|
Ovarian Squamous Cell Carcinoma
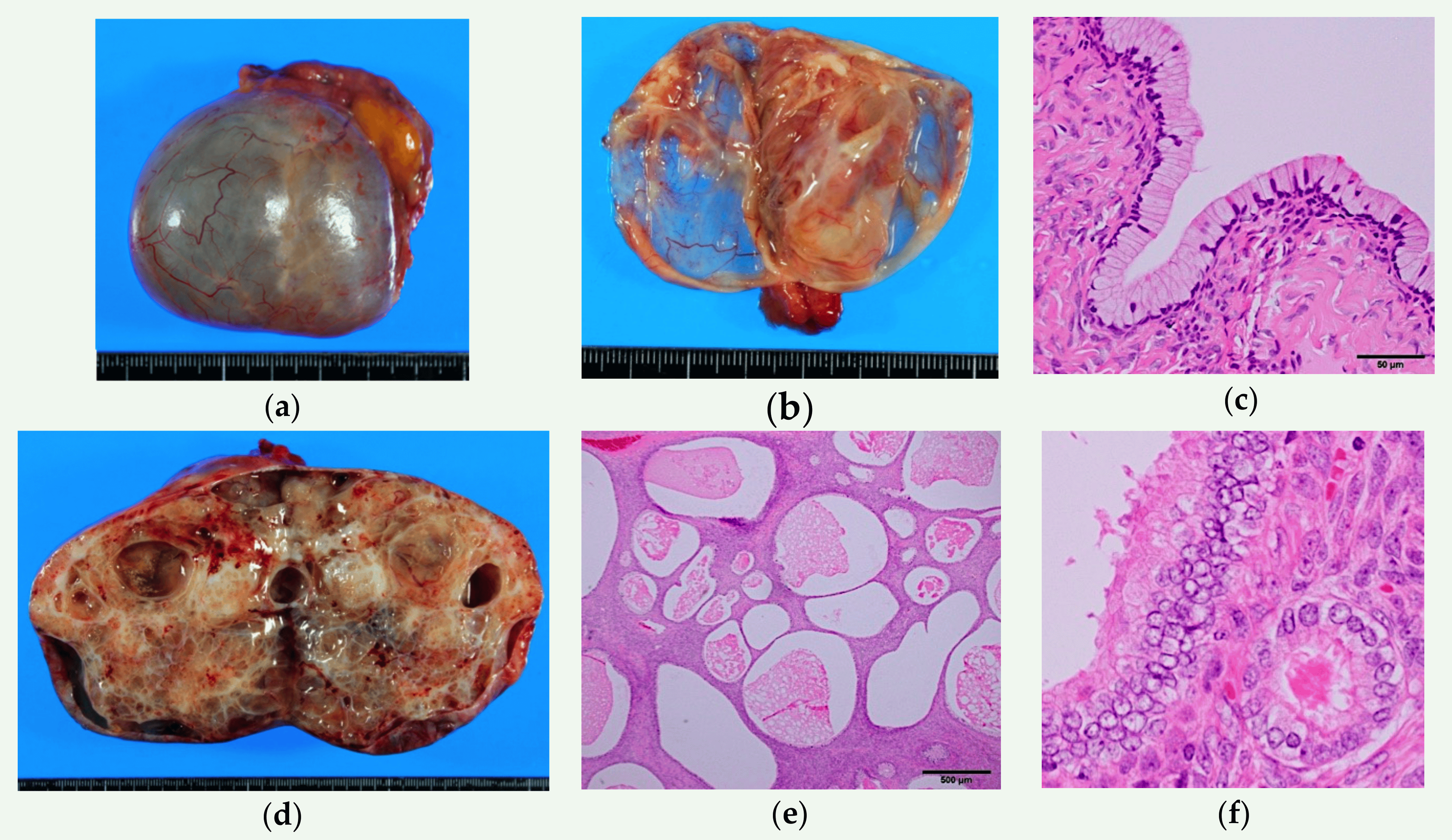
Ovarian squamous cell carcinoma (oSCC) or squamous ovarian carcinoma (SOC) is a rare tumor that accounts for 1% of ovarian cancers. Included in the World Health Organization's classification of ovarian cancer, it mainly affects women above 45 years of age. Survival depends on how advanced the disease is and how different or similar the individual cancer cells are. Squamous ovarian carcinoma is a recognized but uncommon diagnosis, often originating from a transformation of Teratoma, mature cystic teratoma (MCT). Unlike other Squamous-cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinomas, factors like UV exposure and tobacco use play a less significant role. Chronic inflammation in MCT and Human papillomavirus infection, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection are linked to its development. The tumor emerges through metaplasia of the ovarian surface epithelium. While MCT is the primary source in most cases, others are associated with endometriosis or Brenner tumour, Brenner tumor, and rare metastasis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Ovarian Cell Carcinoma
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of Cell (biology), cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial (Mesothelium, mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organ (anatomy), organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal Tissue (biology), tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |