|
Outline Of Computing
The following Outline (list), outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to computing: Computing – activity of using and improving computer hardware and software, computer software. Branches of computing * Computer science (see also Outline of computer science) * Information technology – refers to the application (esp in businesses and other organisations) of computer science, that is, its use by mankind (see also Outline of information technology) * Information systems – refers to the study of the application of IT to business processes * Computer engineering (see also Outline of computer engineering) * Software engineering (see also Outline of software engineering) Computer science Computer science – (Outline of computer science, outline) * Computer science * Theory of computation * Scientific computing * Metacomputing * Autonomic computing Computers See information processor for a high-level block diagram. * Computer * Computer h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Scientific Computing
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science, and more specifically the Computer Sciences, which uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex physical problems. While this typically extends into computational specializations, this field of study includes: * Algorithms ( numerical and non-numerical): mathematical models, computational models, and computer simulations developed to solve sciences (e.g, physical, biological, and social), engineering, and humanities problems * Computer hardware that develops and optimizes the advanced system hardware, firmware, networking, and data management components needed to solve computationally demanding problems * The computing infrastructure that supports both the science and engineering problem solving and the developmental computer and information science In practical use, it is typically the application of computer simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Superscalar
A superscalar processor (or multiple-issue processor) is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single instruction per clock cycle, a superscalar processor can execute or start executing more than one instruction during a clock cycle by simultaneously dispatching multiple instructions to different execution units on the processor. It therefore allows more throughput (the number of instructions that can be executed in a unit of time which can even be less than 1) than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate. Each execution unit is not a separate processor (or a core if the processor is a multi-core processor), but an execution resource within a single CPU such as an arithmetic logic unit. While a superscalar CPU is typically also pipelined, superscalar and pipelining execution are considered different performance enhancement techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Complex Instruction Set Computer
A complex instruction set computer (CISC ) is a computer architecture in which single instructions can execute several low-level operations (such as a load from memory, an arithmetic operation, and a memory store) or are capable of multi-step operations or addressing modes within single instructions. The term was retroactively coined in contrast to reduced instruction set computer (RISC) and has therefore become something of an umbrella term for everything that is not RISC, where the typical differentiating characteristic is that most RISC designs use uniform instruction length for almost all instructions, and employ strictly separate load and store instructions. Examples of CISC architectures include complex mainframe computers to simplistic microcontrollers where memory load and store operations are not separated from arithmetic instructions. Specific instruction set architectures that have been retroactively labeled CISC are System/360 through z/Architecture, the PDP-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
RISC
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set computer (CISC), a RISC computer might require more instructions (more code) in order to accomplish a task because the individual instructions perform simpler operations. The goal is to offset the need to process more instructions by increasing the speed of each instruction, in particular by implementing an instruction pipeline, which may be simpler to achieve given simpler instructions. The key operational concept of the RISC computer is that each instruction performs only one function (e.g. copy a value from memory to a register). The RISC computer usually has many (16 or 32) high-speed, general-purpose registers with a load–store architecture in which the code for the register-register instructions (for performing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Instruction Set Architecture
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA) is an abstract model that generally defines how software controls the CPU in a computer or a family of computers. A device or program that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ''implementation'' of that ISA. In general, an ISA defines the supported instructions, data types, registers, the hardware support for managing main memory, fundamental features (such as the memory consistency, addressing modes, virtual memory), and the input/output model of implementations of the ISA. An ISA specifies the behavior of machine code running on implementations of that ISA in a fashion that does not depend on the characteristics of that implementation, providing binary compatibility between implementations. This enables multiple implementations of an ISA that differ in characteristics such as performance, physical size, and monetary cost (among other things), but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Random-access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of Computer memory, electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read (computer), read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks and Magnetic tape data storage, magnetic tape), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. In today's technology, random-access memory takes the form of integrated circuit (IC) chips with MOSFET, MOS (metal–oxide–semiconductor) Memory cell (computing), memory cells. RAM is normally associated with Volatile memory, volatile types of memory where s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Computer Performance By Orders Of Magnitude
This list compares various amounts of computing power in instructions per second organized by order of magnitude in FLOPS. Scientific E notation index: 2 , 3 , 6 , 9 , 12 , 15 , 18 , 21 , 24 , >24 __TOC__ Milliscale computing (10−3) * 2×10−3: average human multiplication of two 10-digit numbers using pen and paper without aids Deciscale computing (10−1) * 1×10−1: multiplication of two 10-digit numbers by a 1940s electromechanical desk calculator * 3×10−1: multiplication on Zuse Z3 and Z4, first programmable digital computers, 1941 and 1945 respectively * 5×10−1: computing power of the average human mental calculation for multiplication using pen and paper Scale computing (100) * 1.2 OP/S: addition on Z3, 1941, and multiplication on Bell Model V, 1946 * 2.4 OP/S: addition on Z4, 1945 Decascale computing (101) * 1.8×101: ENIAC, first programmable electronic digital computer, 1945 * 5×101: upper end of serialized human percepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Computer Network
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or by wireless communication. The devices may be connected in a variety of network topologies. In order to communicate over the network, computers use agreed-on rules, called communication protocols, over whatever medium is used. The computer network can include personal computers, Server (computing), servers, networking hardware, or other specialized or general-purpose Host (network), hosts. They are identified by network addresses and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes and are rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Processor Design
Processor design is a subfield of computer science and computer engineering (fabrication) that deals with creating a processor, a key component of computer hardware. The design process involves choosing an instruction set and a certain execution paradigm (e.g. VLIW or RISC) and results in a microarchitecture, which might be described in e.g. VHDL or Verilog. For microprocessor design, this description is then manufactured employing some of the various semiconductor device fabrication processes, resulting in a die which is bonded onto a chip carrier. This chip carrier is then soldered onto, or inserted into a socket on, a printed circuit board (PCB). The mode of operation of any processor is the execution of lists of instructions. Instructions typically include those to compute or manipulate data values using registers, change or retrieve values in read/write memory, perform relational tests between data values and to control program flow. Processor designs are often tested an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
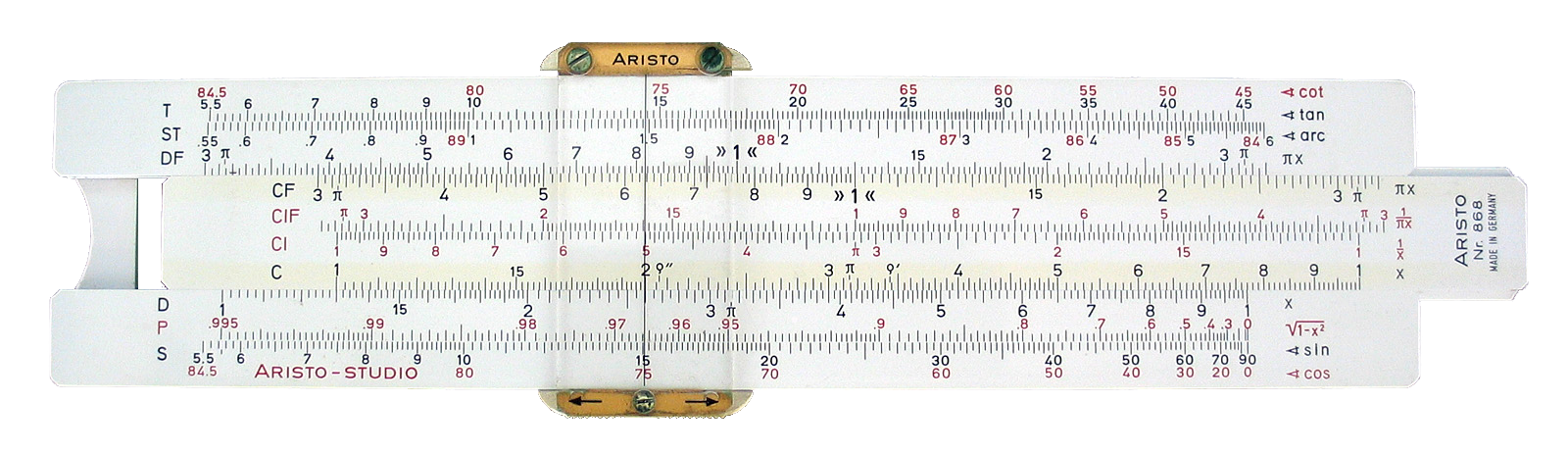 |
History Of Computing Hardware
The history of computing hardware spans the developments from early devices used for simple calculations to today's complex computers, encompassing advancements in both analog and digital technology. The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. In later stages, computing devices began representing numbers in continuous forms, such as by distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a specific voltage level. Numbers could also be represented in the form of digits, automatically manipulated by a mechanism. Although this approach generally required more complex mechanisms, it greatly increased the precision of results. The development of transistor technology, followed by the invention of integrated circuit chips, led to revolutionary breakthroughs. Transistor-based computers and, later, integrated circuit-based computers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Computer Hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the central processing unit (CPU), random-access memory (RAM), motherboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, and computer case. It includes external devices such as a Computer monitor, monitor, Computer mouse, mouse, Computer keyboard, keyboard, and Computer speakers, speakers. By contrast, software is a set of written instructions that can be stored and run by hardware. Hardware derived its name from the fact it is ''Hardness, hard'' or rigid with respect to changes, whereas software is ''soft'' because it is easy to change. Hardware is typically directed by the software to execute any command or Instruction (computing), instruction. A combination of hardware and software forms a usable computing system, although Digital electronics, other systems exist with only hardware. History Early computing devices were more complicated than the ancient abacus date to the seventeenth century. French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |