|
PSR B1509−58
__NOTOC__ PSR B1509−58 is a pulsar approximately at a distance of 17,000 light-years in the constellation of Circinus discovered by the Einstein Observatory, Einstein X-Ray Observatory in 1982. Its diameter is only . It is located in a Pulsar wind nebula created by itself, that was caused as a Supernova remnant, remnant of the Supernova (SNR) MSH 15−52 visual approximately 1,700 years ago at the southern celestial hemisphere not visible in the northern hemisphere.Oxford AcademicModelling spectral evolution of pulsar wind nebulae inside supernova remnants, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society , Oxford Academic, access-date 13. November 2024 The nebula spans about 150 light years. The 150 ms Stellar rotation, pulsations ("almost 7 times per second") are detected in the Radio wave, radio, X-ray, and Gamma ray, γ-ray bands. NASA described the star as "a rapidly spinning neutron star which is spewing energy out into the space around it to create complex an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Wave
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths greater than , about the diameter of a grain of rice. Radio waves with frequencies above about 1 GHz and wavelengths shorter than 30 centimeters are called microwaves. Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a slightly lower speed. Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical radio source, astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects. Radio waves are generated artificially by an electronic device called a transmitter, which is connected to an antenna (radio), antenna, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsars
A pulsar (''pulsating star, on the model of quasar'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth (similar to the way a lighthouse can be seen only when the light is pointed in the direction of an observer), and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very dense and have short, regular rotational periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays (see also centrifugal mechanism of acceleration). Pulsars’ highly regular pulses make them very useful tools for astronomers. For example, observations of a pulsar in a binary neutron star system were used to indirectly confirm the existence of gravitational radiation. The first ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Daily
''ScienceDaily'' is an American website launched in 1995 that aggregates press releases and publishes lightly edited press releases (a practice called churnalism) about science, similar to Phys.org and EurekAlert!. History The site was founded by married couple Dan and Michele Hogan in 1995; Dan Hogan formerly worked in the public affairs department of Jackson Laboratory writing press releases. The site makes money from selling advertisements. the site said that it had grown "from a two-person operation to a full-fledged news business with worldwide contributors". At the time, it was run out of the Hogans' home, had no reporters, and only reprinted press releases. In 2012, Quantcast ranked it at 614 with 2.6 million U.S. visitors. Sections As of August 2023, ''ScienceDaily'' mainly has five sections, Health, Tech, Enviro, Society, and Quirky, the last of which includes the top news. References External links * Alexa - ScienceDaily��{{Webarchive, url=https://web.a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'' (''ApJ'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. The journal discontinued its print edition and became an electronic-only journal in 2015. Since 1953, ''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series'' (''ApJS'') has been published in conjunction with ''The Astrophysical Journal'', with generally longer articles to supplement the material in the journal. It publishes six volumes per year, with two 280-page issues per volume. ''The Astrophysical Journal Letters'' (''ApJL''), established in 1967 by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar as Part 2 of ''The Astrophysical Journal'', is now a separate journal focusing on the rapid publication of high-impact astronomical research. The three journals were published by the University of Chicago Press for the American Astronomical Society until, in January 2009, publication was transferred to IOP Publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. Its influence, wealth, and rankings have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world. Harvard was founded and authorized by the Massachusetts General Court, the governing legislature of colonial-era Massachusetts Bay Colony. While never formally affiliated with any denomination, Harvard trained Congregational clergy until its curriculum and student body were gradually secularized in the 18th century. By the 19th century, Harvard emerged as the most prominent academic and cultural institution among the Boston elite. Following the American Civil War, under Harvard president Charles William Eliot's long tenure from 1869 to 1909, Harvard developed multiple professional schools, which transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard–Smithsonian Center For Astrophysics
The Center for Astrophysics , Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA), previously known as the Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, is an astrophysics research institute jointly operated by the Harvard College Observatory and Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Founded in 1973 and headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, the CfA leads a broad program of research in astronomy, astrophysics, Earth and space sciences, as well as science education. The CfA either leads or participates in the development and operations of more than fifteen ground- and space-based astronomical research observatories across the electromagnetic spectrum, including the forthcoming Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory, one of NASA's Great Observatories. Hosting more than 850 scientists, engineers, and support staff, the CfA is among the largest astronomical research institutes in the world. Its projects have included Nobel Prize-winning advances in cosmolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsar Planet
Pulsar planets are planets that are orbiting pulsars. The first such planets to be discovered were around a millisecond pulsar in 1992 and were the first extrasolar planets to be confirmed as discovered. Pulsars are extremely precise clocks and even small planets can create detectable variations in pulsar traits; the smallest-known exoplanet is a pulsar planet. They are extremely rare, with only half a dozen listed by the NASA Exoplanet Archive. Only special processes can give rise to planet-sized companions around pulsars, and many are thought to be exotic bodies, such as planets made of diamond, that were formed through the partial destruction of a companion star. The intense radiation and winds consisting of electron-positron pairs would tend to strip atmospheres away from such planets, thus making them unlikely abodes for life. Formation The formation of planets requires the existence of a protoplanetary disk, most theories also require a "dead zone" within it where there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Neutron Stars
Neutron stars are the collapsed cores of supergiant stars. They are created as a result of supernovas and gravitational collapse, and are the second-smallest and densest class of stellar objects. In the cores of these stars, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. Neutron stars can be classified as pulsars if they are magnetized, if they rotate, and if they emit beams of electromagnetic radiation out of their magnetic poles. They may include soft gamma repeaters (SGR) and radio-quiet neutron stars, as well as pulsars such as radio pulsars, recycled pulsars, low mass X-ray pulsars, and accretion-powered pulsars. A notable grouping of neutron stars includes the Magnificent Seven. List of neutron stars Anomalous X-ray pulsars * Anomalous X-ray pulsar (AXP) * AXP 1E 1048-59 * AXP 1E2259+586 * AXP4U 0142+61 * AXP 1RXS 1708–40 * AXP 1E 1841–045 * AXP AXJ1844-0258 * AXP CXJ0110-7211 * Vela X-1 * 4U 0352+309 * Bursting Pulsar * Vela Junior * LMC N49 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations M1, NGC 1952, Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus (constellation), Taurus. The common name comes from a drawing that somewhat resembled a crab with arms produced by William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, in 1842 or 1843 using a telescope. The nebula was discovered by English astronomer John Bevis in 1731. It corresponds with SN 1054, a bright supernova observed in 1054 C.E. by Native American, Japanese, and Arabic stargazers; this supernova was also recorded by Chinese astronomy, Chinese astronomers as a Guest star (astronomy), guest star. The nebula was the first astronomical object identified that corresponds with a historically-observed supernova explosion. At an apparent magnitude of 8.4, comparable to that of Titan (moon), Saturn's moon Titan, it is not visible to the naked eye but can be made out using binoculars under favourable conditions. The nebula lies in the Perseus Arm of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
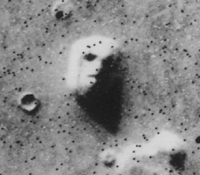
Pareidolia
Pareidolia (; ) is the tendency for perception to impose a meaningful interpretation on a nebulous stimulus (physiology), stimulus, usually visual, so that one detects an object, pattern, or meaning where there is none. Pareidolia is a specific but common type of apophenia (the tendency to perceive meaningful connections between unrelated things or ideas). Common examples include Cloud#In culture and religion, perceived images of animals, faces, or objects in cloud formations; seeing faces in inanimate objects; or lunar pareidolia like the Man in the Moon or the Moon rabbit. The concept of pareidolia may extend to include hidden messages in recorded music played in reverse or at higher- or lower-than-normal speeds, and hearing voices (mainly indistinct) or music in random noise, such as that produced by air conditioners or by fans. Face pareidolia has also been demonstrated in Rhesus macaque, rhesus macaques. Etymology The word derives from the Greek words ''wikt:para-, pará'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |