|
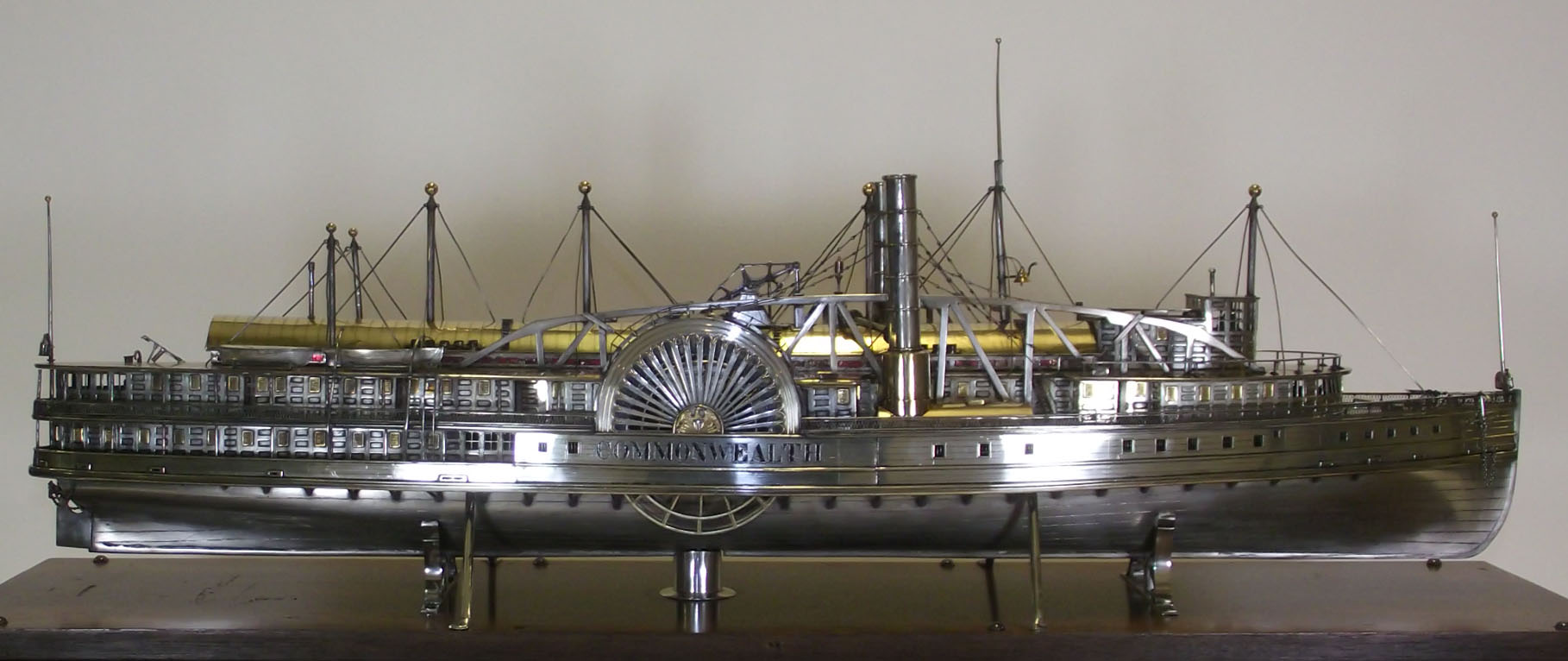
PS Commonwealth (1854)
''Commonwealth'' was a large sidewheel steamboat built in 1854–55 for passenger service on Long Island Sound. The most celebrated Sound steamer of her day, ''Commonwealth'' was especially noted for the elegance and comfort of her passenger accommodations, which included gas lighting, steam heating, and an "enchantingly beautiful" domed roof in her upper saloon. Her stability of motion led her captain to describe ''Commonwealth'' as the finest rough weather steamboat ever built in the United States. ''Commonwealth'' would spend her entire career on Long Island Sound routes, first from New York to Allyn's Point, Connecticut under the management of the Norwich and New London Steamboat Company, and later to Stonington and Groton with the New Jersey Steam Navigation and the Merchants' Steamship companies. During the American Civil War, she was part of the transport network that moved northern state Union regiments to the battlefront. ''Commonwealth''s end came prematurely when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth (steamboat 1854) By Bard
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth or the common wealth – echoed in the modern synonym "public wealth"), it comes from the old meaning of " wealth", which is "well-being", and is itself a loose translation of the Latin res publica (republic). The term literally meant "common well-being". In the 17th century, the definition of "commonwealth" expanded from its original sense of " public welfare" or "commonweal" to mean "a state in which the supreme power is vested in the people; a republic or democratic state". The term evolved to become a title to a number of political entities. Three countries – Australia, the Bahamas, and Dominica – have the official title "Commonwealth", as do four U.S. states and two U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williamsburg, Brooklyn
Williamsburg is a neighborhood in the New York City borough of Brooklyn, bordered by Greenpoint to the north; Bedford–Stuyvesant to the south; Bushwick and East Williamsburg to the east; and the East River to the west. As of the 2020 United States census, the neighborhood's population is 151,308. Since the late 1990s, Williamsburg has undergone significant gentrification characterized by a contemporary art scene, hipster culture, and vibrant nightlife that has projected its image internationally as a "Little Berlin". During the early 2000s, the neighborhood became a center for indie rock and electroclash. Numerous ethnic groups inhabit enclaves within the neighborhood, including Italians, Jews, Hispanics, Poles, Puerto Ricans, and Dominicans. Williamsburg is part of Brooklyn Community District 1, and its primary ZIP Codes are 11211 and 11206. It is patrolled by the 90th and 94th Precincts of the New York City Police Department. Politically, it is represented by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Steam Engine
A marine steam engine is a steam engine that is used to power a ship or boat. This article deals mainly with marine steam engines of the reciprocating type, which were in use from the inception of the steamboat in the early 19th century to their last years of large-scale manufacture during World War II. Reciprocating steam engines were progressively replaced in marine applications during the 20th century by steam turbines and marine diesel engines. History The first commercially successful steam engine was developed by Thomas Newcomen in 1712. The steam engine improvements brought forth by James Watt in the later half of the 18th century greatly improved steam engine efficiency and allowed more compact engine arrangements. Successful adaptation of the steam engine to marine applications in England would have to wait until almost a century after Newcomen, when Scottish engineer William Symington built the world's "first practical steamboat", the '' Charlotte Dundas'', in 1802 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (engine)
In a reciprocating engine, the cylinder is the space in which a piston travels. The inner surface of the cylinder is formed from either a thin metallic liner (also called "sleeve") or a surface coating applied to the engine block. A piston is seated inside each cylinder by several metal piston rings, which also provide seals for compression and the lubricating oil. The piston rings do not actually touch the cylinder walls, instead they ride on a thin layer of lubricating oil. Steam engines The cylinder in a steam engine is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in cast iron and later in steel. The cylinder casting can include other features such as valve ports and mounting feet. Internal combustion engines The cylinder is the space through which the piston travels, propelled to the energy generated from the combustion of the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. In an ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the mechanical horsepower (or imperial horsepower), which is about 745.7 watts, and the metric horsepower, which is approximately 735.5 watts. The term was adopted in the late 18th century by Scottish engineer James Watt to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses. It was later expanded to include the output power of other types of piston engines, as well as turbines, electric motors and other machinery. The definition of the unit varied among geographical regions. Most countries now use the SI unit watt for measurement of power. With the implementation of the EU Directive 80/181/EEC on 1 January 2010, the use of horsepower in the EU is permitted only as a supplementary unit. History The development of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hogging And Sagging
In solid mechanics, structural engineering, and shipbuilding, hogging and sagging describe the shape that a beam or similar long object will deform into when loading is applied. ''Hogging'' describes a beam that curves upwards in the middle, and ''sagging'' describes a beam that curves downwards. Ships Dynamic stress Hogging is the stress a ship's hull or keel experiences that causes the center or the keel to bend upward. Sagging is the stress a ship's hull or keel is placed under when a wave is the same length as the ship and the ship is in the trough of two waves. This causes the middle of the ship to bend down slightly, and depending on the level of bend, may cause the hull to snap or crack. Sagging or dynamic hogging may have been what sank the '' Prestige'' off Spain on 19 November 2002. The 2013 loss of container ship '' MOL Comfort'' off the coast of Yemen was attributed to hogging. Subsequent lawsuits blamed the shipbuilder for design flaws. Time-induced stress Hoggi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Post
A king post (or king-post or kingpost) is a central vertical post used in architectural or bridge designs, working in tension to support a beam below from a truss apex above (whereas a crown post, though visually similar, supports items above from the beam below). In aircraft design a strut called a king post acts in compression, similarly to an architectural crown post. Usage in mechanical plant and marine engineering differs again, as noted below. Architecture A king post extends vertically from a crossbeam (the tie beam) to the apex of a triangular truss. The king post, itself in tension, connects the apex of the truss with its base, holding up the tie beam (also in tension) at the base of the truss. The post can be replaced with an iron rod called a king rod (or king bolt) and thus a king rod truss. The king post truss is also called a "Latin truss". In traditional timber framing, a crown post looks similar to a king post, but it is very different structurally: wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
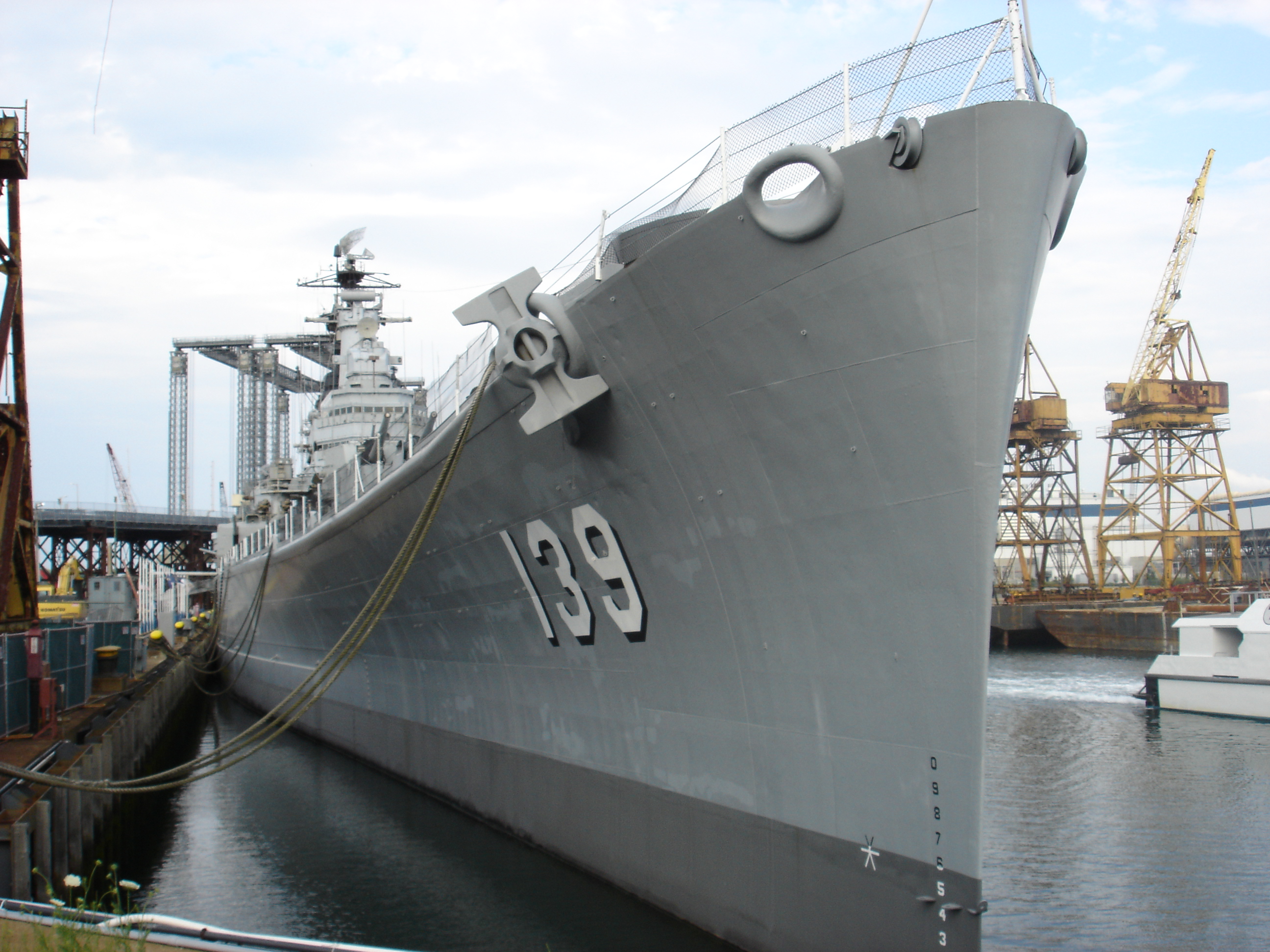
Bow (ship)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in British and American shipbuilding traditions the construction is dated from this event. Etymology The word "keel" comes from Old English , Old Norse , = "ship" or "keel". It has the distinction of being regarded by some scholars as the first word in the English language recorded in writing, having been recorded by Gildas in his 6th century Latin work '' De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', under the spelling ''cyulae'' (he was referring to the three ships that the Saxons first arrived in). is the Latin word for "keel" and is the origin of the term careen (to clean a keel and the hull in general, often by rolling the ship on its side). An example of this use is Careening Cove, a suburb of Sydney, Australia, where careening was carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline. General features There is a wide variety of hull types that are chosen for suitability for different usages, the hull shape being dependent upon the needs of the design. Shapes range from a nearly perfect box in the case of scow barges to a needle-sharp surface of revolution in the case of a racing multihull sailboat. The shape is chosen to strike a balance between cost, hydrostatic considerations (accommodation, load carrying, and stability), hydrodynamics (speed, power requirements, and motion and behavior in a seaway) and special considerations for the ship's role, such as the rounded bow of an icebreaker or the flat bottom of a landing craft. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (nautical)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)



