|
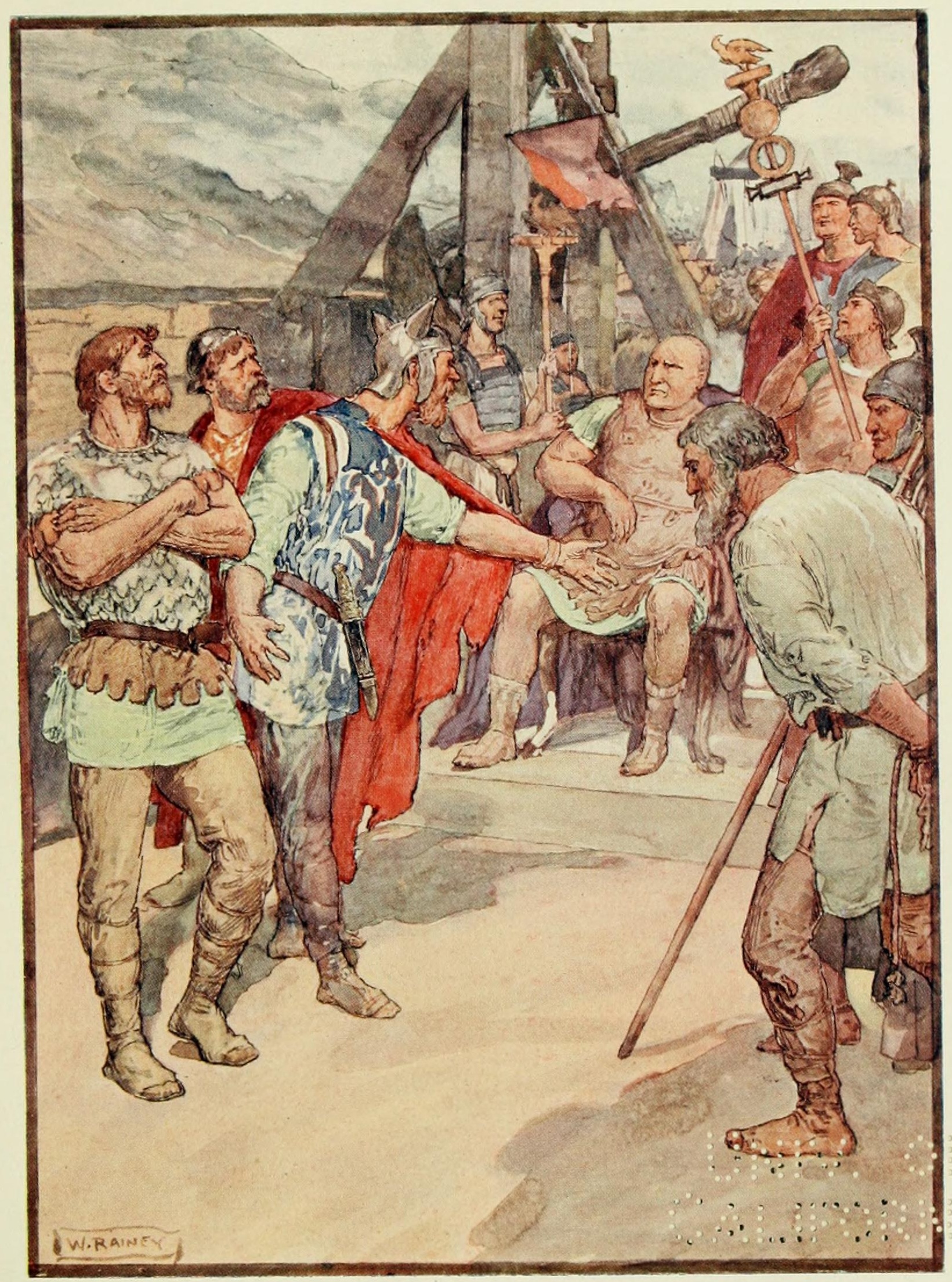
Oxyntas
Oxyntas was a son of the Numidian King Jugurtha. He walked with his brother Iampsas in the Roman Gaius Marius' triumphal parade of 104 BC. His father died soon afterward, but Oxyntas was sent to the town of Venusia, in the Southern Italian region of Basilicata, where he remained until 89 BC. In the Marsic War, Gaius Papius Mutilus used Oxyntas to inspire defections among the Numidian troops serving under the Roman general Sextus Julius Caesar (Appian Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Hadr ..., Civil Wars, 1.42). It is not known what happened to Oxyntas after the Marsic War (91–88 BC). See also * List of Kings of Numidia {{DEFAULTSORT:Oxyntas 1st-century BC Berber people 2nd-century BC Berber people Kingdom of Numidia Ancient African people Roman-era inhabitants o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen ( Libyco-Berber ''Yugurten'' or '' Yugarten'', c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Jugurtha and his two adoptive brothers, Hiempsal and Adherbal, succeeded him. Jugurtha arranged to have Hiempsal killed and, after a civil war, defeated and killed Adherbal in 112 BC. The death of Adherbal, which was against the wishes of Rome, along with the growing popular anger in Rome at Jugurtha's success in bribing Roman senators and thus avoiding retribution for his crimes, led to the Jugurthine War between Rome and Numidia. After a number of battles in Numidia between Roman and Numidian forces, Jugurtha was captured in 105 BC and paraded through Rome as part of Gaius Marius' Roman triumph. He was thrown into the Tullianum prison, where he was executed by strangulation in 104 BC. Jugurtha was survived by his son Oxyntas. Etymology The Numidian name Jugurtha matches the ancient na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia, Libya, and some parts of Morocco. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii in the east and the Masaesyli in the west. During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state. Numidia, at its largest extent, was bordered by Mauretania to the west, at the Moulouya River, Africa Proconsularis to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara to the south. It was one of the first major states in the history of Algeria and the Berbers. History Independence The Greek historians referred to these peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important reforms of Roman armies. He set the precedent for the shift from the militia levies of the middle Republic to the professional soldiery of the late Republic; he also improved the ''pilum'', a javelin, and made large-scale changes to the logistical structure of the Roman army. Rising from a well-off provincial Italian family in Arpinum, Marius acquired his initial military experience serving with Scipio Aemilianus at the Siege of Numantia in 134 BC. He won election as tribune of the plebs in 119 BC and passed a law limiting aristocratic interference in elections. Barely elected praetor in 115 BC, he next became the governor of Further Spain where he campaigned against bandits. On his return from Spain he married Julia, the aunt o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Triumph
The Roman triumph (') was a civil ceremony and religious rite of ancient Rome, held to publicly celebrate and sanctify the success of a military commander who had led Roman forces to victory in the service of the state or in some historical traditions, one who had successfully completed a foreign war. On the day of his triumph, the general wore a crown of laurel and an all-purple, gold-embroidered triumphal '' toga picta'' ("painted" toga), regalia that identified him as near-divine or near-kingly. In some accounts, his face was painted red, perhaps in imitation of Rome's highest and most powerful god, Jupiter. The general rode in a four-horse chariot through the streets of Rome in unarmed procession with his army, captives, and the spoils of his war. At Jupiter's temple on the Capitoline Hill, he offered sacrifice and the tokens of his victory to the god Jupiter. In Republican tradition, only the Senate could grant a triumph. The origins and development of this honour wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venusia
Venosa ( Lucano: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Potenza, in the southern Italian region of Basilicata, in the Vulture area. It is bounded by the comuni of Barile, Ginestra, Lavello, Maschito, Montemilone, Palazzo San Gervasio, Rapolla and Spinazzola. History Ancient The city was known as Venusia ("City of Venus") to the Romans, who credited its establishment—as Aphrodisia ("City of Aphrodite")—to the Homeric hero Diomedes. He was said to have moved to Magna Graecia in southern Italy following the Trojan War, seeking a life of peace and building the town and its temples to appease the anger of Aphrodite for the destruction of her beloved Troy. The town was taken by the Romans after the Third Samnite War in 291 BC and became a colony for its strategical position between Apulia and Lucania. No fewer than 20,000 men were sent there, owing to its military importance. Throughout the Hannibalic wars, it remained faithful to Rome, and had a further con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilicata
it, Lucano (man) it, Lucana (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-77 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €12.6 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €22,200 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2018) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.853 · 17th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITF , we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsic War
Kappa Herculis (κ Herculis, abbreviated Kappa Her, κ Her) is an optical double star in the constellation of Hercules. The two components, Kappa Herculis A (Marsic , the traditional name of the system) and B, were 27.3 arc seconds apart in 2000. Based on parallax measurements from the Hipparcos mission, κ Her A is about 113 parsecs (370 light-years) from the Sun and κ Her B is 600 parsecs (2,000 light-years); more recent parallax measurements suggest that B is around 5% more distant than A. A faint third component Kappa Herculis C is just over 1 arc-minute away. It is at the same distance as κ Her A and has an almost-identical space motion. The star 8 Herculis forms a naked eye pair with Kappa Herculis away. Nomenclature κ Herculis ( Latinised to ''Kappa Herculis'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the components as ''Kappa Herculis A'', ''B'' and ''C'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Papius Mutilus
Gaius Papius Mutilus was a Samnite noble who is best known for being the leader of the southern rebels who fought against the army of Rome in the Social War of 91-88 BC (also known as the Italic War); was member of the clan Variani/Varriano.Hornblower, Simon; Antony Spawforth 996 The Oxford classical dictionary, 3rd, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 922. His father was Gaius Papius Mutilus, who held the highest Samnite magistracy in Bovianum a number of times in the second half of the 2nd century BC The Southern Forces Under Gaius Papius The Samnite army, consisting of southern rebels, was very similar to that of the Romans. Two men were elected consuls while another twelve were granted the position of praetor. The consuls were the leaders of their respective armies and are referred to as “commanders in chief". Papius became the consul for the southern rebel forces, known as the Samnites, in 90 BC. His fellow consul was Quintus Poppaedius Silo; the leader of a centrally loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextus Julius Caesar (consul 91 BC)
Sextus Julius Caesar was a Roman statesman, who held the consulship in 91 BC. He died during the Social War. He was the uncle of Gaius Julius Caesar, the dictator.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. I, p. 539. Family Sextus was the son of Gaius Julius Caesar and Marcia. Little is known of his father, except that he might have been the praetor Caesar who died suddenly at Rome. Wilhelm Drumann suspected that his grandfather was the senator Gaius Julius who wrote a history of Rome in Greek around 143 BC. Sextus had a brother, Gaius, who was praetor in an uncertain year (Broughton suggests BC 92). Gaius was probably the elder brother, as he was named after his father. Following the ''cursus honorum'', Sextus would have been at least forty years old when he obtained the consulship, placing his birth no later than 133 BC. Of Sextus' descendants, we know that he had an eponymous son, who was ''Flamen Quirinalis'' in BC 57; the Sextus Julius Caesar who se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Ancient Greeks, Greek historian with Ancient Rome, Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Roman Emperor, Emperors of Rome Trajan, Hadrian, and Antoninus Pius. He was born c. 95 in Alexandria. After holding the senior offices in the Roman province, province of Aegyptus Province, Aegyptus (Egypt), he went to Rome c. 120, where he practised as an advocate, pleading cases before the emperors (probably as ''advocatus fisci'', an important official of the imperial treasury). It was in 147 at the earliest that he was appointed to the office of procurator (Roman), procurator, probably in Egypt, on the recommendation of his friend Marcus Cornelius Fronto, an influential rhetorician and advocate. Because the position of procurator was open only to members of the equestrian (Roman), equestrian order (the "knightly" class), his possession ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |