|
Pabasa
The ancient Egyptian noble Pabasa was chief steward of the God's Wife of Amun Nitocris I during the Saite Period. He is buried in tomb TT279, which is located in the El-Assasif, part of the Theban Necropolis, near Thebes. His sarcophagus was acquired in Paris in 1836 by Alexander Douglas-Hamilton, 10th Duke of Hamilton and was kept at Hamilton Palace until it was given to the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum in Glasgow by the Hamilton Estate Trustees in 1922. One of Pabasa's grandsons was Pedubast, the chief steward and overseer of Upper Egypt, whose burial was discovered in 2015, located within the tomb TT391 at El-Assasif. File:TT279.jpg, Plan of Pabasa's tomb, TT279 File:Nitocris Psammetique Ier T Pabasa.jpg, Relief from TT279 depicting Nitocris I (left) and her father Psamtik I (center) before Ra-Horakhty Ra (; egy, rꜥ; also transliterated ; cuneiform: ''ri-a'' or ''ri-ia''; Phoenician: 𐤓𐤏,CIS I 3778 romanized: rʿ) or Re (; cop, ⲣⲏ, trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psamtik I
Wahibre Psamtik I ( Ancient Egyptian: ) was the first pharaoh of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, the Saite period, ruling from the city of Sais in the Nile delta between 664–610 BC. He was installed by Ashurbanipal of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, against the Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty, but later gained more autonomy as the Assyrian Empire declined. Name The Egyptian name , pronounced as , was a short form of , meaning "the man of (the Libyan deity) Meṯek." His name was rendered by the Assyrians as Pishamilki (Akkadian: ), by the Ancient Greeks as (), and by the Romans as . Psamtik was also called Nabu-shezibanni (Akkadian: and ), meaning "O Nabu, save me!" by the Assyrians. Background In 671 BCE, the Assyrian king Esarhaddon invaded Egypt. This invasion was directed against the Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, who had been in control of Upper Egypt, rather than against the native Egyptian rulers. The Assyrians created an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvingrove Art Gallery And Museum
Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum is a museum and art gallery in Glasgow, Scotland. It reopened in 2006 after a three-year refurbishment and since then has been one of Scotland's most popular visitor attractions. The museum has 22 galleries, housing a range of exhibits, including Renaissance art, taxidermy, and artefacts from ancient Egypt. Location The gallery is located on Argyle Street, in the West End of the city, on the banks of the River Kelvin (opposite the architecturally similar Kelvin Hall, which was built in matching style in the 1920s, after the previous hall had been destroyed by fire). It is adjacent to Kelvingrove Park and is near the main campus of the University of Glasgow on Gilmorehill. Original museum The original Kelvingrove Museum opened in 1876. It was housed in a much enlarged 18th-century mansion called Kelvingrove House, to the north-east of the current site, that was originally the home of Lord Provost Patrick Colquhoun. Creation (1888–1901) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedubast (high Steward)
Pedubast (also Padibast, or Padibastet) was an ancient Egyptian official during the 26th Dynasty. He is so far only known from his burial, found within the larger and earlier (25th Dynasty) tomb complex of the ''mayor of Thebes'' Karabasken ( TT391), located at South El-Assasif within the Theban Necropolis, in Upper Egypt. Pedubast's burial was found in 2015 and announced shortly after. He was most likely the grandson of the well known ''chief steward of the God's Wife'' Pabasa who was buried in another large funerary complex at Thebes ( TT279). Pedubast was ''overseer of Upper Egypt'' and ''chief steward of the God's Wife''; in the latter position he managed the estates of the ''God's Wife of Amun God's Wife of Amun ( Egyptian: ''ḥm.t nṯr n ỉmn'') was the highest-ranking priestess of the Amun cult, an important religious institution in ancient Egypt. The cult was centered in Thebes in Upper Egypt during the Twenty-fifth and Twent ...'', the leading religious figure i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton Palace
Hamilton Palace was a country house in Hamilton, South Lanarkshire, Scotland. The former seat of the Dukes of Hamilton, it dated from the 14th century and was subsequently much enlarged in the 17th and 19th centuries.Hamilton's royal past South Lanarkshire Council Widely acknowledged as having been one of the grandest houses in the , the palace was situated at the centre of the extensive Low Parks (now |
Alexander Douglas-Hamilton, 10th Duke Of Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton, 10th Duke of Hamilton, 7th Duke of Brandon KG PC FRS FSA (3 October 1767 – 18 August 1852) was a Scottish politician and art collector. Life Born on 3 October 1767 at St. James's Square, London, a son of Archibald Hamilton, 9th Duke of Hamilton, he was educated at Harrow School and at Christ Church, Oxford, where he matriculated on 4 March 1786. He received his MA on 18 February 1789. Hamilton was a Whig, and his political career began in 1802, when he became MP for Lancaster. He remained in the House of Commons until 1806, when he was appointed to the Privy Council, and Ambassador to the court of St. Petersburg until 1807; additionally, he was Lord Lieutenant of Lanarkshire from 1802 to 1852. He received the numerous titles at his father's death in 1819. He was Lord High Steward at King William IV's coronation in 1831 and Queen Victoria's coronation in 1838, and remains the last person to have undertaken this duty twice. He became a Knigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El-Assasif
El-Assasif ( ar, العساسيف) is a necropolis near Luxor on the West Bank at Thebes, Egypt, Upper Egypt. It is located in the dry bay that leads up to Deir el-Bahari and south of the necropolis of Dra' Abu el-Naga'. El-Assasif contains burials from the 18th, 22nd, 25th and 26th dynasties of ancient Egypt, covering the period c. 1550 to 525 BC across all three dynasties. Archaeology In November 2018, France's University of Strasbourg announced the discovery of two sarcophagi thought to be more than 3,500 years old with two perfectly preserved mummies and approximately 1,000 funerary statues in the Assasif valley near Luxor. One of the tombs with paintings where the female body found, was opened to the public in front of the international media, but the other one was previously opened by Egyptian antiquities officials. In October 2019, 30 coffins (3.000 year-old) were uncovered and presented, dating back to the Twenty-second Dynasty by the Egyptian archaeological mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-sixth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXVI, alternatively 26th Dynasty or Dynasty 26) dynasty was the last native dynasty to rule Egypt before the Persian conquest in 525 BC (although others followed). The dynasty's reign (664–525 BC) is also called the Saite Period after the city of Sais, where its pharaohs had their capital, and marks the beginning of the Late Period of ancient Egypt.Aidan Dodson, Dyan Hilton. ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt''. The American University in Cairo Press, London 2004 History This dynasty traced its origins to the Twenty-fourth Dynasty. Psamtik I was probably a descendant of Bakenranef. Following the Assyrian conquest of Egypt by the Neo-Assyrian Empire during the reigns of Taharqa and Tantamani, and the subsequent collapse of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Psamtik I was recognized as sole king over all of Egypt. Psamtik formed alliances with King Gyges of Lydia, who sent him mercenaries from Caria and anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (plural sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a box-like funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and φαγεῖν ' meaning "to eat"; hence ''sarcophagus'' means "flesh-eating", from the phrase ''lithos sarkophagos'' ( λίθος σαρκοφάγος), "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself. History of the sarcophagus Sarcophagi were most often designed to remain above ground. The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 B.C. The Hagia Triada sarcophagus is a stone sarcophagus elaborately painted in fresco; one style of late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT391
The Theban Tomb TT391 is located in South El-Assasif, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian ''mayor of Thebes'' and ''fourth priest of Amun'' Karabasken, who lived during the reign of the 25th Dynasty pharaohs Piye and Shabaka. The tomb itself was built around 715–705 BCE under Shebitku, and it is the earliest one in South El-Assasif. It was first discovered in 1820 by John Gardner Wilkinson, Robert Hay and James Burton, then by Karl Richard Lepsius; it was reopened in 2001. In August 2015, an excavation led by Elena Pischikova discovered that the tomb was later partially redecorated and reused for the ''Overseer of Upper Egypt'' Pedubast, who lived during the 26th Dynasty. See also * List of Theban tombs The Theban Necropolis is located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Luxor, in Egypt. As well as the more famous royal tombs located in the Valley of the Kings and the Valley o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseer Of Upper Egypt
The Overseer of Upper Egypt was an important Ancient Egyptian title during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods. The title appears first in the early Fifth Dynasty. The first title holder is the vizier Kay, who possibly lived during the reigns of Neferirkare Kakai and Nyuserre Ini. The office is well attested in the following years. Most titles holders had other high titles, many of them were viziers. In the Fifth Dynasty, the Egyptian provinces became more important. The central government installed an office in charge of the provinces. The first title holders were all officials at the royal residence A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which .... In later times also local officials were bearing the title.Juan Carlos Moreno García: ''The territorial Administration of the Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
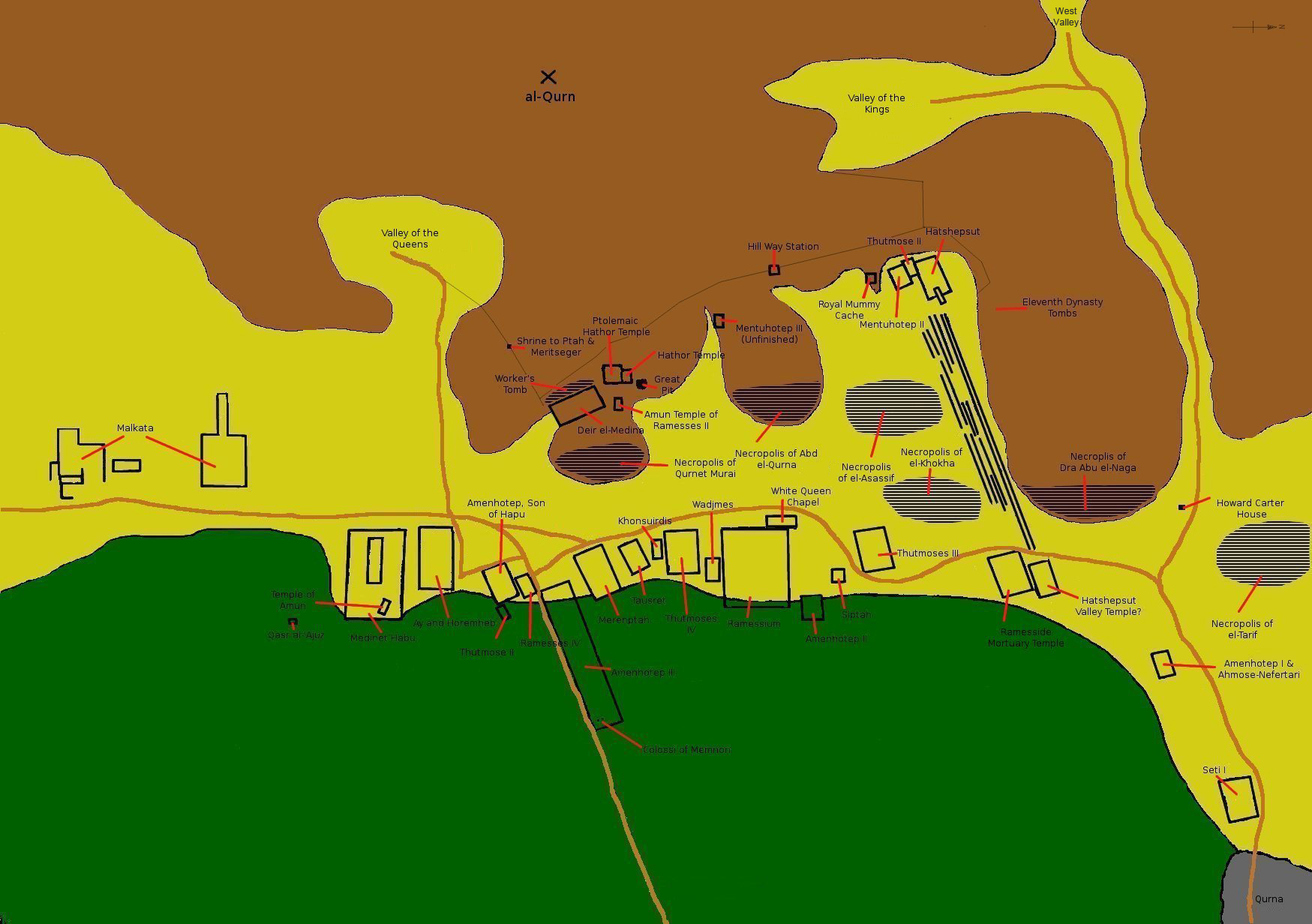
Theban Necropolis
The Theban Necropolis is a necropolis on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes ( Luxor) in Upper Egypt. It was used for ritual burials for much of the Pharaonic period, especially during the New Kingdom. Mortuary temples * Deir el-Bahri ** Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut ** Mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II ** Mortuary temple of Thutmose III * Medinet Habu ** Mortuary temple and palace of Ramesses III ** Mortuary Temple of Ay & Horemheb * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep III ** Colossi of Memnon * Mortuary Temple of Merneptah * Mortuary Temple of Ramesses IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose III * Mortuary Temple of Twosret * Temple of Nebwenenef * Qurna ** Mortuary Temple of Seti I * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep II * Ramesseum (Mortuary Temple of Ramesses II) Royal Necropolis * Valley of the Kings (Modern: "''Wadi el-Muluk''") * Valley of the Queens (Modern: "''Biban el-Harim''") * Royal Cache * Bab el-Gasus Necropolis * Deir el-Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |