|
PC97
The PC System Design Guide (also known as the PC-97, PC-98, PC-99, or PC 2001 specification) is a series of hardware design requirements and recommendations for IBM PC compatible personal computers, compiled by Microsoft and Intel Corporation during 1997–2001. They were aimed at helping manufacturers provide hardware that made the best use of the capabilities of the Microsoft Windows operating system, and to simplify setup and use of such computers. Every part of a standard computer and the most common kinds of peripheral devices are defined with specific requirements. Systems and devices that meet the specification should be automatically recognized and configured by the operating system. Versions Four versions of the PC System Design Guide were released. In PC-97, a distinction was made between the requirements of a ''Basic PC'', a ''Workstation PC'' and an ''Entertainment PC''. In PC-98, the ''Mobile PC'' was added as a category. In PC 2001, the ''Entertainment PC'' was dropp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC Compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central processing unit, sourced either from Intel or a second source like AMD, Cyrix or other vendors such as Texas Instruments, Fujitsu, OKI, Mitsubishi or NEC and is capable of using interchangeable commodity hardware such as expansion cards. Initially such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones, but the term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, as the vast majority of microcomputers produced since the 1990s are IBM compatible. IBM itself no longer sells personal computers, having sold its division to Lenovo in 2005. " Wintel" is a similar description that is more commonly used for modern computers. The designation "PC", as used in much of personal computer history, has not meant "pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L2 Cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. Most CPUs have a hierarchy of multiple cache levels (L1, L2, often L3, and rarely even L4), with different instruction-specific and data-specific caches at level 1. The cache memory is typically implemented with static random-access memory (SRAM), in modern CPUs by far the largest part of them by chip area, but SRAM is not always used for all levels (of I- or D-cache), or even any level, sometimes some latter or all levels are implemented with eDRAM. Other types of caches exist (that are not counted towards the "cache size" of the most important caches mentioned above), such as the translation lookaside buffer (TLB) which is part of the memory management unit (MMU) whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and computer memory, memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the CPU, the chipset's input/output and Memory controller, memory controllers, interface (computing), interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use. Nomenclature ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the word ''motherboard'' to 1965, its earliest-found attestation occurring in the magazine ''Electronics (magazine), Electronics''. The term alludes to its importance and size compared to the components attached to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Code
A color code is a system for encoding and representing non-color information with colors to facilitate communication. This information tends to be categorical (representing unordered/qualitative categories) though may also be sequential (representing an ordered/quantitative variable). History The earliest examples of color codes in use are for long-distance communication by use of flags, as in semaphore communication. The United Kingdom adopted a color code scheme for such communication wherein red signified danger and white signified safety, with other colors having similar assignments of meaning. As chemistry and other technologies advanced, it became expedient to use coloration as a signal for telling apart things that would otherwise be confusingly similar, such as wiring in electrical and electronic devices, and pharmaceutical pills. Encoded Variable A color code encodes a variable, which may have different representations, where the color code type should match th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A20 Line
The A20, or address line 20, is one of the electrical lines that make up the system bus of an x86-based computer system. The A20 line in particular is used to transmit the 21st bit on the address bus. A microprocessor typically has a number of address lines equal to the base-two logarithm of the number of words in its physical address space. For example, a processor with 4 GB of byte-addressable physical space requires 32 lines (log2(4 GB) = log2(232 B) = 32), which are named A0 through A31. The lines are named after the zero-based number of the bit in the address that they are transmitting. The least significant bit is first and is therefore numbered bit 0 and signaled on line A0. A20 transmits bit 20 (the 21st bit) and becomes active once addresses reach 1 MB, or 220. Overview The Intel 8086, Intel 8088, and Intel 80186 processors had 20 address lines, numbered A0 to A19; with these, the processor can access 220 bytes, or 1 MB. Internal address re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legacy-free PC
A legacy-free PC is a type of personal computer that lacks a floppy or optical disc drive, legacy ports, and an Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bus (or sometimes, any internal expansion bus at all). According to Microsoft, "The basic goal for these requirements is that the operating system, devices, and end users cannot detect the presence of the following: ISA slots or devices; legacy floppy disk controller (FDC); and PS/2, serial, parallel, and game ports." The legacy ports are usually replaced with Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports. A USB adapter may be used if an older device must be connected to a PC lacking these ports. According to the 2001 edition of Microsoft's PC System Design Guide, a legacy-free PC must be able to boot from a USB device. Removing older, usually bulkier ports and devices allows a legacy-free PC to be much more compact than earlier systems and many fall into the nettop or all-in-one form factor. Netbooks and ultrabooks could also be considered a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller
In computing, Intel's Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) is a family of programmable interrupt controllers. As its name suggests, the APIC is more advanced than Intel's 8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC), particularly enabling the construction of multiprocessor systems. It is one of several architectural designs intended to solve interrupt routing efficiency issues in multiprocessor computer systems. The APIC is a split architecture design, with a local component (LAPIC) usually integrated into the processor itself, and an optional I/O APIC on a system bus. The first APIC was the 82489DX it was a discrete chip that functioned both as local and I/O APIC. The 82489DX enabled construction of symmetric multiprocessor (SMP) systems with the Intel 486 and early Pentium processors; for example, the reference two-way 486 SMP system used three 82489DX chips, two as local APICs and one as I/O APIC. Starting with the P54C processor, the local APIC functionality was in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industry Standard Architecture
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus (computing), bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles. Originally referred to as the PC bus (8-bit) or AT bus (16-bit), it was also termed ''I/O Channel'' by IBM. The ISA term was coined as a retronym by IBM PC clone manufacturers in the late 1980s or early 1990s as a reaction to IBM attempts to replace the AT bus with its new and incompatible Micro Channel architecture. The 16-bit ISA bus was also used with 32-bit processors for several years. An attempt to extend it to 32 bits, called Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA), was not very successful, however. Later buses such as VESA Local Bus and Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI were used instead, often along with ISA slots on the same mainbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-and-play
In computing, a plug and play (PnP) device or computer bus is one with a specification that facilitates the recognition of a hardware component in a system without the need for physical device configuration or user intervention in resolving resource conflicts. The term "plug and play" has since been expanded to a wide variety of applications to which the same lack of user setup applies. Expansion devices are controlled and exchange data with the host system through defined memory or I/O space port addresses, direct memory access channels, interrupt request lines and other mechanisms, which must be uniquely associated with a particular device to operate. Some computers provided unique combinations of these resources to each slot of a motherboard or backplane. Other designs provided all resources to all slots, and each peripheral device had its own address decoding for the registers or memory blocks it needed to communicate with the host system. Since fixed assignments made expansi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preboot Execution Environment
In computing, the Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE; often pronounced as ''pixie''), often called PXE boot (''pixie boot''), is a specification describing a standardized client–server environment that boots a software assembly, retrieved from a network, on PXE-enabled clients. On the client side it requires only a PXE-capable network interface controller (NIC), and uses a small set of industry-standard network protocols such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP). The concept behind the PXE originated in the early days of protocols like BOOTP/DHCP/TFTP, and it forms part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard. In modern data centers, PXE is the most frequent choice for operating system booting, installation and deployment. Overview Since the beginning of computer networks, there has been a persistent need for client systems which can boot appropriate software images, with appropriate configu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
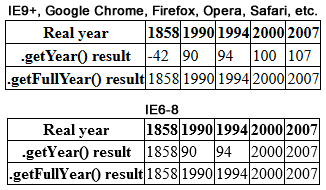
Year 2000 Problem
The term year 2000 problem, or simply Y2K, refers to potential computer errors related to the Time formatting and storage bugs, formatting and storage of calendar data for dates in and after the year 2000. Many Computer program, programs represented four-digit years with only the final two digits, making the year 2000 indistinguishable from 1900. Computer systems' inability to distinguish dates correctly had the potential to bring down worldwide infrastructures for computer-reliant industries. In the years leading up to the turn of the millennium, the public gradually became aware of the "Y2K scare", and individual companies predicted the global damage caused by the bug would require anything between $400 million and $600 billion to rectify. A lack of clarity regarding the potential dangers of the bug led some to stock up on food, water, and firearms, purchase backup generators, and withdraw large sums of money in anticipation of a computer-induced Global catastrophic risk, ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |