|
PAM16
Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit TIM16 also known as presequence translocated-associated motor subunit PAM16, mitochondria-associated granulocyte macrophage CSF-signaling molecule, or presequence translocated-associated motor subunit PAM16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PAM16 gene. Structure The ''PAM16'' gene is located on the p arm of chromosome 16 at position 13.3 and it spans 11,150 base pairs. The ''PAM16'' gene produces a 15.1 kDa protein composed of 137 amino acids. The structure has been found to contain a 21-residue mitochondrial targeting leader sequence. Function The ''PAM16'' gene encodes for a mitochondrial protein with multiple functions. It is responsible for the regulation of ATP-dependent protein translocation into the mitochondrial matrix, inhibition of DNAJC19 stimulation of HSPA9/ Mortalin ATPase activity, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) signaling. Furthermore, PAM16 plays a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNAJC19
Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit TIM14 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DNAJC19'' gene on chromosome 3. TIM14 belongs to the DnaJ family, which has been involved in Hsp40/Hsp70 chaperone systems. As a mitochondrial chaperone, TIM14 functions as part of the TIM23 complex import motor to facilitate the import of nuclear-encoded proteins into the mitochondria. TIM14 also complexes with prohibitin complexes to regulate mitochondrial morphogenesis, and has been implicated in dilated cardiomyopathy with ataxia. Structure The ''DNAJC19'' gene is located on the q arm of chromosome 3 at position 26.33 and it spans 6,065 base pairs. The ''DNAJC19'' gene produces a 6.29 kDa protein composed of 59 amino acids. The protein encoded by the ''DNAJC19'' gene possesses an unusual structure compared to the rest of the DNAJ protein family. Notably, the DNAJ domain of TIM14 is located at the C-terminal rather than the N-terminal, and the transmembrane d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FEZ1
Fasciculation and elongation protein zeta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FEZ1'' gene. This gene is an ortholog of the C. elegans unc-76 gene, which is necessary for normal axonal bundling and elongation within axon bundles. Expression of this gene in C. elegans unc-76 mutants can restore to the mutants partial locomotion and axonal fasciculation, suggesting that it also functions in axonal outgrowth. The N-terminal half of the gene product is highly acidic. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms of this protein have been described. This protein is present in neurons, and it is believed to block the process of infection of these cells by HIV. Interactions FEZ1 has been shown to interact with Protein kinase Mζ, NBR1 Neighbor of BRCA1 gene 1 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NBR1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene was originally identified as an ovarian tumor antigen monitored in ovarian cancer. The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TIMM17A
Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim17-A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''TIMM17A'' gene. See also * Mitochondria Inner Membrane Translocase * TIMM22 * TIMM23 * TIMM44 Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit TIM44 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''TIMM44'' gene. Interactions TIMM44 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with ARAF. See also * Translocase of the in ... References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub Mitochondrial proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal skeleton supported by fluid pressure. Vertebrates are animals with a vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bone and cartilage. Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column. The skeletons of invertebrates vary, including hard exoskeleton shells, plated endoskeletons, or spicules. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. Etymology The term ''skeleton'' comes . ''Sceleton'' is an archaic form of the word. Classification Skeletons can be defined by several attributes. Solid skeletons consist of hard substances, such as bone, cartilage, or cuticle. These can be further divided by locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abnormalities
The Spill Canvas is an American alternative rock band from Sioux Falls, South Dakota. Known for their hits "All Over You" "Our Song" and "Staplegunned", as well as several emo classics like "All Hail the Heartbreaker" "The Tide" and "Polygraph, Right Now!" Career Lead singer and guitarist Nick Thomas (born May 26, 1984) grew up in Sioux Falls, South Dakota and began learning how to play guitar at 11 years old. Thomas attended Roosevelt High School and sang with the school concert choir and men's choir. He began performing at local venues on his acoustic guitar at 15-years-old and self-released his first punk rock and acoustic CD titled ''The Blur of Motions'' in 2000 with Prairie Dog Studios. Thomas envisioned the Spill Canvas in the summer of 2001 as a collage of unique musical sounds and ideas coming together to form a unique palette. Vocalist Becca Flinn approached Thomas following a solo show and the two formed the beginnings of the band, adding bassist Alan Burkhard and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limb (anatomy)
A limb (from the Old English ''lim'', meaning "body part") or leg is a jointed, muscled appendage that tetrapod vertebrates use for weight-bearing and terrestrial locomotion such as walking, running and jumping, for paddle-swimming, or for grasping and climbing. The distalmost portion of a limb is known as its extremity. The limbs' bony endoskeleton, known as the appendicular skeleton, is homologous among all tetrapods. All tetrapods have four limbs that are organized into two bilaterally symmetrical pairs, with one pair at each end of the torso. The cranial pair are known as the forelimbs or ''front legs'', and the caudal pair the hindlimbs or ''back legs''. In animals with more upright posture (mainly hominid primates, particularly humans), the forelimbs and hindlimbs are often called upper and lower limbs, respectively. The fore-/upper limbs are connected to the thoracic cage via the shoulder girdles, and the hind-/lower limbs are connected to the pelvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
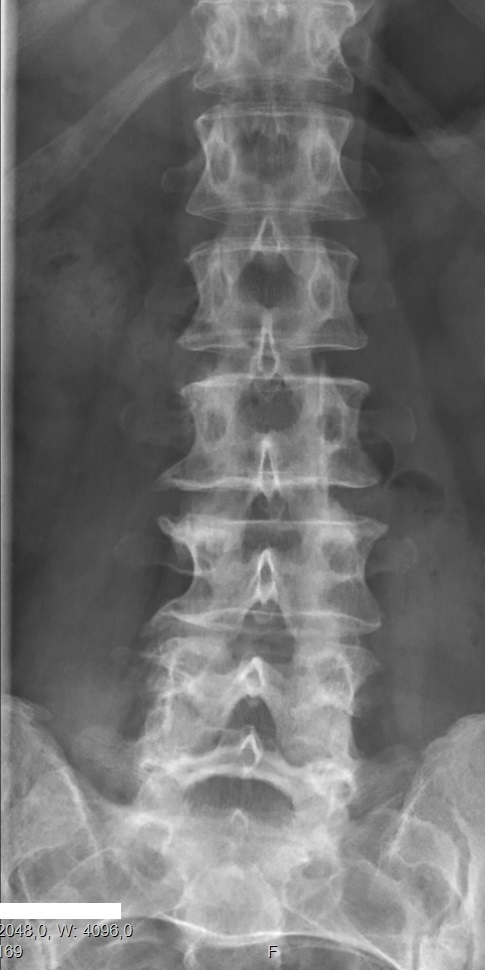
Platyspondyly
Congenital vertebral anomalies are a collection of malformations of the spine. Most, around 85%, are not clinically significant, but they can cause compression of the spinal cord by deforming the vertebral canal or causing instability. This condition occurs in the womb. Congenital vertebral anomalies include alterations of the shape and number of vertebrae. Lumbarization and sacralization ''Lumbarization'' is an anomaly in the spine. It is defined by the nonfusion of the first and second segments of the sacrum. The lumbar spine subsequently appears to have six vertebrae or segments, not five. This sixth lumbar vertebra is known as a transitional vertebra. Conversely the sacrum appears to have only four segments instead of its designated five segments. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae consist of the process of the last lumbar vertebra fusing with the first sacral segment. While only around 10 percent of adults have a spinal abnormality due to genetics, a sixth lumbar verteb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between L5 and S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at front and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' " breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |