|
PEG Ratio
The 'PEG ratio' ( price/earnings to growth ratio) is a valuation metric for determining the relative trade-off between the price of a stock, the earnings generated per share (EPS), and the company's expected growth. In general, the P/E ratio is higher for a company with a higher growth rate. Thus, using just the P/E ratio would make high-growth companies appear overvalued relative to others. It is assumed that by dividing the P/E ratio by the earnings growth rate, the resulting ratio is better for comparing companies with different growth rates. The PEG ratio is considered to be a convenient approximation. It was originally developed by Mario Farina who wrote about it in his 1969 Book, ''A Beginner's Guide To Successful Investing In The Stock Market''. It was later popularized by Peter Lynch, who wrote in his 1989 book ''One Up on Wall Street'' that "The P/E ratio of any company that's fairly priced will equal its growth rate", i.e., a fairly valued company will have its PEG equ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penny Stock
Penny stocks are common shares of small public companies that trade for less than five dollars per share. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) uses the term "penny stock" to refer to a security, a financial instrument which represents a given financial value, issued by small public companies that trade at less than $5 per share. The term "penny stock" refers to shares that, prior to the SEC's classification, traded for "pennies on the dollar". In 1934, when the United States government passed the Securities Exchange Act to regulate any and all transactions of securities between parties which are "not the original issuer", the SEC at the time disclosed that equity securities which trade for less than $5 per share could not be listed on any national stock exchange or index. In countries other than the United States, where stock prices are denoted in local currencies, a US$5.00 value does not have any necessary implication. In China, for example, it is common for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
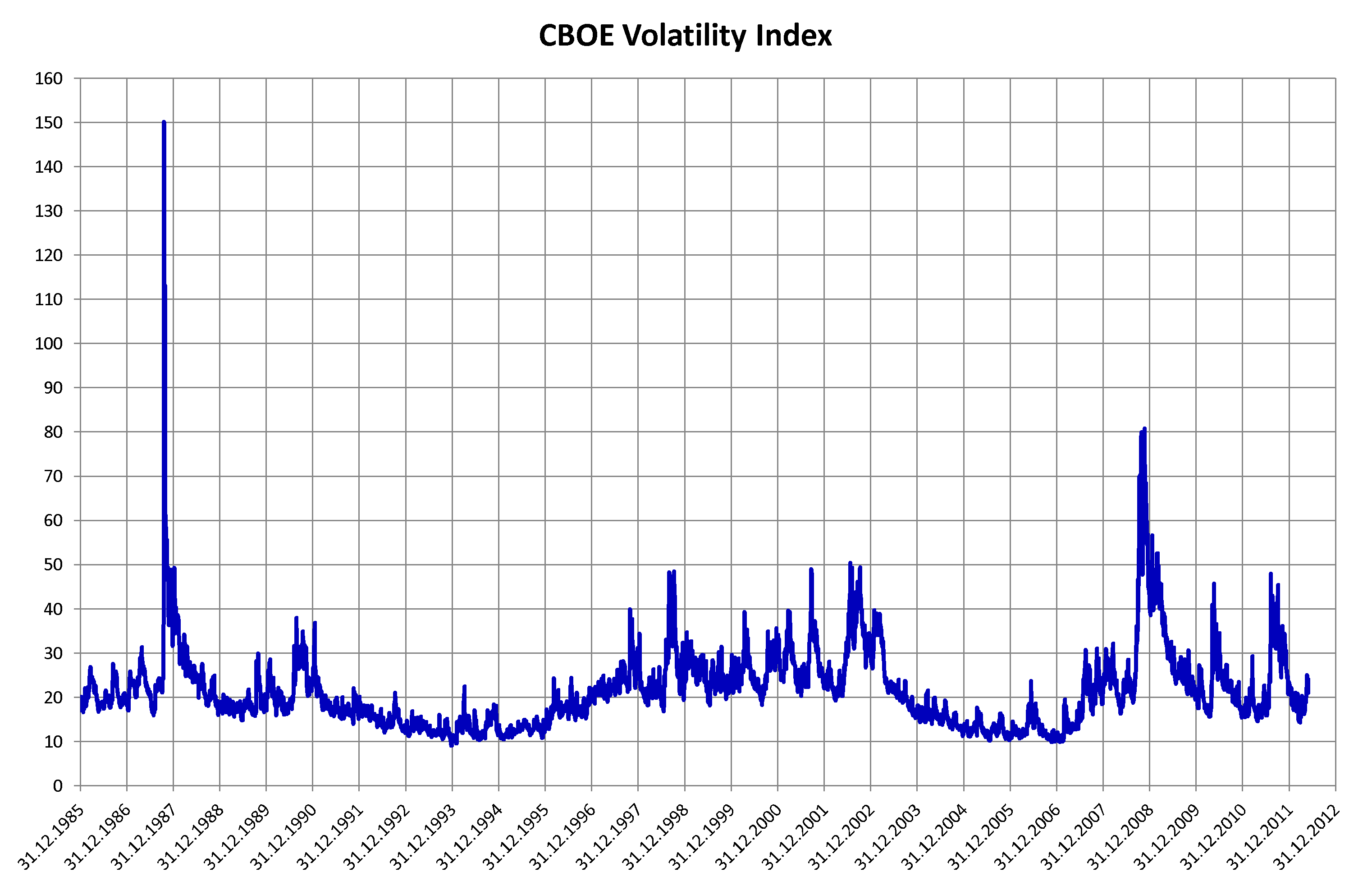
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madoff Investment Scandal
The Madoff investment scandal was a major case of stock and securities fraud discovered in late 2008. In December of that year, Bernie Madoff, the former Nasdaq chairman and founder of the Wall Street firm Bernard L. Madoff Investment Securities LLC, admitted that the wealth management arm of his business was an elaborate multi-billion-dollar Ponzi scheme. Madoff founded Bernard L. Madoff Investment Securities LLC in 1960, and was its chairman until his arrest. The firm employed Madoff's brother Peter Madoff, Peter as senior managing director and chief compliance officer, Peter's daughter Shana Madoff as rules and compliance officer and attorney, and Madoff's sons Mark Madoff, Mark and Andrew Madoff, Andrew. Peter was sentenced to 10 years in prison, and Mark died by suicide two years to the day after his father's arrest. Alerted by Madoff's sons, federal authorities arrested Madoff on December 11, 2008. On March 12, 2009, Madoff pleaded guilty to 11 federal crimes and admitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dividend
A dividend is a distribution of profits by a corporation to its shareholders, after which the stock exchange decreases the price of the stock by the dividend to remove volatility. The market has no control over the stock price on open on the ex-dividend date, though more often than not it may open higher. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, it is able to pay a portion of the profit as a dividend to shareholders. Any amount not distributed is taken to be re-invested in the business (called retained earnings). The current year profit as well as the retained earnings of previous years are available for distribution; a corporation is usually prohibited from paying a dividend out of its capital. Distribution to shareholders may be in cash (usually by bank transfer) or, if the corporation has a dividend reinvestment plan, the amount can be paid by the issue of further shares or by share repurchase. In some cases, the distribution may be of assets. The dividend received by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Analyst
A financial analyst is a professional undertaking financial analysis for external or internal clients as a core feature of the job. "Financial Analyst" '''' The role may specifically be titled securities analyst, research analyst, equity analyst, investment analyst, or ratings analyst. Financial Analysts |
Return On Equity
The return on equity (ROE) is a measure of the profitability of a business in relation to its equity; where: : Jason Fernando (2023)"Return on Equity (ROE) Calculation and What It Means" Investopedia Thus, ROE is equal to a fiscal year's net income (after preferred stock dividends, before common stock dividends), divided by total equity (excluding preferred shares), expressed as a percentage. Because shareholder's equity can be calculated by taking all assets and subtracting all liabilities, ROE can also be thought of as a return on NAV, or ''assets less liabilities''. Usage ROE measures how many dollars of profit are generated for each dollar of shareholder's equity, and is thus a metric of how well the company utilizes its equity to generate profits. ROE is especially used for comparing the performance of companies in the same industry. As with return on capital, an ROE is a measure of management's ability to generate income from the equity available to it. ROEs of 15–2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacks
Zacks is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Gordon Zacks (1933–2014), American businessman and writer * Jeff Zacks, American psychologist See also * Zack (other) * Zaks (other) {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earnings Growth
Earnings growth is the annual compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of earnings from investments. Overview When the dividend payout ratio is the same, the dividend growth rate is equal to the earnings growth rate. Earnings growth rate is a key value that is needed when the Discounted cash flow model, or the Gordon's model is used for stock valuation. The present value is given by: :P = D\cdot\sum_^\left(\frac\right)^ . where P = the present value, k = discount rate, D = current dividend and g_i is the revenue growth rate for period i. If the growth rate is constant for i=n+1 to \infty, then, :P = D\cdot\frac + D\cdot(\frac)^2 +...+ D\cdot(\frac)^n+ D\cdot\sum_^\left(\frac\right)^ The last term corresponds to the terminal case. When the growth rate is always the same for perpetuity, Gordon's model results: :P = D\times\frac. As Gordon's model suggests, the valuation is very sensitive to the value of g used. Part of the earnings is paid out as dividends and part of it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PVGO
In corporate finance, Alex Stomper (N.D.Finance Theory I MIT OpenCourseWare the present value of growth opportunities (PVGO) is a valuation measure applied to growth stocks. It represents the component of the company's stock value that corresponds to (expected) growth in earnings. It thus allows an analyst to assess the extent to which the share price represents the current business, and to what extent it reflects assumptions about the future. PVGO can then also be used in relative valuation, i.e. when comparing between two investments (see similar re PEG ratio). PVGO is calculated as follows: : This formula arises by thinking of the value of a company as inhering two components: (i) the present value of existing earnings, i.e. the company continuing as if under a "no-growth policy"; and (ii) the present value of the company's growth opportunities. PVGO can then simply be calculated as the difference between the stock price and the present value of its zero-growth-earnings; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of CPI inflation is deflation, a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. Changes in inflation are widely attributed to fluctuations in Real versus nominal value (economics), real demand for goods and services (also known as demand shocks, including changes in fiscal policy, fiscal or monetary policy), changes in available supplies such as during energy crisis, energy crises (also known as supply shocks), or changes in inflation expectations, which may be self-fulfilling. Moderat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |