|
PSAT1
Phosphoserine aminotransferase (PSA) also known as phosphohydroxythreonine aminotransferase (PSAT) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PSAT1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is likely a phosphoserine aminotransferase, based on similarity to proteins in mouse, rabbit, and ''Drosophila''. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Clinical significance Homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in ''PSAT1'' cause Neu–Laxova syndrome and phosphoserine aminotransferase deficiency. See also * Phosphoserine transaminase Phosphoserine transaminase (, ''PSAT'', ''phosphoserine aminotransferase'', ''3-phosphoserine aminotransferase'', ''hydroxypyruvic phosphate-glutamic transaminase'', ''L-phosphoserine aminotransferase'', ''phosphohydroxypyruvate transaminase'', '' ... References Further reading * * * * * External links * Genes mutated in mice EC 2.6.1 {{gene-9-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoserine Transaminase
Phosphoserine transaminase (, ''PSAT'', ''phosphoserine aminotransferase'', ''3-phosphoserine aminotransferase'', ''hydroxypyruvic phosphate-glutamic transaminase'', ''L-phosphoserine aminotransferase'', ''phosphohydroxypyruvate transaminase'', ''phosphohydroxypyruvic-glutamic transaminase'', ''3-O-phospho-L-serine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase'', ''SerC'', ''PdxC'', ''3PHP transaminase'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''O-phospho-L-serine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : (1) O-phospho-L-serine + 2- oxoglutarate \rightleftharpoons 3-phosphonooxypyruvate + L-glutamate Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ... : (2) 4-phosphonooxy-L-threonine + 2-oxoglutarate \rightleftharpoons (3R)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-phosphonoox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neu–Laxova Syndrome
Neu–Laxova syndrome (NLS, also known as Neu syndrome; Neu-Povýsilová syndrome; or 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency, neonate form) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe intrauterine growth restriction and multiple congenital malformations. Neu–Laxova syndrome is a very severe disorder, leading to stillbirth or death shortly after birth. It was first described by Dr. Richard Neu in 1971 and Dr. Renata Laxova in 1972 as a lethal disorder in siblings with multiple malformations. Neu–Laxova syndrome is an extremely rare disorder with fewer than 100 cases reported in medical literature. Signs and symptoms Neu-Laxova syndrome presents with severe malformations leading to prenatal or neonatal death. Typically, NLS involves characteristic facial features, decreased fetal movements and skin abnormalities. Fetuses or newborns with Neu–Laxova syndrome have typical facial characteristics which include proptosis (bulging eyes) with eyelid malform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoserine
Phosphoserine (abbreviated as SEP or J) is an ester of serine and phosphoric acid. Phosphoserine is a component of many proteins as the result of posttranslational modifications. The phosphorylation of the alcohol functional group in serine to produce phosphoserine is catalyzed by various types of kinases. Through the use of technologies that utilize an expanded genetic code, phosphoserine can also be incorporated into proteins during translation. It is a normal metabolite In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ... found in human biofluids. Phosphoserine has three potential coordination sites (carboxyl, amine and phosphate group) Determination of the mode of coordination between phosphorylated ligands and metal ions occurring in an organism is a first step to explain the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminotransferase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α- keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins. Function and mechanism An amino acid contains an amino (NH2) group. A keto acid contains a keto (=O) group. In transamination, the NH2 group on one molecule is exchanged with the =O group on the other molecule. The amino acid becomes a keto acid, and the keto acid becomes an amino acid. Transaminases require the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate, which is converted into pyridoxamine in the first half-reaction, when an amino acid is converted into a keto acid. Enzyme-bound pyridoxamine in turn reacts with pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or alpha-ketoglutarate, giving alanine, aspartic acid, or glutamic acid, respectively. Many transamination reactions occur in tissues, catalysed by transaminases specific for a particular amino/keto acid pair. The reactions are readily reversible, the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila
''Drosophila'' (), from Ancient Greek δρόσος (''drósos''), meaning "dew", and φίλος (''phílos''), meaning "loving", is a genus of fly, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, ''Drosophila melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
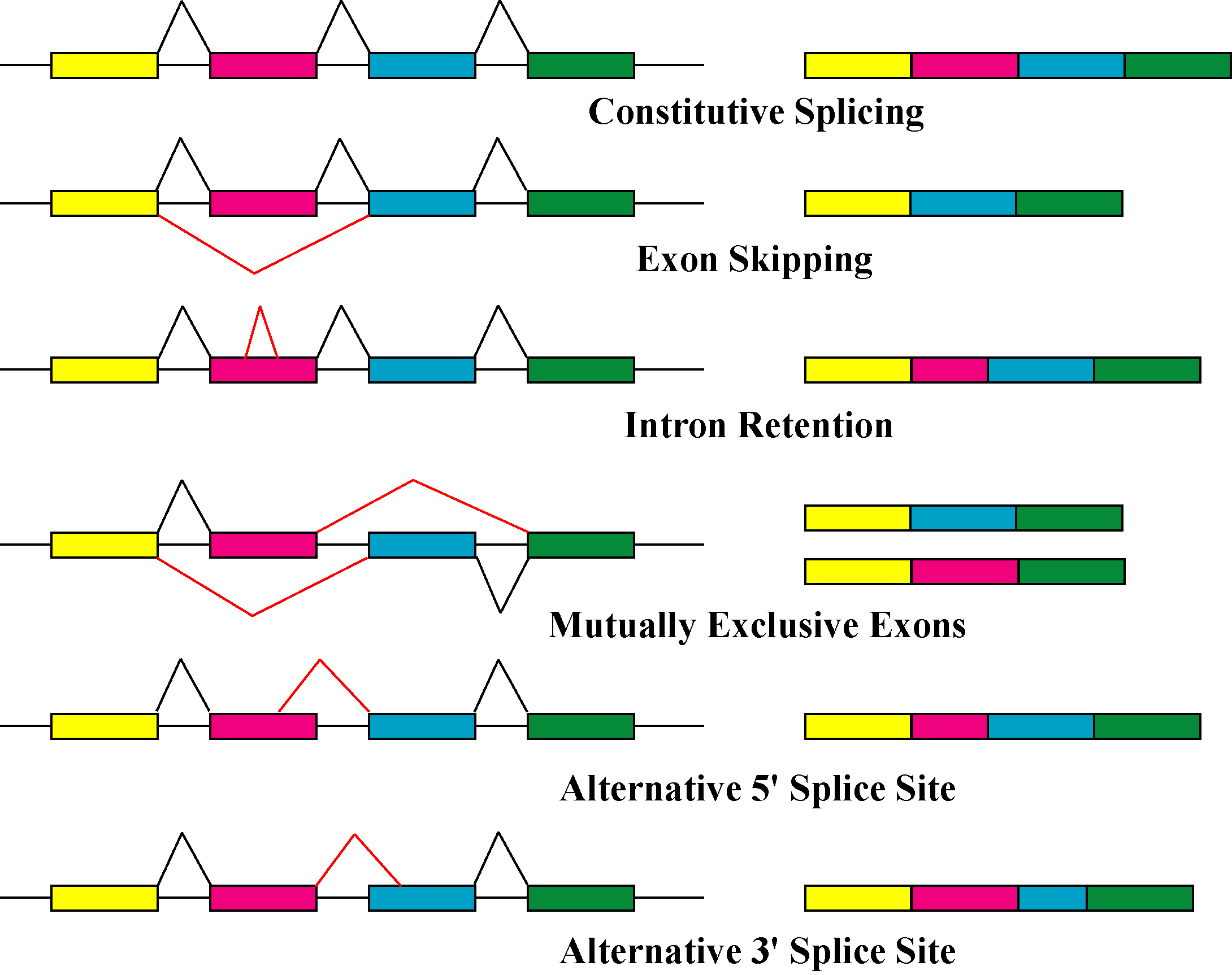
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions of genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different proteins e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genes Mutated In Mice
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first copied into RNA. RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype of the individual. Most biological traits occur under the combined influence of polygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |