|
PRR B1
The Pennsylvania Railroad's class B1 comprised 42 electric switcher locomotives built between 1926 and 1935. They were of 0-6-0 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation with 700 horsepower. As built, the first 28 locomotives in the 1926 order formed semi-permanently coupled pairs grouped in three classes. The first, class BB1, were AC powered and served as prototypes. The second, class BB2, were DC powered and served in the New York Terminal district, specifically between Sunnyside Yard and New York Penn Station. The third, class BB3, was AC powered and built for the Long Island Rail Road's electrified freight operation on the Bay Ridge Branch. In 1934 a follow-up order of 14 locomotives were built as single unit class B1 for the expanding main line AC electrification system. In addition to these new units all previous BB classes were split into single units and the BB2 class were re-powered for AC operation as that system replaced the old 650 V DC system in the New York termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad Museum Of Pennsylvania
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed. Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by diesel or electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or animal power have existed since antiquity, but modern rail transport began with the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom at the beginning of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switcher Locomotive
A switcher locomotive (American English), shunter locomotive (British English), station pilot (British English), or shifter locomotive (Pennsylvania Railroad terminology) is a locomotive used for maneuvering railway vehicles over short distances. Switchers do not usually move train A train (from Old French , from Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles th ...s over long distances. Instead, they typically assemble trains in order for another locomotive to take over. Switchers often operate in a railyard or make short transfer runs. They may serve as the primary motive power on short branch lines or switching and terminal railroads. A hybrid type known as a road switcher can both shunt and haul trains. Switchers are optimized for their role, being relatively low-powered but with a high starting tractive eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
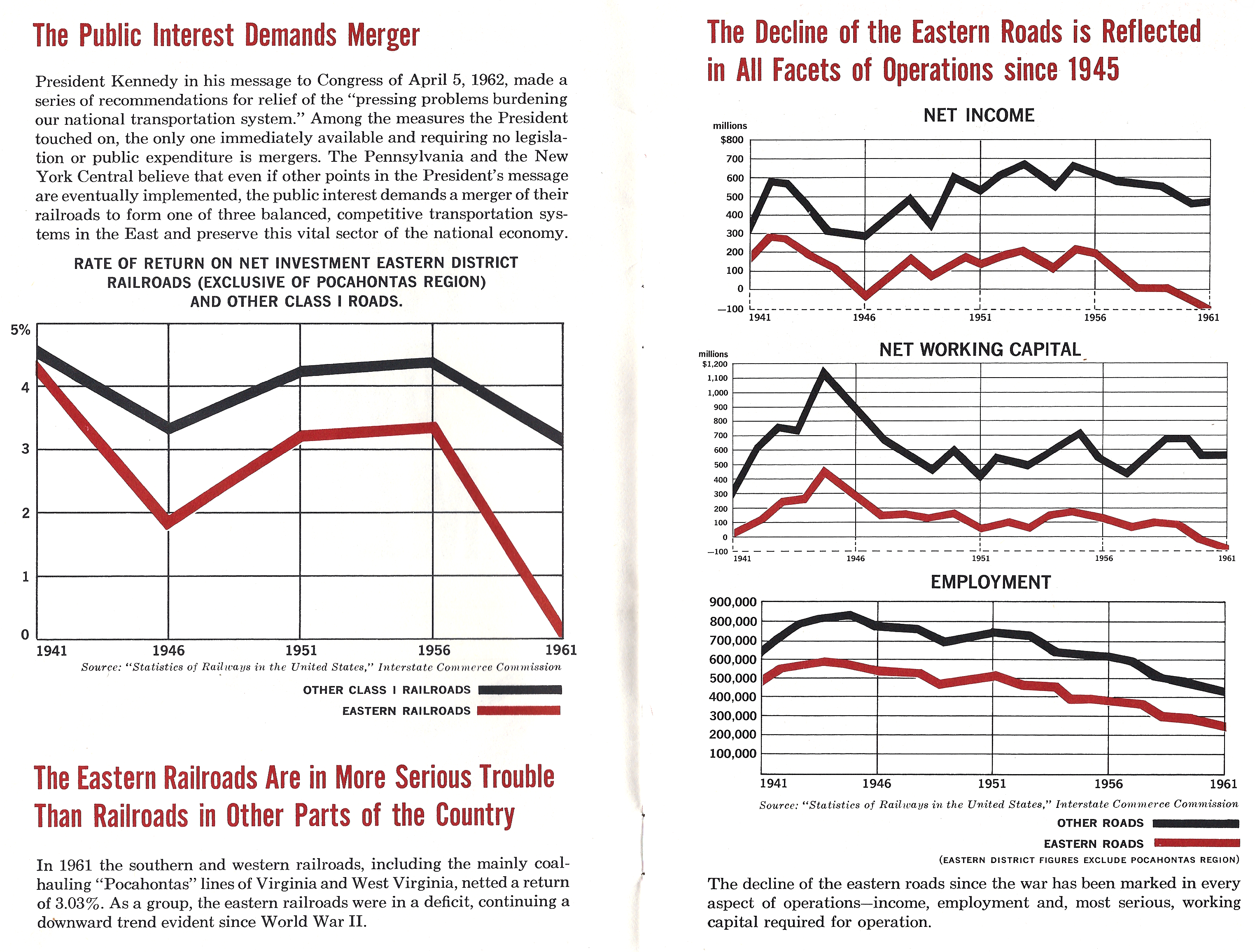
Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals, the Pennsylvania, New York Central and the New York, New Haven and Hartford railroad, each of which were united by large-scale service into the New York metropolitan area and to a lesser extent New England and Chicago. The new company failed barely two years after formation, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at the time. Penn Central's railroad assets were nationalized into Conrail along with those of other bankrupt northeastern railroads; its real estate and insurance holdings successfully reorganized into American Premier Underwriters. History Pre-merger The Penn Central railroad system developed in response to challenges facing northeastern American railroads during the late 1960s. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew revenues from long-distance shipment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrisburg Transportation Center
The Harrisburg Transportation Center (HTC, formerly Pennsylvania Station, Harrisburg or Harrisburg Central Railroad Station) is a railway station and transportation hub in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. It is located on the eastern edge of Downtown Harrisburg between the intersections of Aberdeen and Market Streets and 4th and Chestnut Streets. The station is the primary hub for passenger rail and intercity bus services in the Harrisburg metropolitan area and South Central Pennsylvania. History The current station is the third on the site. Though technically a union station, which is a station used by several railways, it was never identified as such in publications such as the Official Guide of the Railroads and Steam Navigation Lines or Pennsylvania Railroad Timetables. The first two stations were shared by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR), Reading Railroad, Northern Central Railway (NCR), and the Cumberland Valley Railroad (CVR). The third and current station excluded the Rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
30th Street Station
30th Street Station, officially William H. Gray III 30th Street Station, is a major intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transit station in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The station opened in 1933 as Pennsylvania Station–30th Street, replacing the 1881 Broad Street Station (Philadelphia), Broad Street station as the Pennsylvania Railroad's main station in the city. The station is List of busiest Amtrak stations, third-busiest Amtrak station in the nation with over 4.1 million passengers as of 2023. 30th Street Station is currently Delaware Valley, metropolitan Philadelphia's main train station, railroad station and a major stop on Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Northeast and Keystone Corridor, Keystone corridors. The station is also a major commuter rail station served by all SEPTA Regional Rail lines and is the western terminus for NJ Transit Rail Operations, NJ Transit's Atlantic City Line. The station is also served by several SEPTA-managed SEPTA City Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Ridge Branch
The Bay Ridge Branch is a rail line in New York City, owned by the Long Island Rail Road (LIRR) and operated by the New York and Atlantic Railway. It is the longest freight-only line of the LIRR, connecting the Montauk Branch and CSX Transportation's Fremont Secondary (to the Hell Gate Bridge) at Glendale, Queens, with the Upper New York Bay at Bay Ridge, Brooklyn. Car float service provided by New York New Jersey Rail operates between Greenville Yard at Greenville, Jersey City and the 65th Street Yard at the Bay Ridge end of the line. History Early history The first part of the line was opened by the New York, Bay Ridge and Jamaica Railroad in 1876, from Bay Ridge to the crossing of the Brooklyn, Bath and Coney Island Railroad near New Utrecht. , April 2005 Edition An extension from New Utrecht east and northeast to New Lots opened in 1877, and at the same time the New York and Manhattan Beach Railway opened the line from New Lots north to East New York. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island Rail Road , or LIRR, is a Rail transport, railroad in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County, New York, Suffolk County on Long Island. The railroad currently operates a public commuter rail service, with its freight operations contracted to the New York and Atlantic Railway. With an average weekday ridership of 354,800 passengers in 2016, it is the List of United States commuter rail systems by ridership, busiest commuter railroad in North America. It is also one of the world's few commuter systems that run 24/7 year-round. It is Government-owned corporation, publicly owned by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, which refers to it as MTA Long Island Rail Road. In , the system had a ridership of , or about per weekday as of . The LIRR logo combines the circular MTA logo with the text ''Long Island Rail Road'', and appears on the sides of trains. The LIRR is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Station (1910–1963)
Pennsylvania Station (often abbreviated to Penn Station) was a historic railroad station in New York City that was built for, named after, and originally occupied by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR). The station occupied an plot bounded by Seventh Avenue (Manhattan), Seventh and Eighth Avenue (Manhattan), Eighth Avenues and 31st and 33rd Streets in Midtown Manhattan. Because the station shared its name with several stations in other cities, it was sometimes called New York Pennsylvania Station. Originally completed in 1910, the aboveground portions of the building were demolished between 1963 and 1966, and the underground concourses and platforms were heavily renovated to form the current Pennsylvania Station (New York City), Pennsylvania Station within the same footprint. Designed by McKim, Mead, and White and completed in 1910, the station enabled direct rail access to New York City from the south for the first time. Its above ground head house and train shed were considered a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunnyside Yard
Sunnyside Yard is a large coach yard, a railroad yard for passenger cars in the Sunnyside neighborhood of Queens in New York City. The yard is owned by Amtrak and is also used by New Jersey Transit. The Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) completed construction of the yard in 1910; it was originally the largest coach yard in the world, occupying 192 acres (0.78 km2). Harold Interlocking, the United States' busiest rail junction, is part of the yard. The shared tracks of the Long Island Rail Road (LIRR) Main Line and Amtrak's Northeast Corridor pass along the southern edge of the yard. Northeast of the yard a balloon track (or reverse loop) is used for "U-turning" Amtrak and NJ Transit trains which terminate at Penn Station. Leading eastward near the south side of the yard, this balloon track switches off and turns left under the LIRR/Amtrak tracks, turns left once again, and merges with the Sunnyside Yard track to turn the train west toward Penn Station. History The Penn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Married Pair
A twin unit, twinset, or double unit is a set of two railroad Railway car, cars or locomotives which are permanently coupled and treated as if they were a single unit. A twinset of cars or coaches can also be called a twin car. In US passenger railroad parlance, twin units are also known as married pairs. On passenger railroads, light rail, and monorail services, married pairs may have machinery necessary for full operation of the cars split between them. Items that are typically shared include transformers, motor controllers, dynamic braking grids, cabs, current collectors, batteries, and air compressors. This provides significant savings in both cost of equipment and weight, which increases performance and decreases energy consumption. The Operating cost, cost of operating such a pair may be slightly higher when the extra car in such a pair is not needed to meet level-of-service demands at a particular time. See also * Cow–calf * Multiple unit References Rolling s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whyte Notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in ''American Engineer and Railroad Journal''. The notation was adopted and remains in use in North America and the United Kingdom to describe the wheel arrangements of steam locomotives, but for modern locomotives, multiple units and trams it has been supplanted by the UIC system in Europe and by the AAR system (essentially a simplification of the UIC system) in North America. However, geared steam locomotives do not use the notation. They are classified by their model and their number of trucks. Structure of the system Basic form The notation in its basic form counts the number of leading wheels, then the number of driving wheels, and finally the number of trailing wheels, numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country. Within a given country, different notations may also be employed for different kinds of locomotives, such as steam, electric, and diesel powered. Especially in steam days, wheel arrangement was an important attribute of a locomotive because there were many different types of layout adopted, each wheel being optimised for a different use (often with only some being actually "driven"). Modern diesel and electric locomotives are much more uniform, usually with all axles driven. Major notation schemes The main notations are the Whyte notation (based on counting the wheels), the AAR wheel arrangement notation (based on counting either the axles or the bogies), and the UIC classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |