|
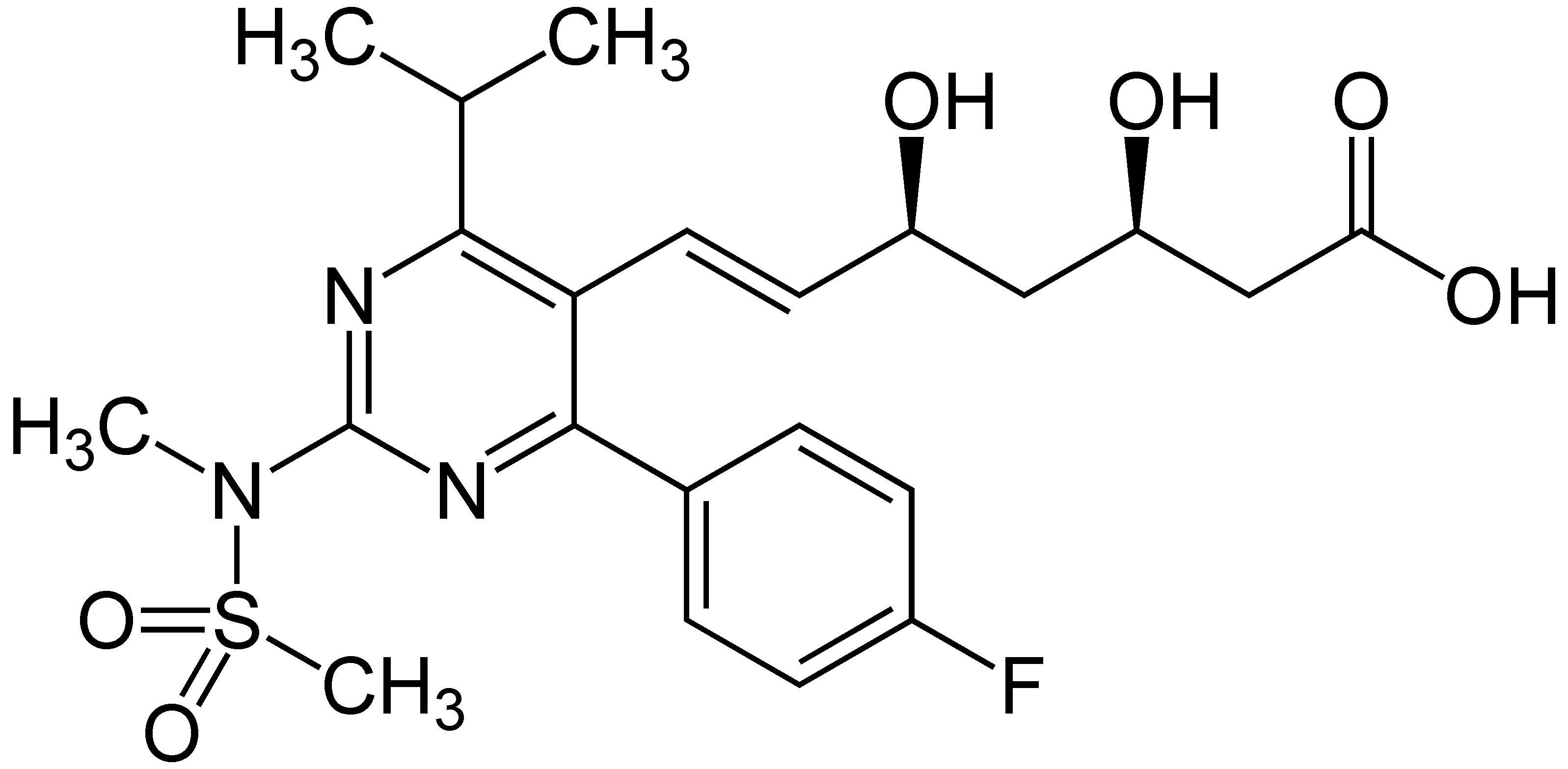
Pacritinib
Pacritinib, sold under the brand name Vonjo, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat myelofibrosis. It is a macrocyclic protein kinase inhibitor. It mainly inhibits Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) and Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3\CD135 (FLT3). Common side effects include diarrhea, low platelet counts, nausea, anemia, and swelling in legs. Medical uses Pacritinib in indicated to treat adults who have a rare form of a bone marrow disorder known as intermediate or high-risk primary or secondary myelofibrosis and who have platelet (blood clotting cells) levels below 50,000/µL. History The effectiveness and safety of pacritinib were demonstrated in a study that included 63 participants with intermediate or high-risk primary or secondary myelofibrosis and low platelets who received pacritinib 200mg twice daily or standard treatment. Effectiveness was determined based upon the proportion of participants who had a 35% or greater spleen volume reduction from baseline to week 24. Nine pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelofibrosis
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer. It is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of cancers in which there is growth of abnormal cells in the bone marrow. This is most often associated with a somatic mutation in the JAK2, CALR, or MPL gene markers. In PMF, the healthy marrow is replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis), resulting in a lack of production of normal blood cells. Symptoms include anemia, increased infection and an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly). In 2016, prefibrotic primary myelofibrosis was formally classified as a distinct condition that progresses to overt PMF in many patients, the primary diagnostic difference being the grade of fibrosis. Signs and symptoms The primary feature of primary myelofibrosis is bone marrow fibrosis, but it is often accompanied by: * Abdominal fullness related to an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly). * Bone pain * Bruising and easy bleeding due to inade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Heterocycles
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drugs
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineoplastic Drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethers
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Track (FDA)
Fast track is a designation by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of an investigational drug for expedited review to facilitate development of drugs that treat a serious or life-threatening condition and fill an unmet medical need. Fast Track designation must be requested by the drug company. The request can be initiated at any time during the drug development process. FDA will review the request and attempt to make a decision within sixty days. Purpose Fast Track is one of five Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approaches to make new drugs available as rapidly as possible: the others are priority review, breakthrough therapy, accelerated approval and Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy. Fast Track was introduced by the FDA Modernization Act of 1997. Requirements Fast track designation is designed to aid in the development and expedite the review of drugs which show promise in treating a serious or life-threatening disease and address an unmet medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |