|
PIEZO1
Piezo1 is a mechanosensitive ion channel protein that in humans is encoded by the gene ''PIEZO1''. Piezo1 and its close homolog Piezo2 were cloned in 2010, using an siRNA-based screen for mechanosensitive ion channels. Structure and function PIEZO1 (this gene) and PIEZO2 share 47% identity with each other and they have no similarity to any other protein and contain no known protein domains. They are predicted to have 24-36 transmembrane domains, depending on the prediction algorithm used. In the original publication the authors were careful not to call the piezo proteins ion channels, but a more recent study by the same lab convincingly demonstrated that indeed piezo1 is the pore-forming subunit of a mechanosensitive channel. This new "PIEZO" family is catalogued as and TCDB . PIEZO1 homologues are found in ''C. elegans'' and ''Drosophila'', which, like other invertebrates, have a single piezo protein. It is known () that Piezo1 channel is a three-bladed propeller-like struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomatocytosis
Hereditary stomatocytosis describes a number of inherited, mostly autosomal dominant human conditions which affect the red blood cell and create the appearance of a slit-like area of central pallor (stomatocyte) among erythrocytes on peripheral blood smear. The erythrocytes' cell membranes may abnormally 'leak' sodium and/or potassium ions, causing abnormalities in cell volume. Hereditary stomatocytosis should be distinguished from acquired causes of stomatocytosis, including dilantin toxicity and alcoholism, as well as artifact from the process of preparing peripheral blood smears. Signs and symptoms Stomatocytosis may present with signs and symptoms consistent with hemolytic anemia as a result of extravascular hemolysis and often intravascular hemolysis. These include fatigue and pallor, as well as signs of jaundice, splenomegaly and gallstone formation from prolonged hemolysis. Certain cases of hereditary stomatocytosis associated with genetic syndromes have additional s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanosensitive Ion Channel
Mechanosensitive channels, mechanosensitive ion channels or stretch-gated ion channels (not to be confused with mechanoreceptors). They are present in the membranes of organisms from the three domains of life: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. They are the sensors for a number of systems including the senses of touch, hearing and balance, as well as participating in cardiovascular regulation and osmotic homeostasis (e.g. thirst). The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes. All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. Under extreme turgor in bacteria, non selective MSCs such as MSCL and MSCS serve as safe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoda1
Yoda1 is a chemical compound which is the first agonist developed for the mechanosensitive ion channel PIEZO1. This protein is involved in regulation of blood pressure and red blood cell Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ... volume, and Yoda1 is used in scientific research in these areas. See also * Jedi1 and Jedi2 References Thioethers Pyrazines Thiadiazoles Chloroarenes {{pharm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PIEZO2
Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PIEZO2 gene. It has a homotrimeric structure, with three blades curving into a nano-dome, with a diameter of 28 nanometers. Function Piezos are large transmembrane proteins conserved among various species, all having between 24 and 36 predicted transmembrane domains. 'Piezo' comes from the Greek 'piesi,' meaning 'pressure.' The PIEZO2 protein has a role in rapidly adapting mechanically activated (MA) currents in somatosensory neurons. Its structure is resolved via a mouse version in 2019, showing the predicted homotrimeric propeller. PIEZO2 is typically found in tissues that respond to physical touch, such as Merkel cells, and is thought to regulate light touch response. Pathology * Gain-of-function mutations in the mechanically activated ion channel PIEZO2 cause a subtype of Distal Arthrogryposis. * Mice without PIEZO2 in their proprioceptive neurons show uncoordinated body mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jedi2
Jedi2 is a chemical compound which acts as an agonist for the mechanosensitive ion channel PIEZO1, and is used in research into the function of touch perception. See also * Yoda1 Yoda1 is a chemical compound which is the first agonist developed for the mechanosensitive ion channel PIEZO1. This protein is involved in regulation of blood pressure and red blood cell Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, re ... and Jedi1 References Furans Thiophenes {{pharm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Domain
A transmembrane domain (TMD) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs generally adopt an alpha helix topological conformation, although some TMDs such as those in porins can adopt a different conformation. Because the interior of the lipid bilayer is hydrophobic, the amino acid residues in TMDs are often hydrophobic, although proteins such as membrane pumps and ion channels can contain polar residues. TMDs vary greatly in length, sequence, and hydrophobicity, adopting organelle-specific properties. Functions of transmembrane domains Transmembrane domains are known to perform a variety of functions. These include: * Anchoring transmembrane proteins to the membrane. *Facilitating molecular transport of molecules such as ions and proteins across biological membranes; usually hydrophilic residues and binding sites in the TMDs help in this process. *Signal transduction across the membrane; many transmembrane proteins, such as G protein-coupled receptors, receive extracel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium and calcium ions, as well as that of the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in the optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms: it is thought to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
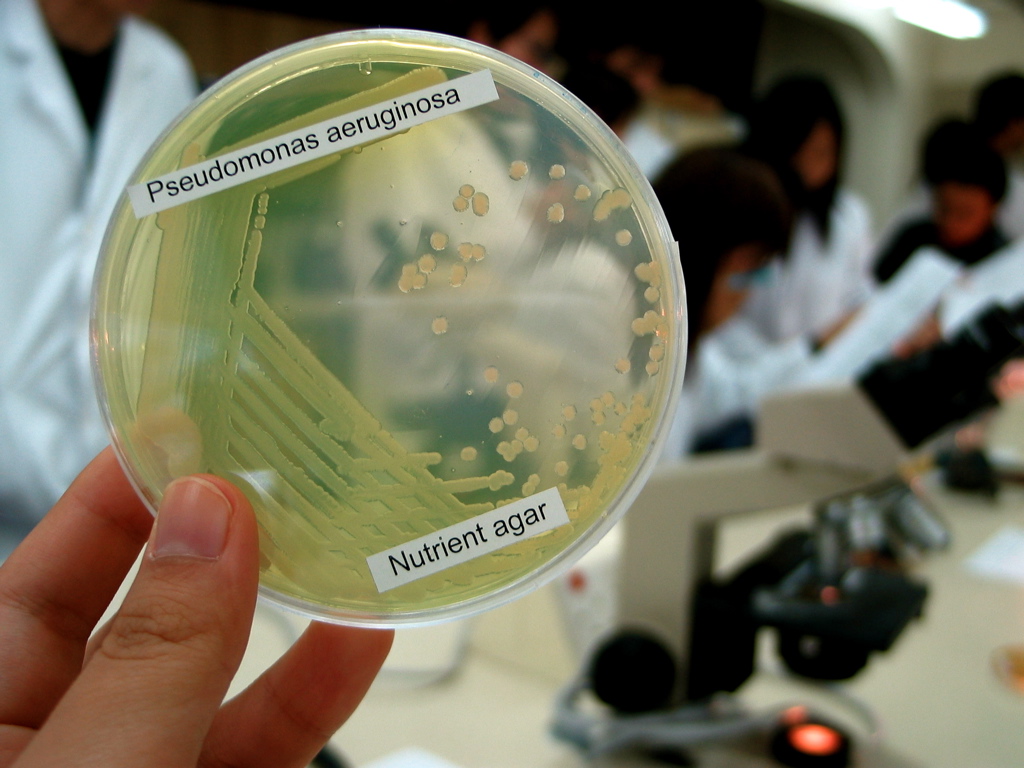
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. The organism is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of ''P. aeruginosa'' infections can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
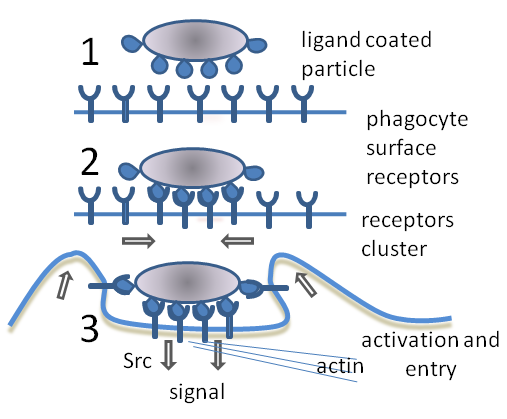
Innate Immune Cell
A non-specific immune cell is an immune cell (such as a macrophage, neutrophil, or dendritic cell) that responds to many antigens, not just one antigen. Non-specific immune cells function in the first line of defense against infection or injury. The innate immune system is always present at the site of infection and ready to fight the bacteria; it can also be referred to as the "natural" immune system. The cells of the innate immune system do not have specific responses and respond to each foreign invader using the same mechanism. The innate immune system There are two categories to which parts of the immune system are assigned: the non-specific, or innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The non-specific response is a generalized response to pathogen infections involving the use of several white blood cells and plasma proteins. Non-specific immunity, or innate immunity, is the immune system with which you were born, made up of phagocytes and barriers. Phagocytosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolayer
A monolayer is a single, closely packed layer of atoms, molecules, or cells. In some cases it is referred to as a self-assembled monolayer. Monolayers of layered crystals like graphene and molybdenum disulfide are generally called 2D materials. Chemistry A Langmuir monolayer or insoluble monolayer is a one-molecule thick layer of an insoluble organic material spread onto an aqueous sub phase in a Langmuir-Blodgett trough. Traditional compounds used to prepare Langmuir monolayers are amphiphilic materials that possess a hydrophilic headgroup and a hydrophobic tail. Since the 1980s a large number of other materials have been employed to produce Langmuir monolayers, some of which are semi-amphiphilic, including polymeric, ceramic or metallic nanoparticles and macromolecules such as polymers. Langmuir monolayers are extensively studied for the fabrication of Langmuir-Blodgett film (LB films), which are formed by transferred monolayers on a solid substrate. A Gibbs monolayer o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells known as circulating tumor cells acquire the ability to penetrate the walls of lymphatic or blood vessels, after which they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as '' Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)