|
P-norm
In mathematics, the spaces are function spaces defined using a natural generalization of the -norm for finite-dimensional vector spaces. They are sometimes called Lebesgue spaces, named after Henri Lebesgue , although according to the Bourbaki group they were first introduced by Frigyes Riesz . spaces form an important class of Banach spaces in functional analysis, and of topological vector spaces. Because of their key role in the mathematical analysis of measure and probability spaces, Lebesgue spaces are used also in the theoretical discussion of problems in physics, statistics, economics, finance, engineering, and other disciplines. Preliminaries The -norm in finite dimensions The Euclidean length of a vector x = (x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n) in the n-dimensional real vector space \Reals^n is given by the Euclidean norm: \, x\, _2 = \left(^2 + ^2 + \dotsb + ^2\right)^. The Euclidean distance between two points x and y is the length \, x - y\, _2 of the straight line between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norm (mathematics)
In mathematics, a norm is a function (mathematics), function from a real or complex vector space to the non-negative real numbers that behaves in certain ways like the distance from the Origin (mathematics), origin: it Equivariant map, commutes with scaling, obeys a form of the triangle inequality, and zero is only at the origin. In particular, the Euclidean distance in a Euclidean space is defined by a norm on the associated Euclidean vector space, called the #Euclidean norm, Euclidean norm, the #p-norm, 2-norm, or, sometimes, the magnitude or length of the vector. This norm can be defined as the square root of the inner product of a vector with itself. A seminorm satisfies the first two properties of a norm but may be zero for vectors other than the origin. A vector space with a specified norm is called a normed vector space. In a similar manner, a vector space with a seminorm is called a ''seminormed vector space''. The term pseudonorm has been used for several related meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric Space
In mathematics, a metric space is a Set (mathematics), set together with a notion of ''distance'' between its Element (mathematics), elements, usually called point (geometry), points. The distance is measured by a function (mathematics), function called a metric or distance function. Metric spaces are a general setting for studying many of the concepts of mathematical analysis and geometry. The most familiar example of a metric space is 3-dimensional Euclidean space with its usual notion of distance. Other well-known examples are a sphere equipped with the angular distance and the hyperbolic plane. A metric may correspond to a Conceptual metaphor , metaphorical, rather than physical, notion of distance: for example, the set of 100-character Unicode strings can be equipped with the Hamming distance, which measures the number of characters that need to be changed to get from one string to another. Since they are very general, metric spaces are a tool used in many different bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set (mathematics), set whose elements, often called vector (mathematics and physics), ''vectors'', can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called scalar (mathematics), ''scalars''. The operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called ''vector axioms''. Real vector spaces and complex vector spaces are kinds of vector spaces based on different kinds of scalars: real numbers and complex numbers. Scalars can also be, more generally, elements of any field (mathematics), field. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of Physical quantity, physical quantities (such as forces and velocity) that have not only a Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude, but also a Orientation (geometry), direction. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for linear algebra, together with the concept of matrix (mathematics), matrices, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Inequality
In mathematics, the triangle inequality states that for any triangle, the sum of the lengths of any two sides must be greater than or equal to the length of the remaining side. This statement permits the inclusion of Degeneracy (mathematics)#Triangle, degenerate triangles, but some authors, especially those writing about elementary geometry, will exclude this possibility, thus leaving out the possibility of equality. If , , and are the lengths of the sides of a triangle then the triangle inequality states that :c \leq a + b , with equality only in the degenerate case of a triangle with zero area. In Euclidean geometry and some other geometries, the triangle inequality is a theorem about vectors and vector lengths (Norm (mathematics), norms): :\, \mathbf u + \mathbf v\, \leq \, \mathbf u\, + \, \mathbf v\, , where the length of the third side has been replaced by the length of the vector sum . When and are real numbers, they can be viewed as vectors in \R^1, and the triang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-space
In functional analysis, an F-space is a vector space X over the real or complex numbers together with a metric d : X \times X \to \R such that # Scalar multiplication in X is continuous with respect to d and the standard metric on \R or \Complex. # Addition in X is continuous with respect to d. # The metric is translation-invariant; that is, d(x + a, y + a) = d(x, y) for all x, y, a \in X. # The metric space (X, d) is complete. The operation x \mapsto \, x\, := d(0, x) is called an F-norm, although in general an F-norm is not required to be homogeneous. By translation-invariance, the metric is recoverable from the F-norm. Thus, a real or complex F-space is equivalently a real or complex vector space equipped with a complete F-norm. Some authors use the term rather than , but usually the term "Fréchet space" is reserved for locally convex F-spaces. Some other authors use the term "F-space" as a synonym of "Fréchet space", by which they mean a locally convex complete metri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manhattan Distance
Taxicab geometry or Manhattan geometry is geometry where the familiar Euclidean distance is ignored, and the distance between two point (geometry), points is instead defined to be the sum of the absolute differences of their respective Cartesian coordinates, a distance function (or Metric (mathematics), metric) called the ''taxicab distance'', ''Manhattan distance'', or ''city block distance''. The name refers to the island of Manhattan, or generically any planned city with a rectangular grid of streets, in which a taxicab can only travel along grid directions. In taxicab geometry, the distance between any two points equals the length of their shortest grid path. This different definition of distance also leads to a different definition of the length of a curve, for which a line segment between any two points has the same length as a grid path between those points rather than its Euclidean length. The taxicab distance is also sometimes known as ''rectilinear distance'' or distanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normed Vector Space
The Ateliers et Chantiers de France (ACF, Workshops and Shipyards of France) was a major shipyard that was established in Dunkirk, France, in 1898. The shipyard boomed in the period before World War I (1914–18), but struggled in the inter-war period. It was badly damaged during World War II (1939–45). In the first thirty years after the war the shipyard again experienced a boom and employed up to 3,000 workers making oil tankers, and then liquid natural gas tankers. Demand dropped off in the 1970s and 1980s. In 1972 the shipyard became Chantiers de France-Dunkerque, and in 1983 merged with others yards to become part of Chantiers du Nord et de la Mediterranee, or Normed. The shipyard closed in 1987. Foundation (1898–99) The Ateliers et Chantiers de France (ACF) company was officially founded on 6 July 1898 by a consortium of six shipping brokers, the Dunkirk chamber of commerce and the state. The state asked that the shipyard be able to build steamships and also four-maste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Metric Space
In mathematical analysis, a metric space is called complete (or a Cauchy space) if every Cauchy sequence of points in has a limit that is also in . Intuitively, a space is complete if there are no "points missing" from it (inside or at the boundary). For instance, the set of rational numbers is not complete, because e.g. \sqrt is "missing" from it, even though one can construct a Cauchy sequence of rational numbers that converges to it (see further examples below). It is always possible to "fill all the holes", leading to the ''completion'' of a given space, as explained below. Definition Cauchy sequence A sequence x_1, x_2, x_3, \ldots of elements from X of a metric space (X, d) is called Cauchy if for every positive real number r > 0 there is a positive integer N such that for all positive integers m, n > N, d(x_m, x_n) < r. Complete space A metric space is complete if any of the following equivalent conditions are satisfied: #Every Cauchy seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous Function
In mathematics, a homogeneous function is a function of several variables such that the following holds: If each of the function's arguments is multiplied by the same scalar (mathematics), scalar, then the function's value is multiplied by some power of this scalar; the power is called the degree of homogeneity, or simply the ''degree''. That is, if is an integer, a function of variables is homogeneous of degree if :f(sx_1,\ldots, sx_n)=s^k f(x_1,\ldots, x_n) for every x_1, \ldots, x_n, and s\ne 0. This is also referred to a ''th-degree'' or ''th-order'' homogeneous function. For example, a homogeneous polynomial of degree defines a homogeneous function of degree . The above definition extends to functions whose domain of a function, domain and codomain are vector spaces over a Field (mathematics), field : a function f : V \to W between two -vector spaces is ''homogeneous'' of degree k if for all nonzero s \in F and v \in V. This definition is often further generalized to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
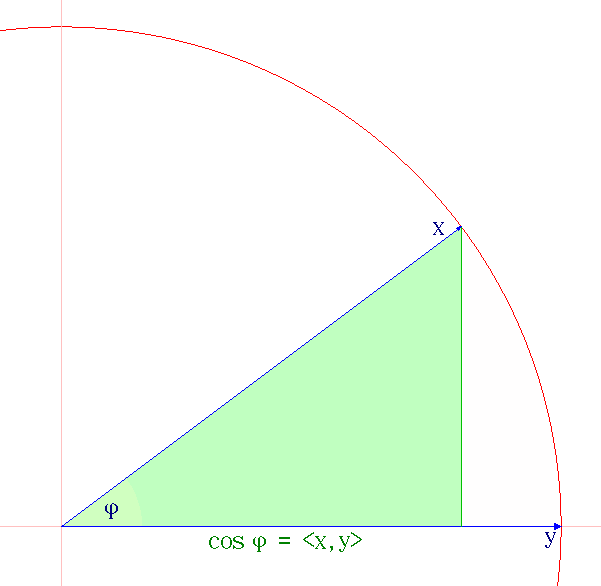
Cauchy–Schwarz Inequality
The Cauchy–Schwarz inequality (also called Cauchy–Bunyakovsky–Schwarz inequality) is an upper bound on the absolute value of the inner product between two vectors in an inner product space in terms of the product of the vector norms. It is considered one of the most important and widely used inequalities in mathematics. Inner products of vectors can describe finite sums (via finite-dimensional vector spaces), infinite series (via vectors in sequence spaces), and integrals (via vectors in Hilbert spaces). The inequality for sums was published by . The corresponding inequality for integrals was published by and . Schwarz gave the modern proof of the integral version. Statement of the inequality The Cauchy–Schwarz inequality states that for all vectors \mathbf and \mathbf of an inner product space where \langle \cdot, \cdot \rangle is the inner product. Examples of inner products include the real and complex dot product; see the examples in inner product. Every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |