|
PRIX Index
The PRIX index (or Political Risk for Oil Exports Index) is a financial indicator for international oil markets to understand the political risks associated with oil exports. The index forecasts and sums up political risks around the world that may affect the supply of oil to international markets. It is based on the same methodology as a Purchasing Managers' Index. Around 250 country analysts provide input, which is subsequently used to calculate an index value for each of the world’s 20 largest oil-exporting countries. Each of these country values is subsequently weighted by the exports of the countries in order to compute a single, weighted, global PRIX index number that sums up the political risk for international oil markets during the coming three months. Variations in oil exports are an important component of global oil price formation. Thus, the PRIX index forecast may help identify potential trajectories of international price of oil The price of oil, or the oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Risk
Political risk is a type of risk faced by investors, corporations, and governments that political decisions, events, or conditions will significantly affect the profitability of a business actor or the expected value of a given economic action. Political risk can be understood and managed with reasoned foresight and investment. The term political risk has had many different meanings over time. Broadly speaking, however, political risk refers to the complications businesses and governments may face as a result of what are commonly referred to as political decisions—or "any political change that alters the expected outcome and value of a given economic action by changing the probability of achieving business objectives". Political risk faced by firms can be defined as "the risk of a strategic, financial, or personnel loss for a firm because of such nonmarket factors as macroeconomic and social policies (fiscal, monetary, trade, investment, industrial, income, labour, and developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index (economics)
In economics, statistics, and finance, an index is a number that measures how a group of related data points—like prices, company performance, productivity, or employment—changes over time to track different aspects of economic health from various sources. Consumer-focused indices include the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which shows how retail prices for goods and services shift in a fixed area, aiding adjustments to salaries, Bond (finance), bond interest rates, and tax thresholds for inflation. The cost-of-living index (COLI) compares living expenses over time or across places.Turvey, Ralph. (2004) Consumer Price Index Manual: Theory And Practice.' Page 11. Publisher: International Labour Organization. . ''The Economist''’s Big Mac Index uses a Big Mac’s cost to explore currency values and purchasing power. Market performance indices track trends like company value or employment. Stock market index, Stock market indices include the Dow Jones Industrial Average and S&P 500, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purchasing Managers' Index
Purchasing managers' indexes (PMI) are economic indicators derived from monthly surveys of private sector companies. The three principal producers of PMIs are S&P Global (from 2022 merger with IHS Markit), which produces PMIs for over 30 countries worldwide and developed the first service sector PMIs, and the Institute for Supply Management (ISM), which originated the manufacturing surveys produced for the United States. Other producers include the Singapore Institute of Purchasing and Materials Management (SIPMM), which produces the Singapore PMI, Swedbank in Sweden, NBS in mainland China, and Credit Suisse in Switzerland. An official global PMI is produced by S&P Global in association with J.P.Morgan, the ISM and IFPSM, which also includes detailed sector survey results. Regional headline indicators and detailed sector data are also compiled by S&P Global. The purchasing managers' index (PMI) surveys are compiled on a monthly basis by polling businesses which represent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
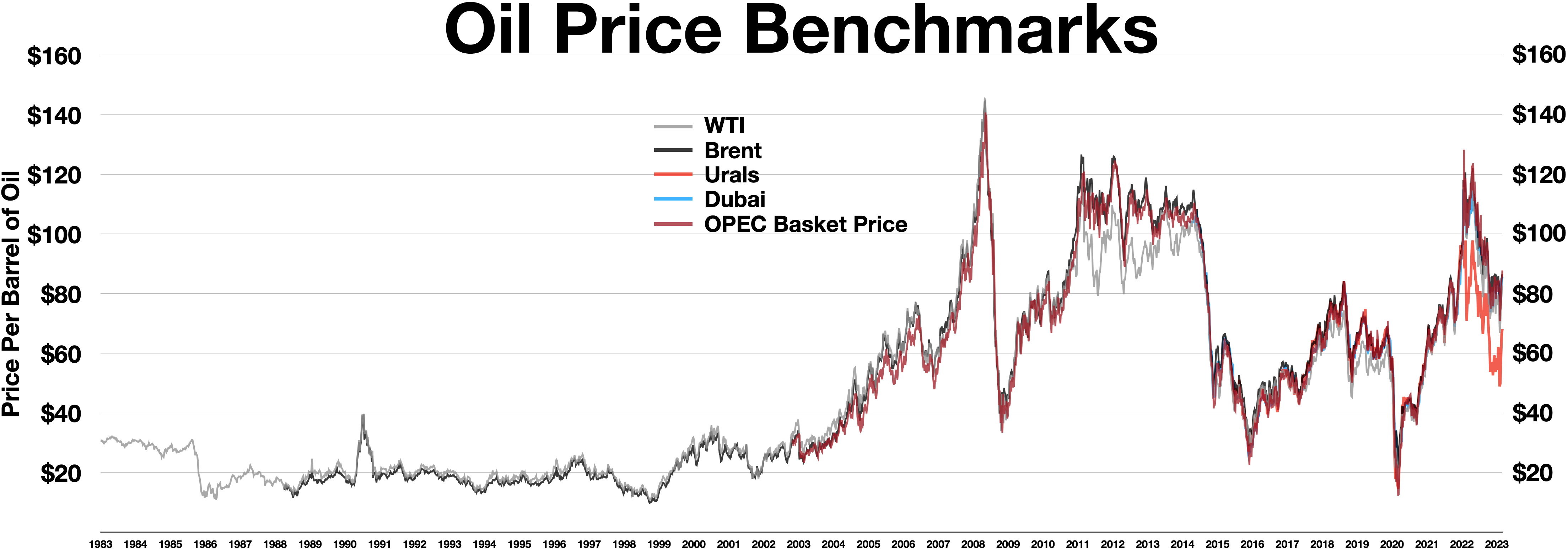
Price Of Oil
The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel () of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus, and Western Canadian Select (WCS). Oil prices are determined by global supply and demand, rather than any country's domestic production level. Through the years The global price of crude oil was relatively consistent in the nineteenth century and early twentieth century. This changed in the 1970s, with a significant increase in the price of oil globally. There have been a number of structural drivers of global oil prices historically, including oil supply, demand, and storage shocks, and shocks to global economic growth affecting oil prices. Notable events driving significant price fluctuations include the 1973 OPEC oil embargo targeting nations that had supported I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Economics
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil, as well as to petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil. Petroleum is a fossil fuel formed over millions of years from anaerobic decay of organic materials from buried prehistoric organisms, particularly planktons and algae, and 70% of the world's oil deposits were formed during the Mesozoic. Conventional reserves of petroleum are primarily recovered by drilling, which is done after a study of the relevant structural geology, analysis of the sedimentary basin, and characterization of the petroleum reservoir. There are also unconventional reserves such as oil sands and oil shale which are recovered by other means such as fracking. Once extracted, oil is refined and separated, most easily by distil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |