written in metrical form and is governed by a set of strict conventions. In traditional Javanese society, prose (''gancaran'') was not considered to be ''belles letters'' but was considered to be merely sets of notes or ''aide-mémo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suma Oriental
Suma may refer to: Places * Suma, Azerbaijan, a village * Suma, East Azerbaijan, a village in Iran * Sowmaeh, Ardabil, also known as Şūmā, a village in Iran * Suma-ku, Kobe, one of nine wards of Kobe City in Japan ** Suma Station, a railway station in the ward * Suma Municipality, Yucatán, Mexico * Suma (ward), an administrative ward in Rungwe District, Mbeya Region, Tanzania * Suma River, Mbeya Region, Tanzania People Ethnic groups * Suma people, an indigenous people of Mexico and the United States * The Suma, a subgroup of the African Gbaya people Given name * Suma Akhter, Bangladeshi kabaddi player * Suma Bhattacharya, British fintech entrepreneur, dancer, and actress * Suma Josson, Indian-American journalist and filmmaker * Suma Kanakala (born 1975), Indian television presenter * Suma Shirur (born 1974), Indian sport shooter * Suma Sudhindra, Indian classical musician Nickname * Suma Chakrabarti (born 1959), British civil servant * Peter Sumic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carita Parahyangan
Carita Parahyangan (, official Sundanese script: ) is a text contained in a single manuscript written around the late 16th century, registered as Kropak 406 from the former collection of the Bataviaasch Genootschap voor Kunsten en Wetenschappen (Batavian Society of Arts and Sciences), now in the ''Perpustakaan Nasional'' (National Library) in Jakarta. It was identified as early as 1882 by Holle as the "Carita Parahyangan", the name derived from Parahyangan highlands in West Java, originated from Sundanese words which mean "the abode of hyangs (gods)". Since that time the manuscript has received much scholarly attention. The Carita Parahyangan tells the history of the Sunda Kingdom, from the early Galuh period in the early 8th century, during the era of Wretikandayun and King Sanjaya, until the fall of Pakuan Pajajaran in the 16th century, the capital of Sunda kingdom under invasion by the Banten Sultanate assisted by the Cirebon and Demak Sultanates. The manuscript consists of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bujangga Manik
Bujangga Manik is one of the precious remnants of Old Sundanese literature. It is told in octosyllabic lines — the metrical form of Old Sundanese narrative poetry — in palm-leaf manuscript kept in the Bodleian Library of Oxford University in England, since 1627 or 1629 (MS Jav. b. 3 (R), cf. Noorduyn 1968:469, Ricklefs/Voorhoeve 1977: 181). Bujangga Manik altogether consists of 29 palm leaves, each containing approximately some 56 lines of 8 syllables. The final part of the text has been transmitted in a lacunary form. Not only is the end lacking, there are two other lacunae. The first break occurs after leaf 26, line 1476. Main character The hero of the literature is Prabu (English: Prince) Jaya Pakuan alias Bujangga Manik, a Sundanese Hindu rishi, who, though a prince at the court of Pakuan Pajajaran (capital city of Sunda kingdom, which was located near present-day Bogor city in western part of Java island), preferred to live a life of a man of religion. As a hermit he m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscription
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literature, literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
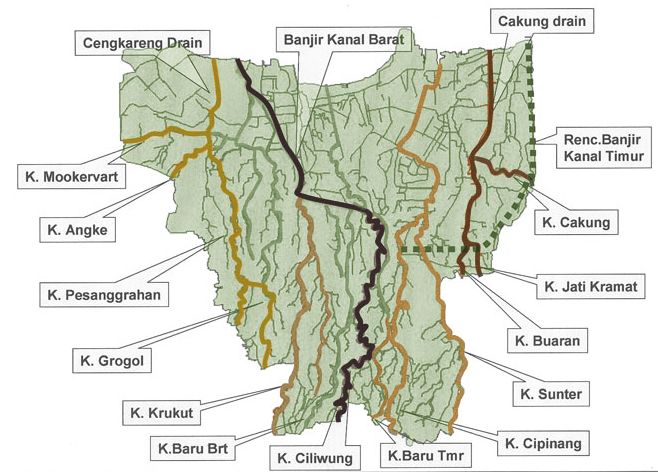
Ciliwung
The Ciliwung (often written as Ci Liwung as the "ci" prefix simply translates as "river"; also as Tjiliwoeng in Dutch, Sundanese: ᮎᮤᮜᮤᮝᮥᮀ) is a 119 km long river in the northwestern region of Java where it flows through two provinces, West Java and the special region of Jakarta. The natural estuary of the Ciliwung, known as the Kali Besar ("Big River"), was an important strategic point for trade in the precolonial and colonial periods and was instrumental in the founding of the port city of Jakarta, but has been lost from a reorganization of the watercourse of the rivers around the area into canals. Etymology The etymology of ''Ciliwung'' is uncertain; the initial syllable "ci" means "river"; of the "liwung" part, the two least implausible assumptions are "the whirlpool" (compare Sundanese ''liwung'' "be distressed, upset") or "the meandering one" (compare Malay ''liuk'', ''liut'' "to twist"). It is possible that the name originated from one of the many epit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisadane River
The Cisadane River is a long river in northern West Java, Indonesia. Note that the prefixed syllable "Ci" means river, so to avoid tautology the true translation is "Sadane River". The river has its source at Mount Pangrango and passes through Bogor and Tangerang before flowing to the Java Sea. The rivers in Banten, the westernmost province of Java, run roughly parallel to each other. The main ones are the Peteh, called the Banten on the lower reaches near the city of Kota Banten, the Ujung, which enters the sea at Pontang, the Durian, which enters the sea at Tanara, the Manceuri, and the Sadane. The Ci Sadane rises in the mountainous region of Priyangan and 1682 formed the border between the Dutch East India Company (VOC) territory and Batavia (modern Jakarta). The Durian, Manceuri, and Sadane rivers flow through the Tangerang Plain. In 1911 the colonial government started to prepare an irrigation plan, and in 1914 determined that various tracts in the plain should be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |