|
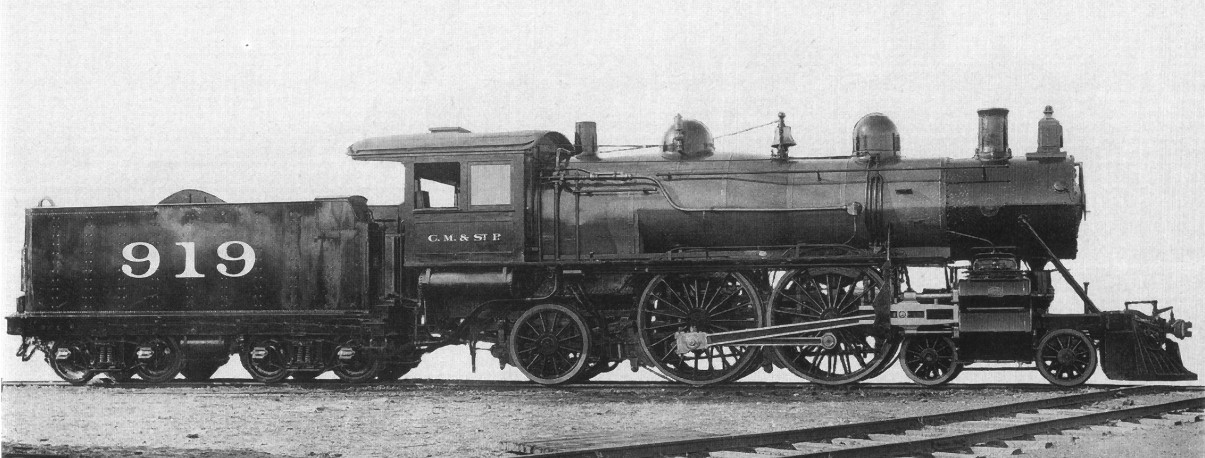
PKP Class Pd1
The Prussian Class S 3s were saturated steam locomotives developed by Hanomag for the Prussian state railways and were built from 1893. Design They were a further development of the S 2 and used the same boiler. The "S" stood for ''Schnellzuglokomotive'', or express locomotive, of which the S 3 was a large and powerful type. Because larger turntables with a 16-metre diameter were then being built, the wheelbase could be longer, which gave it better riding qualities. The locomotive had one high-pressure and one low-pressure cylinder, coupled to four driving wheels in a configuration. They were the first class of locomotives to use superheating, a process in which the steam leaving the boiler is re-heated, resulting in better efficiency. Procurement The railway procured a total of 1,027 locomotives of this class up to 1904, and they were stabled at almost all locomotive depots (''Betriebswerk'' or ''Bw''), making them the most numerous German express train locomotives. In additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanomag
Hanomag (Hannoversche Maschinenbau AG, ) was a German producer of steam locomotives, tractors, trucks and military vehicles in Hanover. Hanomag first achieved international fame by delivering numerous steam locomotives to Finland, Romania and Bulgaria before World War I and making of first tractor Hanomag R26 in 1924 in Germany. In 1925, they added automobiles to their line, additionally moving in 1931 into the production of construction machinery. Since 1989, the company has been part of the Komatsu company. History The company dates back to 1835 when Georg Egestorff founded in Linden near Hanover a company called ''Eisen-Giesserey und Maschinenfabrik Georg Egestorff'' to build small steam engines. They soon started making farm machinery and in 1846 built their first railway locomotive for the Royal Hanoverian State Railways. By 1870 they had made 500 locomotives and in 1871 changed their name to ''Hannoversche Maschinenbau Actien-Gesellschaft vorm. Georg Egestorff, Lind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, in some steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. There are three types of superheaters: radiant, convection, and separately fired. A superheater can vary in size from a few tens of feet to several hundred feet (a few metres to some hundred metres). Types * A radiant superheater is placed directly in the radiant zone of the combustion chamber near the water wall so as to absorb heat by radiation. * A convection superheater is located in the convective zone of the furnace, in the path of the hot flue gases, usually ahead of an economizer. A convection superheater is also called a primary superheater. * A separately fired superheater is a superheater that is placed outside the main boiler and has its own separate combustion system. This superheater design incorporates additional burners i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotive
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound steam engine, compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to a perceived increased maintenance requirement. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway up to 1952 and more importantly, Compound locomotives continued to be designed and built in France until the end of steam in the 1970's. French compounding of railway engines became so highly developed, eventually incorporating reheaters between the high and low pressure stages as well as the initial use of superh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Renumbering Plan
In 1922, the Deutsche Reichsbahn began to develop a renumbering plan to standardize the numbering of steam locomotives that had been taken over from the state railways (''Länderbahnen''). Its basis was the corresponding DRG classification system. The first renumbering plan in 1922 envisaged more class numbers than the later plans. The development of this scheme was discontinued because it was seen that there would be problems in practically adopting it. The second, provisional, renumbering plan of 25 July 1923 was very like the final version of 1925 in its basic structure. It incorporated space for the new standard locomotives ('' Einheitslokomotiven'') that were planned. The third and final renumbering plan of 1925 differed from its predecessor primarily in that all the locomotives retired up to that point – in some cases entire classes – were deleted; in addition several mistakes in the numbering were corrected. With the exception of Bavarian classes, new locomotives built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the Weimar Republic, German national Rail transport, railway system created after the end of World War I from the regional railways of the individual states of the German Empire. The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' has been described as "the largest enterprise in the capitalist world in the years between 1920 and 1932"; nevertheless, its importance "arises primarily from the fact that the Reichsbahn was at the center of events in a period of great turmoil in German history". Overview The company was founded on 1 April 1920 as the ("German Imperial Railways") when the Weimar Republic, which still used the nation-state term of the previous monarchy, (German Reich, hence the usage of the in the name of the railway; the monarchical term was ), took national control of the German railways, which had previously been run by the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Steam Locomotive S 3 - Stettin 9
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, History of Berlin, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. Prussia formed the German Empire when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by 1932 Prussian coup d'état, an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by Abolition of Prussia, an Allied decree in 1947. The name ''Prussia'' derives from the Old Prussians who were conquered by the Teutonic Knightsan organized Catholic medieval Military order (religious society), military order of Pru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldenburg S 3
The Oldenburg Class S 3 steam locomotive was a German engine built for the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg State Railways (''Großherzoglich Oldenburgische Staatseisenbahnen'') in 1903 and 1904. It was based on a Prussian prototype, the Prussian S 3 (see photo), and procured for the route between Wilhelmshaven, Oldenburg and Bremen. It was the first express train engine built for the Oldenburg state railways and also the first one fitted with a steam dome. It replaced the old P 4 passenger train locomotives. Six engines were built by Hanomag in 1903 and 1904 with numbers 151–154, 160 and 161. They differed in several technical details from their Prussian counterparts, but did not have Lentz valve gear which, later, became common throughout Oldenburg. The Deutsche Reichsbahn took over all six locomotives and grouped them into DRG Class 13.18, allocating them the numbers 13 1801 to 13 1806. They were retired by 1927. See also * Grand Duchy of Oldenburg State Railways *List of Oldenbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Oldenburg State Railways
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg Railway (''Großherzoglich Oldenburgische Eisenbahn or GOE'') was the railway company that was run as a state railway for the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg (''Großherzogtum Oldenburg''), part of the German Empire. History Compared with the other states in the German Empire, Oldenburg's first railway line arrived relatively late. In this sparsely populated and economically poor area, the construction of railways appeared for a long while to be unsustainable due to the financial costs. In addition, the various ideas of its neighboring states, Hanover and Prussia prevented railway projects from coming to fruition for a long time. Finally in 1864 a treaty was agreed between Prussia and Oldenburg over the construction of a railway line from Bremen to Oldenburg. At the same time Prussia committed itself to building a railway line from Heppens – later Wilhelmshaven – to Oldenburg (the Wilhelmshaven–Oldenburg line). The Grand Ducal Railway Commission, set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Railways In Alsace-Lorraine
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism. Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to: Places United States * Imperial, California * Imperial, Missouri * Imperial, Nebraska * Imperial, Pennsylvania * Imperial, Texas * Imperial, West Virginia * Imperial, Virginia * Imperial County, California * Imperial Valley, California * Imperial Beach, California Elsewhere * Imperial (Madrid), an administrative neighborhood in Spain * Imperial, Saskatchewan, a town in Canada Buildings * Imperial Apartments, a building in Brooklyn, New York * Imperial City, Huế, a palace in Huế, Vietnam * Imperial Palace (other) * Imperial Towers, a group of lighthouses on Lake Huron, Canada * The Imperial (Mumbai), a skyscraper apartment complex in India * Imperial War Museum, a British military museum and organisation based in London, UK * * Imperial War Museum Duxford, an aviation museum in Cambridgeshire, UK * * Imperial War Museum North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian P 4
The Prussian P 4 was a derivative of the P 4.1 (Hanover variant) and the second superheated steam locomotive in the world. Design The engine was based on that of the Class P 4.1 that had Hanomag had produced in large numbers since 1892. It had slightly larger wheels and, due to its new design, significantly fewer heating tubes. The superheater and the steam engine were entirely independent designs. Service and preservation In 1898 a one-off was delivered by Hanomag to the Prussian state railways. The economy of the superheated system was soon proven in 1899 by the engine during trial runs from Kassel. Apart from a short stay at Halle the engine was assigned to Kassel as ''Cassel 131'' and, from 1906, as ''P 4 Cassel 1846''. In 1921, after the First World War, the engine was mothballed, along with many other machines of similar class. With its sectioned boiler the P 4 stood for a long time in the Transport and Construction Museums, part of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |