|
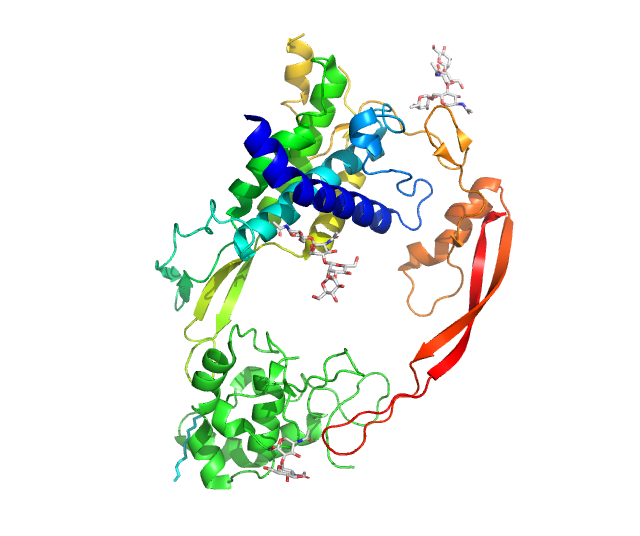
PKD1
Polycystin 1 (PC1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PKD1'' gene. Mutations of ''PKD1'' are associated with most cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, a severe hereditary disorder of the kidneys characterised by the development of renal cysts and severe kidney dysfunction. Protein structure and function PC1 is a membrane-bound protein 4303 amino acids in length expressed largely upon the primary cilium, as well as apical membranes, adherens junctions, and desmosomes. It has 11 transmembrane domains, a large extracellular N-terminal domain, and a short (about 200 amino acid) cytoplasmic C-terminal domain. This intracellular domain contains a coiled-coil domain through which PC1 interacts with polycystin 2 (PC2), a membrane-bound Ca2+-permeable ion channel. PC1 has been proposed to act as a G protein–coupled receptor. The C-terminal domain may be cleaved in a number of different ways. In one instance, a ~35 kDa portion of the tail h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common, life-threatening Genetic disorder, inherited human disorders and the most common hereditary kidney disease. It is associated with large interfamilial and intrafamilial variability, which can be explained to a large extent by its genetic heterogeneity and modifier genes. It is also the most common of the inherited cystic kidney diseases — a group of disorders with related but distinct pathogenesis, characterized by the development of renal cysts and various extrarenal manifestations, which in case of ADPKD include cysts in other organs, such as the liver, seminal vesicles, pancreas, and arachnoid membrane, as well as other abnormalities, such as intracranial aneurysms and Intracranial dolichoectasias, dolichoectasias, aortic root dilatation and aneurysms, mitral valve prolapse, and abdominal wall hernias. Over 50% of patients with ADPKD eventually develop Kidney failure, end stage kidney disease and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystin 2
Polycystin-2 (PC2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PKD2'' gene. The gene ''PKD2'' also known as TRPP2, encodes a member of the polycystin protein family, called TRPP, and contains multiple transmembrane domains, and cytoplasmic N- and C-termini. The protein may be an integral membrane protein involved in cell-cell/matrix interactions. TRPP2 may function in renal tubular development, morphology, and function, and may modulate intracellular calcium homeostasis and other signal transduction pathways. This protein interacts with polycystin 1 (TRPP1) to produce cation-permeable currents. It was discovered by Stefan Somlo at Yale University. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Interactions Polycystin 2 has been shown to interact with the proteins TRPC1, PKD1 and TNNI3. See also * HAX1 * TRPP TRPP (transient receptor potential polycystic) is a family of transient receptor poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Pseudogenes can be formed from both protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. In the case of protein-coding genes, most pseudogenes arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by gene duplication or indirectly by Reverse transcriptase, reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences or are incapable of producing a functional product. Pseudogenes are a type of junk DNA. Most non-bacterial genomes contain many pseudogenes, often as many as functional genes. This is not surprising, since various biological processes are expected to accidentally create pseudogenes, and there are no specialized mechanisms to remove them from genomes. Eventually pseudogenes may be deleted from their genomes by chance of DNA replication or DNA repair errors, or they may accumulate so many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and has a considerable amount of collagen. It contains no nerves or blood vessels, and its structure is relatively simple. Structure Hyaline cartilage is the most common kind of cartilage in the human body. It is primarily composed of type II collagen and proteoglycans. Hyaline cartilage is located in the trachea, nose, epiphyseal plate, sternum, and ribs. Hyaline cartilage is covered externally by a fibrous membrane known as the perichondrium. The primary cells of cartilage are chondrocytes, which are in a Matrix (biology), matrix of fibrous tissue, proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans. As cartilage does not have lymph glands or blood vessels, the movements of solutes, including nutrients, occur via diffusion within the fluid compartments con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanosensation
Mechanosensation is the transduction of mechanical stimuli into neural signals. Mechanosensation provides the basis for the senses of light touch, hearing, proprioception, and pain. Mechanoreceptors found in the skin, called cutaneous mechanoreceptors, are responsible for the sense of touch. Tiny cells in the inner ear, called hair cells, are responsible for hearing and balance. States of neuropathic pain, such as hyperalgesia and allodynia, are also directly related to mechanosensation. A wide array of elements are involved in the process of mechanosensation, many of which are still not fully understood. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors are physiologically classified with respect to conduction velocity, which is directly related to the diameter and myelination of the axon. Rapidly adapting and slowly adapting mechanoreceptors Mechanoreceptors that possess a large diameter and high myelination are called ''low-threshold mechanoreceptors''. Fibers that respond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-gated Ion Channel
Voltage-gated ion channels are a class of transmembrane proteins that form ion channels that are activated by changes in a Cell (biology), cell's electrical membrane potential near the channel. The membrane potential alters the conformation of the channel proteins, regulating their opening and closing. Cell membranes are generally impermeable to ions, thus they must diffuse through the membrane through transmembrane protein channels. Voltage-gated ion channels have a crucial role in excitable cells such as neuronal and muscle tissues, allowing a rapid and co-ordinated depolarization in response to triggering Voltage drop, voltage change. Found along the axon and at the synapse, voltage-gated ion channels directionally propagate electrical signals. Voltage-gated ion-channels are usually ion-specific, and channels specific to Sodium channel#Voltage-gated, sodium (Na+), Voltage-gated potassium channel, potassium (K+), Voltage-dependent calcium channel, calcium (Ca2+), and Chloride ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Electron Microscopy
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a transmission electron microscopy technique applied to samples cooled to cryogenic temperatures. For biological specimens, the structure is preserved by embedding in an environment of vitreous ice. An aqueous sample solution is applied to a grid-mesh and plunge-frozen in liquid ethane or a mixture of liquid ethane and propane. While development of the technique began in the 1970s, recent advances in detector technology and software algorithms have allowed for the determination of biomolecular structures at near-atomic resolution. This has attracted wide attention to the approach as an alternative to X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy in the structural biology field. In 2017, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jacques Dubochet, Joachim Frank, and Richard Henderson "for developing cryo-electron microscopy for the high-resolution structure determination of biomolecules in solution." '' Nature Methods'' also named cryo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wnt Signaling Pathway
In cellular biology, the Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt, pronounced "wint", is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SND1
Staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing protein 1 also known as 100 kDa coactivator or Tudor domain-containing protein 11 (TDRD11) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SND1'' gene. SND1 is a main component of RISC complex and plays an important role in miRNA function. SND1 is Tudor domain containing protein and Tudor Proteins are highly conserved proteins and even present in Drosophila melanogaster. SND1 is also involved in Autism. Clinical significance SND1 acts as oncogene in many cancers and in hepatocellular carcinoma progression. SND1 promotes tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma through a novel pathway which involves NF-kappaB and miR-221. SND1 promotes migration and invasion via angiotensin II type 1 receptor and TGFβ signaling. SND1 expression is regulated by Mir-184 in gliomas. Interactions SND1 has been shown to interact with MYB, * PIM1, POLR2A, RBPJ Recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT6
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) is a transcription factor that belongs to the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) family of proteins. The proteins of STAT family transmit signals from a receptor complex to the nucleus and activate gene expression. Similarly as other STAT family proteins, STAT6 is also activated by growth factors and cytokines. STAT6 is mainly activated by cytokines interleukin-4 and interleukin-13. Molecular biology In the human genome, STAT6 protein is encoded by the STAT6 gene, located on the chromosome 12q13.3-q14.1. The gene encompasses over 19 kb and consists of 23 exons. STAT6 shares structural similarity with the other STAT proteins and is composed of the N-terminal domain, DNA binding domain, SH3- like domain, SH2 domain and transactivation domain (TAD). STAT proteins are activated by the Janus family (JAKs) tyrosine kinases in response to cytokine exposure. STAT6 is activated by cytokines in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have Multinucleate, many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long strands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are Nuclear organization, structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |