|
Pain Management In Children
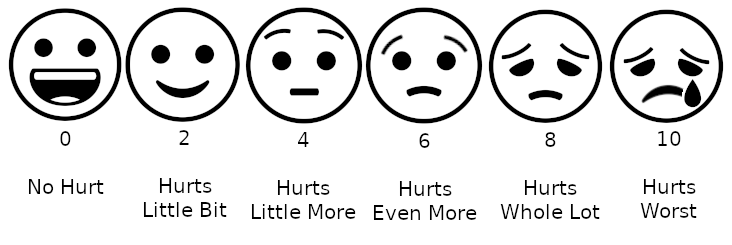
Pain management in children is the assessment and treatment of pain in infants and children. Types Acute Usually, acute pain usually has an obvious cause and is expected to last a few days or weeks. It is usually managed with medication and non-pharmacological treatment to provide comfort. Acute pain indicates assessment, treatment, and prevention are needed. While a child is experiencing pain, physiological consequences can jeopardize healing and recovery. Unrelieved pain can cause alkalosis and hypoxemia that result from rapid, shallow breathing. This shallow breathing can lead to fluid in the lungs, restricting coughing ability. Pain can cause an increase in blood pressure and heart rate, putting stress on the heart. Pain also increases the release of anti-inflammatory steroids that reduce the ability to fight infection, increase the metabolic rate, and affect healing. Another harmful outcome of acute pain is an increase in sympathetic output, such as the inability to urinate. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediatrics
Pediatrics (American English) also spelled paediatrics (British English), is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, Adolescence, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, pediatrics covers many of their youth until the age of 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, but some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults up to 25. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A physician, medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word ''pediatrics'' and its cognates mean "healer of children", derived from the two Ancient Greek, Greek words: (''pais'' "child") and (''iatros'' "doctor, healer"). Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties (e.g. neonatology requires reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord Injury
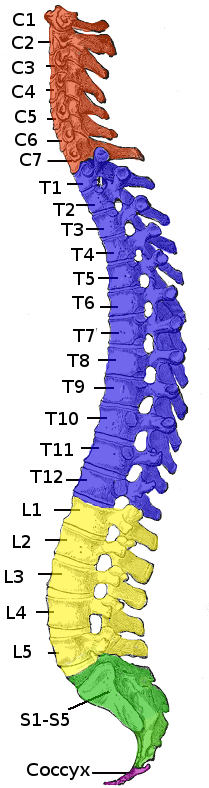
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions. Symptoms of spinal cord injury may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is a human condition involving focused attention (the selective attention/selective inattention hypothesis, SASI), reduced peripheral awareness, and an enhanced capacity to respond to suggestion.In 2015, the American Psychological Association Division 30 defined hypnosis as a "state of consciousness involving focused attention and reduced peripheral awareness characterized by an enhanced capacity for response to suggestion". For critical commentary on this definition, see: There are competing theories explaining hypnosis and related phenomena. ''Altered state'' theories see hypnosis as an altered state of mind or trance, marked by a level of awareness different from the ordinary state of consciousness. In contrast, ''non-state'' theories see hypnosis as, variously, a type of placebo effect,Kirsch, I., "Clinical Hypnosis as a Nondeceptive Placebo", pp. 211–25 in Kirsch, I., Capafons, A., Cardeña-Buelna, E., Amigó, S. (eds.), ''Clinical Hypnosis and Self-Regul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is the technique of gaining greater awareness of many physiology, physiological functions of one's own body by using Electronics, electronic or other instruments, and with a goal of being able to Manipulation (psychology), manipulate the body's systems at will. Humans conduct biofeedback naturally all the time, at varied levels of consciousness and intentionality. Biofeedback and the biofeedback loop can also be thought of as Emotional self-regulation, self-regulation. Some of the processes that can be controlled include Electroencephalography, brainwaves, muscle tone, skin conductance, heart rate and pain perception. Biofeedback may be used to improve health, performance, and the physiological changes that often occur in conjunction with changes to thoughts, emotions, and behavior. Recently, technologies have provided assistance with intentional biofeedback. Eventually, these changes may be maintained without the use of extra equipment, for no equipment is necessar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acupuncture
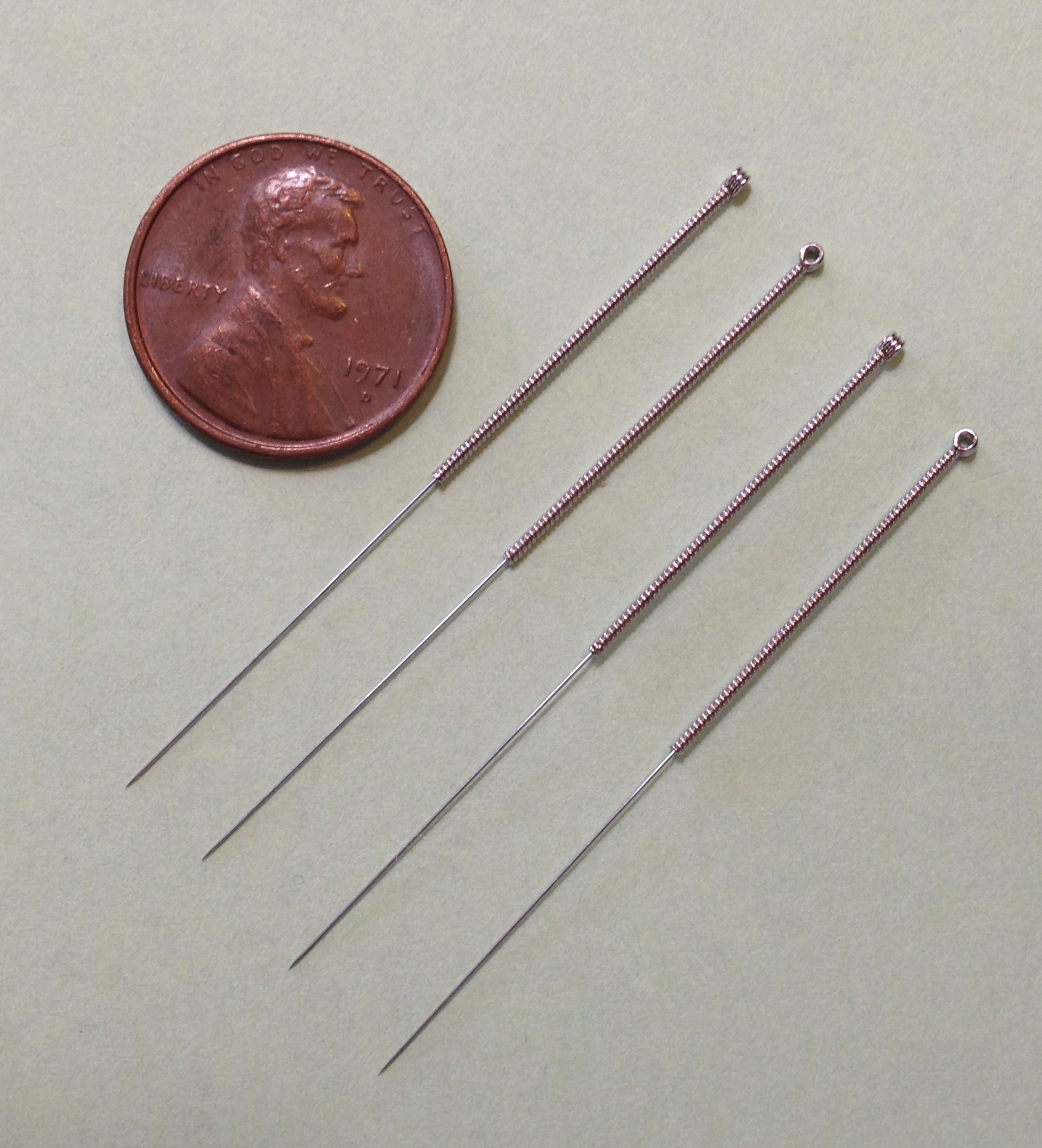
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery. There is a range of acupuncture technological variants that originated in different philosophies, and techniques vary depending on the country in which it is performed. However, it can be divided into two main foundational philosophical applications and approaches; the first being the modern standardized form called eight principles TCM and the second being an older system that is based on the ancient Daoist '' wuxing'', better known as the five elements or phases in the West. Acupuncture is most often used to attempt pain relief, though acupuncturists say that it can also be used for a wide range of other conditions. Acupuncture is typically used in combination with other forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palliative Care
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Many definitions of palliative care exist. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes palliative care as:"an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problem associated with life-threatening illness, through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial, and spiritual". Since the 1990s, many palliative care programs involved a disease-specific approach. However, as the field developed throughout the 2000s, the WHO began to take a broader patient-centered approach that suggests that the principles of palliative care should be applied as early as possible to any chronic and ultimatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Pain
Pain in cancer may arise from a tumor compressing or infiltrating nearby body parts; from treatments and diagnostic procedures; or from skin, nerve and other changes caused by a hormone imbalance or immune response. Most chronic (long-lasting) pain is caused by the illness and most acute (short-term) pain is caused by treatment or diagnostic procedures. However, radiotherapy, surgery and chemotherapy may produce painful conditions that persist long after treatment has ended. The presence of pain depends mainly on the location of the cancer and the stage of the disease. At any given time, about half of all people diagnosed with malignant cancer are experiencing pain, and two-thirds of those with advanced cancer experience pain of such intensity that it adversely affects their sleep, mood, social relations and activities of daily living. With competent management, cancer pain can be eliminated or well controlled in 80% to 90% of cases, but nearly 50% of cancer patients in the devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venlafaxine
Venlafaxine, sold under the brand name Effexor among others, is an antidepressant medication of the serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Studies have shown that venlafaxine improves post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as a recommended first-line treatment. It may also be used for chronic neuropathic pain. It is taken orally (swallowed by mouth). It is also available as the salt venlafaxine besylate (venlafaxine benzenesulfonate monohydrate) in an extended-release formulation (Venbysi XR). Common side effects include loss of appetite, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness, sweating, insomnia, drowsiness and sexual problems. Severe side effects include an increased risk of suicide, mania, and serotonin syndrome. Antidepressant withdrawal syndrome may occur if stopped. A meta-analysis of randomized trials in depression found an inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregabalin
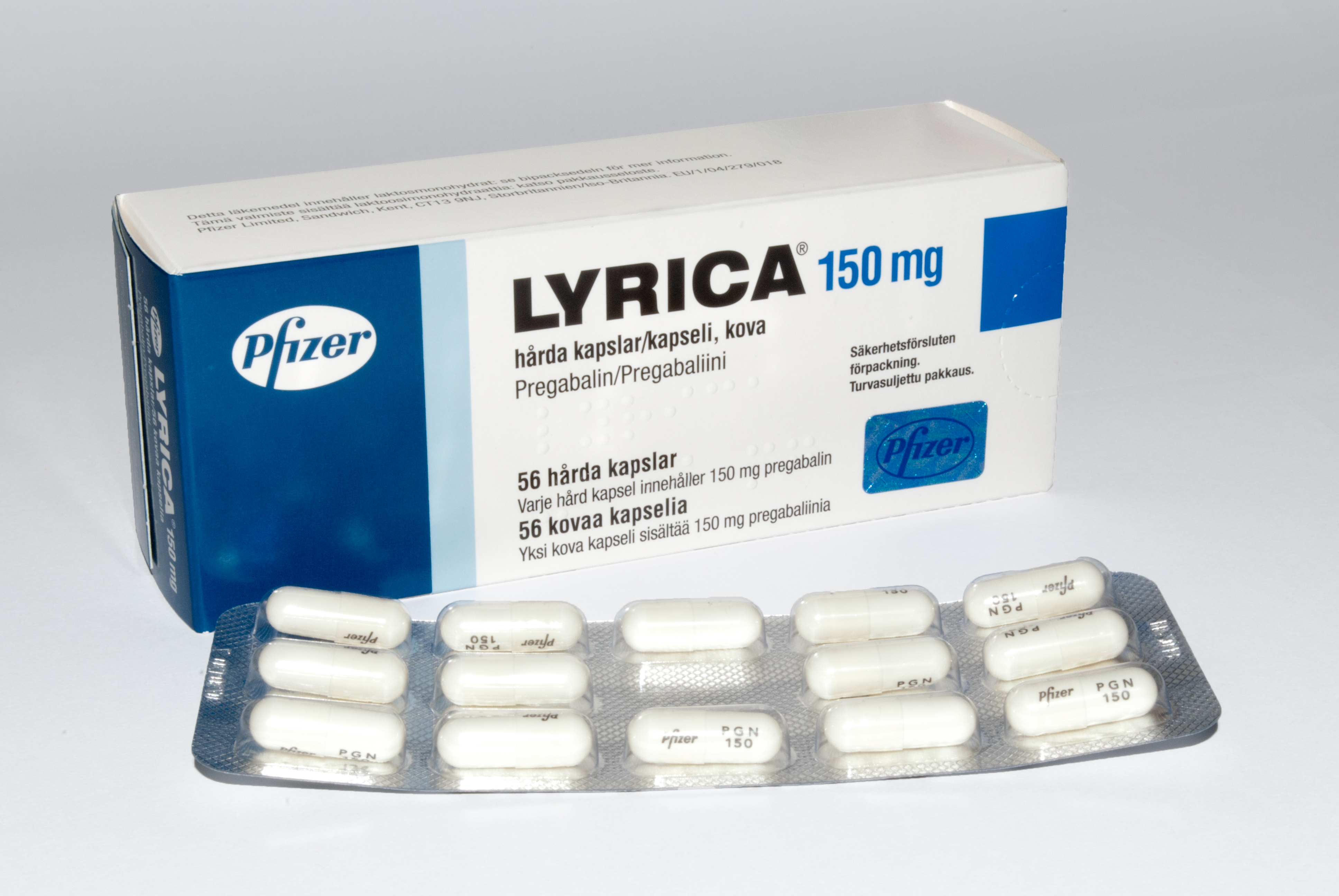
Pregabalin, sold under the brand name Lyrica among others, is an anticonvulsant, analgesic, and anxiolytic amino acid medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, restless legs syndrome, opioid withdrawal, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and shingles. Pregabalin also has allodynia, antiallodynic properties. Its use in epilepsy is as an add-on therapy for partial seizures. When used before surgery, it reduces pain but results in greater sedation and visual disturbances. It is taken oral administration, by mouth. Common side effects can include headache, dizziness, somnolence, sleepiness, euphoria, confusion, trouble with memory, Ataxia, poor coordination, dry mouth, problems with vision, and weight gain. Serious side effects may include angioedema, kidney damage and drug misuse. As with all other drugs approved by the FDA for treating epilepsy, the pregabalin labeling warns of an increased suicide risk when combined with other drugs. When pregabalin i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabapentin
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given gabapentin for diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia have a meaningful benefit. Gabapentin, like other gabapentinoid drugs, acts by decreasing activity of the α2δ-1 protein, coded by the CACNA2D1 gene, first known as an auxiliary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels. However, see Pharmacodynamics, below. By binding to α2δ-1, gabapentin reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters (primarily glutamate) and as a result, reduces excess excitation of neuronal networks in the spinal cord and brain. Sleepiness and dizziness are the most common side effects. Serious side effects in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the uncontrolled and excessive firing of neurons during seizures and in doing so can also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain. Conventional antiepileptic drugs have diverse mechanisms of action but many block sodium channels or enhance γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA) function. Several antiepileptic drugs have multiple or uncertain mechanisms of action. Next to voltage-gated sodium channels and components of the GABA system, their targets include GABAA receptors, the GABA transporter type 1, and GABA transaminase. Additional targets include voltage-gate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |