|
PGF2alpha
Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α in prostanoid nomenclature), pharmaceutically termed dinoprost, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin used in medicine to induce labor and as an abortifacient. Prostaglandins are lipids throughout the entire body that have a hormone-like function. In pregnancy, PGF2α is medically used to sustain contracture and provoke myometrial ischemia to accelerate labor and prevent significant blood loss in labor. Additionally, PGF2α has been linked to being naturally involved in the process of labor. It has been seen that there are higher levels of PGF2α in maternal fluid during labor when compared to at term. This signifies that there is likely a biological use and significance to the production and secretion of PGF2α in labor. Prostaglandin is also used to treat uterine infections in domestic animals. In domestic mammals, it is produced by the uterus when stimulated by oxytocin, in the event that there has been no implantation during the luteal phase. It a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandins
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and of the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives. The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities. A given prostaglandin may have different and even opposite effects in different tissues in some cases. The ability of the same prostaglandin to stimulate a reaction in one tissue and inhibit the same reaction in another tissue is determined by the type of receptor to which the prostaglandin binds. They act as autocrine or paracrine factors with their target cells present in the immediate vicinity of the site of their secretion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiology, physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every Tissue (biology), tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a carbon ring, 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and of the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives. The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities. A given prostaglandin may have different and even opposite effects in different tissues in some cases. The ability of the same prostaglandin to stimulate a reaction in one tissue and inhibit the same reaction in another tissue is determined by the type of receptor (biochemistry), receptor to which the prostaglandin binds. They act as autocrine or paracrine factors with their target cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin F2α Receptor
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and of the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives. The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities. A given prostaglandin may have different and even opposite effects in different tissues in some cases. The ability of the same prostaglandin to stimulate a reaction in one tissue and inhibit the same reaction in another tissue is determined by the type of receptor to which the prostaglandin binds. They act as autocrine or paracrine factors with their target cells present in the immediate vicinity of the site of their secretion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG). Proline is the only proteinogenic amino acid which is a secondary amine, as the nitrogen atom is attached both to the α-carbon and to a chain of three carbons that together form a five-membered ring. History and etymology Proline was first isolated in 1900 by Richard Willstätter who obtained the amino a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abortifacients
An abortifacient ("that which will cause a miscarriage" from Latin: ''abortus'' "miscarriage" and '' faciens'' "making") is a substance that induces abortion. This is a nonspecific term which may refer to any number of substances or medications, ranging from herbs to prescription medications. Common abortifacients used in performing medical abortions include mifepristone, which is typically used in conjunction with misoprostol in a two-step approach. Synthetic oxytocin, which is routinely used safely during term labor, is also commonly used to induce abortion in the second or third trimester. For thousands of years, writers in many parts of the world have described and recommended herbal abortifacients to women who seek to terminate a pregnancy, although their use may carry risks to the health of the woman. Medications Because "abortifacient" is a broad term used to describe a substance's effects on pregnancy, there is a wide range of drugs that can be described as abortifa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboprost
Carboprost (International Nonproprietary Name, INN, trade names for the tromethamine salts Hemabate, Tham) is a synthetic prostaglandin analogue of Prostaglandin F2alpha, PGF2α (specifically, it is 15-methyl-PGF2α) with oxytocic properties. Carboprost's main use is to reduce postpartum bleeding during the obstetrical emergency of postpartum hemorrhage. Indication Carboprost is used in postpartum hemorrhage caused by uterine atony not controlled by other methods. One study has shown that carboprost tromethamine is more effective than oxytocin in preventing postpartum hemorrhage in high-risk patients undergoing cesarean delivery. Carboprost was the first drug widely used for medication abortions. It is still sometimes used for second trimester abortions, but has generally been supplanted by the mifepristone/misoprostol combination.Hemabate [Package Insert]. New York, NY: Pharmacia and Upjohn Company; 2014."Carboprost" - Drug fact sheet, Mayo Clinic. Last updated: July 01, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travoprost
Travoprost, sold under the brand name Travatan among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. Specifically it is used for open angle glaucoma when other agents are not sufficient. It is used as an eye drop. Effects generally occur within two hours. Common side effects include red eyes, blurry vision, eye pain, dry eyes, and change in color of the eyes. Other significant side effects may include cataracts. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is generally not recommended. It is a prostaglandin analog and works by increasing the outflow of aqueous humor, aqueous fluid from the eyes. Travoprost was approved for medical use in the United States and in the European Union in 2001. It is available as a generic medication in the United Kingdom. In 2020, it was the 304th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Medical uses Travoprost is used to treat high pressure inside the eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimatoprost
Bimatoprost, sold under the brand name Lumigan among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. Specifically it is used for open angle glaucoma when other agents are not sufficient. It may also be used to increase the size of the eyelashes. It is used as an eye drop and effects generally occur within four hours. Common side effects include red eyes, dry eyes, change in color of the eyes, blurry vision, and cataracts. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is generally not recommended. It is a prostaglandin analog and works by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes. Bimatoprost was approved for medical use in the United States in 2001. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 195th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Uses Medical Bimatoprost is used for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension in adults, either alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latanoprost
Latanoprost, sold under the brand name Xalatan among others, is a medication used to treat increased pressure inside the eye (intraocular pressure). This includes ocular hypertension and open-angle glaucoma. Latanaprost is applied as eye drops to the eyes. Onset of effects is usually within four hours, and they last for up to a day. Common side effects include blurry vision, redness of the eye, itchiness, and darkening of the iris. Latanoprost is in the prostaglandin analogue family of medications. It works by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes through the uveoscleral tract. Latanoprost was approved for medical use in the United States and the European Union in 1996. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Latanoprost is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 67th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 9million prescriptions. It is available as a fixed-dose combinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin Analogue
Prostaglandin analogues are a class of drugs that bind to a prostaglandin receptor. Wider use of prostaglandin analogues is limited by unwanted side effects and their abortive potential. Uses Prostaglandin analogues such as misoprostol are used in treatment of duodenal and gastric ulcers. Misoprostol and other prostaglandin analogues protect the lining of the gastrointestinal tract from harmful stomach acid and are especially indicated for the elderly on continuous doses of NSAIDs. In the field of ophthalmology, drugs of this class are used to lower intraocular pressure (IOP) in people with glaucoma. Up until the late 1970s prostaglandins were thought to raise IOP, but a paper published in 1977 showed that prostaglandin F2α lowered it, and subsequent studies found that this was due to increasing the outflow of aqueous humor, mainly by relaxing the ciliary muscle, and possibly also due to changes in extracellular matrix and to widening of spaces within the trabecular meshwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin F Synthase
In enzymology, a prostaglandin-F synthase (PGFS; ) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction: :(5''Z'',13''E'')-(15''S'')-9alpha,11alpha,15-trihydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate + NADP+ \rightleftharpoons (5''Z'',13''E'')-(15''S'')-9alpha,15-dihydroxy-11-oxoprosta-5,13-dienoate + NADPH + H+ Thus, the two products of this enzyme are 9α,11β–PGF2 and NADP+, whereas its three substrates are Prostaglandin D2, NADPH, and H+. PGFS is a monomeric wild-type protein that was first purified from bovine lung (PDB ID: 2F38). This enzyme belongs to the family of aldo-keto reductase (AKR) based on its high substrate specificity, its high molecular weight (38055.48 Da) and amino acid sequence. In addition, it is categorized as C3 (AKR1C3) because it is an isoform of 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. The function of PGFS is to catalyze the reduction of aldehydes and ketones to their corresponding alcohols. In humans, these reactions take place mostly in the lungs and in the liver. Mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
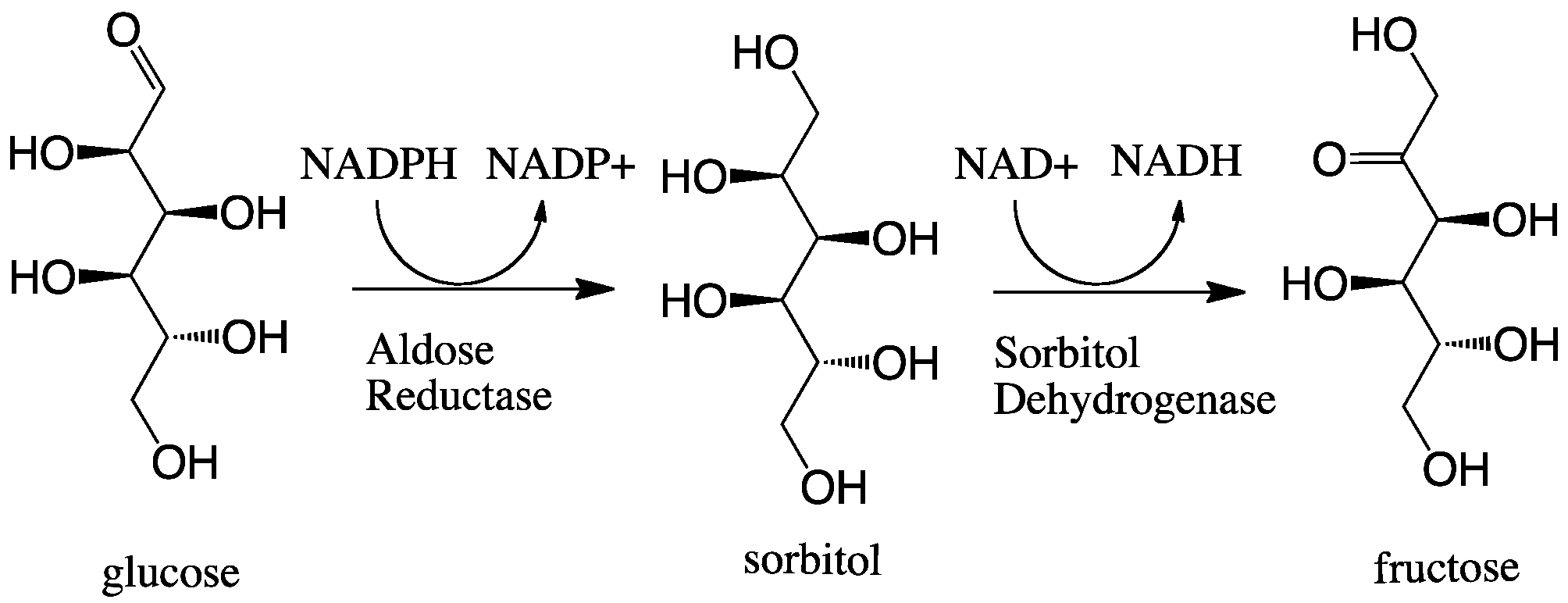
Aldose Reductase
In enzymology, aldose reductase (or aldehyde reductase) () is an enzyme in humans encoded by the gene AKR1B1. It is an cytosolic NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase that catalyzes the reduction of a variety of aldehydes and carbonyls, including monosaccharides, and primarily known for catalyzing the reduction of glucose to sorbitol, the first step in polyol pathway of glucose metabolism. Reactions Aldose reductase catalyzes the NADPH-dependent conversion of glucose to sorbitol, the first step in polyol pathway of glucose metabolism. The second and last step in the pathway is catalyzed by sorbitol dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the NAD-linked oxidation of sorbitol to fructose. Thus, the polyol pathway results in conversion of glucose to fructose with stoichiometric utilization of NADPH and production of NADH. ;glucose + NADPH + H+ \rightleftharpoons sorbitol + NADP+ Galactose is also a substrate for the polyol pathway, but the corresponding keto sugar is not produced because sorbito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |