|
Pablo Fanque
Pablo Fanque (born William Darby; 30 March 1810 – 4 May 1871) was a British Equestrianism, equestrian performer and Circus, circus proprietor, becoming the first recorded Black circus owner in Britain. His circus was popular in Victorian Britain for 30 years, a period that is regarded as the golden age of the circus. Since the 1960s, Pablo Fanque has been best known for being mentioned in the Beatles song "Being for the Benefit of Mr. Kite!" on their 1967 album ''Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band''. Early life Little is known about Pablo Fanque's early life. Church records suggest that he was born in Norwich in 1810 and was one of at least five children, born to John and Mary Darby ( Stamp). They were believed to have resided in Ber Street. When Fanque married in 1848, he said his late father's occupation was "butler" on his marriage certificate. Dr. John M. Turner speculates in his 2003 biography of Fanque that "his father was African born and had been brought to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of the county of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. It lies by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. The population of the Norwich City Council local authority area was estimated to be 144,000 in 2021, which was an increase from 143,135 in 2019. The wider Norwich List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, built-up area had a population of 213,166 at the 2011 census. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of Norwich, the city has one of the country's largest medieval cathedrals. For much of the second millennium, from medieval to just before Industrial Revolution, industrial times, Norwich was one of the most prosperous and largest towns of England; at one point, it was List of towns and cities in England by historical population, second only to London. Today, it is the largest settlement in East Anglia. Heritage and status Norwich claims to be the most complete medie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Thames in southeast England, at the head of a tidal estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for nearly 2,000 years. Its ancient core and financial centre, the City of London, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as Londinium and has retained its medieval boundaries. The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has been the centuries-long host of Government of the United Kingdom, the national government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. London grew rapidly 19th-century London, in the 19th century, becoming the world's List of largest cities throughout history, largest city at the time. Since the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
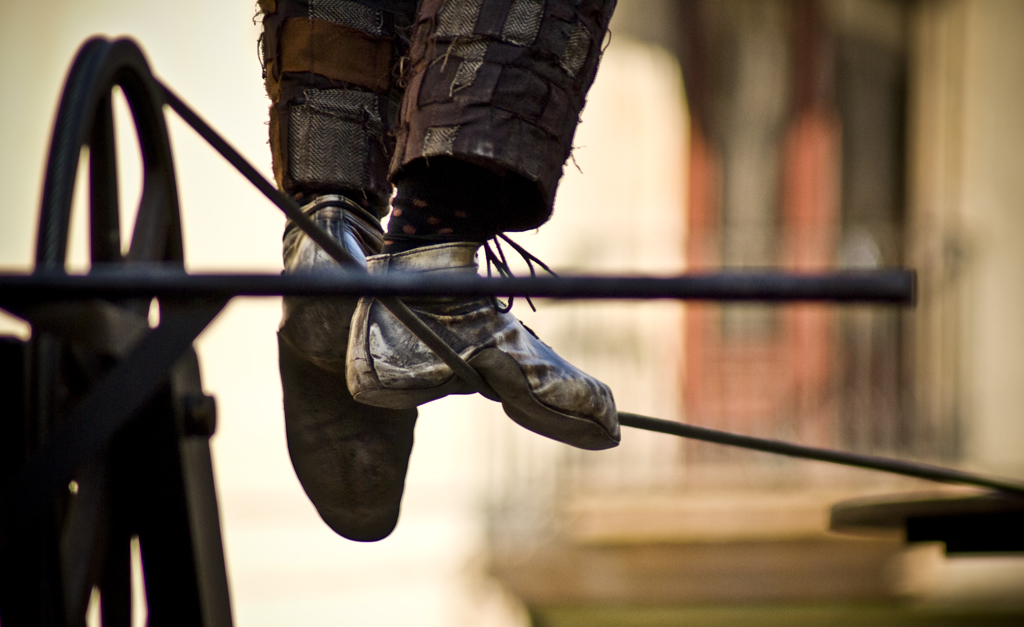
Tightrope
Tightrope walking, also called funambulism, is the skill of walking along a thin wire or rope. It has a long tradition in various countries and is commonly associated with the circus. Other skills similar to tightrope walking include slack rope walking and slacklining. Types Tightwire is the skill of maintaining balance while walking along a tensioned wire between two points. It can be done either using a balancing tool (umbrella, fan, balance pole, etc.) or "freehand", using only one's body to maintain balance. Typically, tightwire performances either include dance or object manipulation. Object manipulation acts include a variety of props in their acts, such as clubs, rings, hats, or canes. Tightwire performers have even used wheelbarrows with passengers, ladders, and animals in their act. The technique to maintain balance is to keep the performer's centre of mass above their support point—usually their feet. Highwire is a form of tightwire walking but performed at much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croydon
Croydon is a large town in South London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a Districts of England, local government district of Greater London; it is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensive shopping area. The entire town had a population of 192,064 as of 2011, whilst the wider borough had a population of 384,837. Historically an ancient parish in the Wallington Hundred of Surrey, at the time of the Norman conquest of England Croydon had a church, a mill, and around 365 inhabitants, as recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086. Croydon expanded in the Middle Ages as a market town and a centre for charcoal production, leather tanning and brewing, with the brewing industry in particular remaining strong for hundreds of years. The Surrey Iron Railway from Croydon to Wandsworth opened in 1803 and was an early public railway. Later 19th century railway building facilitated Croydon's growth as a commuter town for L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hampshire Advertiser
The ''Hampshire Advertiser'' was a British local, broadsheet newspaper, based in Southampton, Hampshire. It ran from 1823 until 1940. Edward Langdon Oke (1775–1840), a corn merchant in the older part of the city (High Street), was credited with establishing the ''Hampshire Advertiser'' (previously the "Herald"). Oke, originally from Sherborne, was elected to the Town Council of Southampton and appointed Consul at Southampton for the Kingdom of Hanover by Prince Regent George IV George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 29 January 1820 until his death in 1830. At the time of his accession to the throne, h ... in 1818. References Publications disestablished in 1900 1823 establishments in England Newspapers established in 1823 Newspapers published in Hampshire {{England-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. The city was a small manorial borough in the 13th century and a market town in the 16th century. It expanded by becoming a major production and trading centre (mainly with wool) in the 17th and 18th centuries. Leeds developed as a mill town during the Industrial Revolution alongside other surrounding villages and towns in the West Riding of Yorkshire. It was also known for its flax industry, iron foundries, engineering and printing, as well as shopping, with several surviving Victorian era arcades, such as Kirkgate Market. City status was awarded in 1893, and a populous urban centre formed in the following century which absorbed surrounding villages and overtook t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
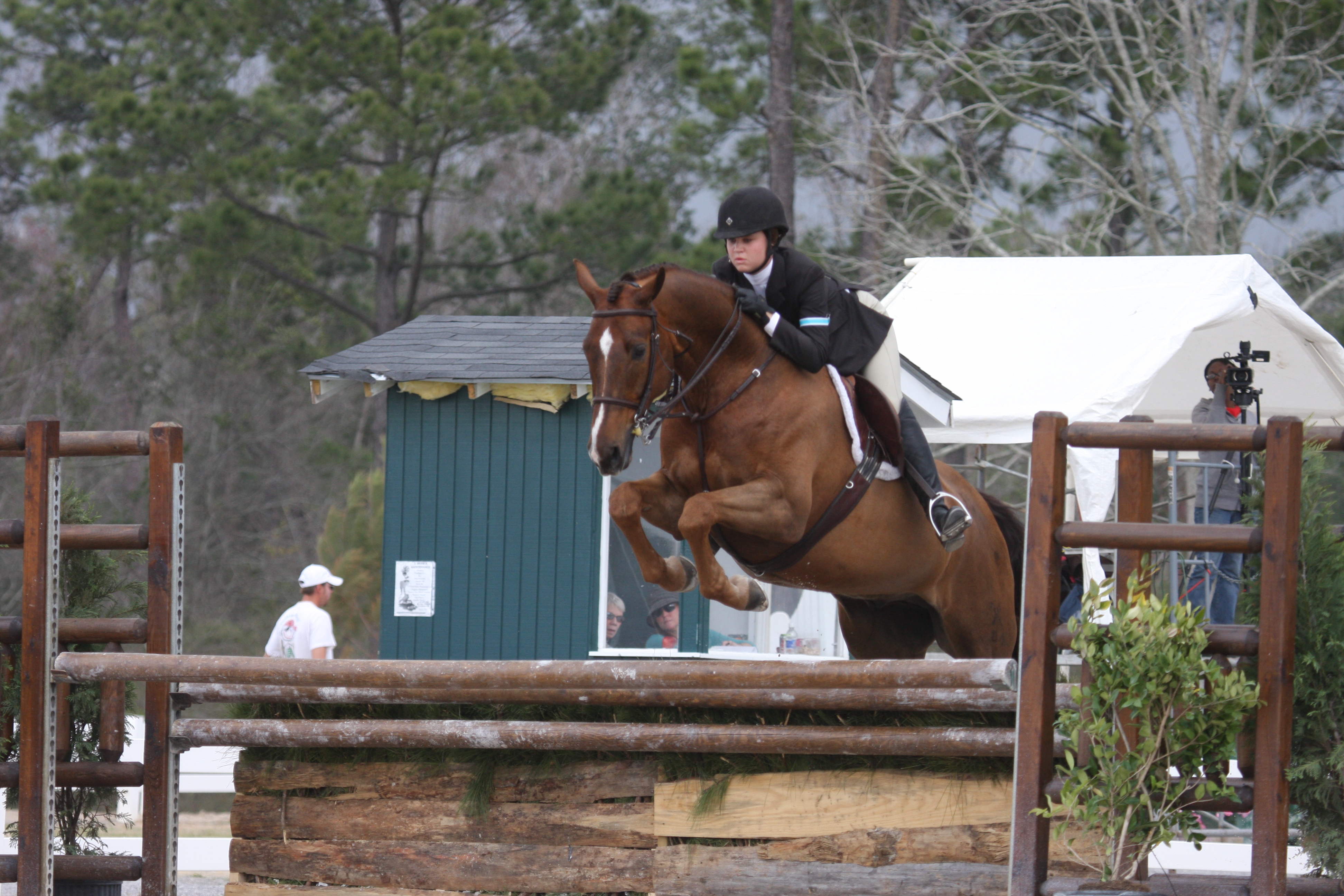
Equitation
Equitation is the art or practice of horse riding or horsemanship. More specifically, equitation may refer to a rider's position while mounted, and encompasses a rider's ability to ride correctly and with effective aids. In horse show competition, the rider, rather than the horse is evaluated. Such classes go by different names, depending on region, including ''equitation classes'', ''rider classes'', or ''horsemanship classes.'' Judging criteria covers the rider's performance and control of the horse, use of riding aids, proper attire, correct form, and usually factor in rider poise and the cleanliness and polish of horse, rider and equipment. The performance of the horse is not judged ''per se'', but a poorly performing horse is considered to reflect the ability of the rider. Equitation classes occur in the Hunt seat, Saddle seat, Dressage, and Western disciplines. A good equitation rider is always in balance with the horse, maintains a correct position in every gait, moveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dressage
Dressage ( or ; , most commonly translated as "training") is a form of horse riding performed in exhibition and competition, as well as an art sometimes pursued solely for the sake of mastery. As an equestrianism, equestrian sport defined by the International Federation for Equestrian Sports, International Equestrian Federation, dressage is described as "the highest expression of horse training" where "horse and rider are expected to perform from memory a series of predetermined movements". Competitions are held at all levels from amateur to the Olympic Games and World Equestrian Games. Its fundamental purpose is to develop, through standardized progressive training methods, a horse's natural athletic ability and willingness to perform, thereby maximizing its potential as a Equestrianism, riding horse. At the peak of a dressage horse's gymnastic development, the horse responds smoothly to a skilled rider's riding aids, minimal aids. The rider is relaxed and appears effort-free w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadside (printing)
A broadside is a large sheet of paper printed on one side only. Historically in Europe, broadsides were used as posters, announcing events or proclamations, giving political views, commentary in the form of broadside ballad, ballads, or simply advertisements. In Japan, Chromoxylography, chromoxylographic broadsheets featuring artistic prints were common. Description and history The historical type of broadsides, designed to be plastered onto walls as a form of street literature, were ephemera, i.e., temporary documents created for a specific purpose and intended to be thrown away. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries. They were often advertisements, but could also be used for news information or proclamations. Broadsides were a very popular medium for printing topical ballads starting in the 16th century. Broadside (music), Broadside ballads were usually printed on the cheapest type of paper available. Initiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equestrian Facility
An equestrian facility is created and maintained for the purpose of accommodating, training or competing equids, especially horses. Based on their use, they may be known as a barn, stables, or riding hall and may include commercial operations described by terms such as a boarding stable, livery yard, or livery stable. Larger facilities may be called equestrian centers and co-located with complementary services such as a riding school, farriers, vets, tack shops, or equipment repair. Horse accommodation Horses are often kept inside buildings known as barns or stables, which provide shelter for the animals. These buildings are normally subdivided to provide a separate stall or box for each horse, which prevents horses injuring each other, separates horses of different genders, allows for individual care regimens such as restricted or special feeding, and makes handling easier. The design of stables can vary widely, based on climate, building materials, historical period, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated ''Lancs'') is a ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Cumbria to the north, North Yorkshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Greater Manchester and Merseyside to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The largest settlement is Preston, Lancashire, Preston, and the county town is the city of Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster. The county has an area of and a population of 1,490,300. Preston is located near the centre of the county, which is urbanised and includes the towns of Blackburn and Burnley; the seaside resort of Blackpool lies to the west, and Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster is in the north. For Local government in England, local government purposes the county comprises a non-metropolitan county, with twelve districts, and two Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas: Blackburn with Darwen and Borough of Blackpool, Blackpool. Lancashire County Council and the two unitary councils collaborate through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wigan
Wigan ( ) is a town in Greater Manchester, England. The town is midway between the two cities of Manchester, to the south-east, and Liverpool, to the south-west. It is the largest settlement in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan and is its administrative centre. The town has a population of 107,732 and the wider borough of 330,714. Wigan is part of the Historic counties of England, historic county of Lancashire. Wigan was in the territory of the Brigantes, an ancient List of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes, Celtic tribe that ruled much of what is now Northern England. The Brigantes were subjugated in the Roman conquest of Britain and the Roman settlement of was established where Wigan lies. Wigan was incorporated as a Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in 1246, following the issue of a charter by Henry III of England, King Henry III of England. At the end of the Middle Ages, it was one of four boroughs in Lancashire established by royal charter. The Industrial Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |