|
Outline Of Cannabis
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the plant '' Cannabis sativa'' and its relatives '' Cannabis indica'' and '' Cannabis ruderalis'', the drug cannabis (drug) and the industrial product hemp. Botany *'' Cannabis indica'' *'' Cannabis ruderalis'' *'' Cannabis sativa'' * Autoflowering cannabis *Cannabis strains Economy Cannabis industry *List of cannabis companies Cannabis drug Cannabis (drug) * Cannabis consumption ** Adult lifetime cannabis use by country ** Cannabis edible *** Bhang ***Cannabis tea ***Dawamesc **Cannabis smoking ** *Chemicals ** Cannabinoids ***Cannabichromene (CBC) *** Cannabidiol (CBD) *** Cannabigerol (CBG) ***Cannabicyclol (CBL) ***Cannabinol (CBN) *** Cannabidivarin (CBDV) ***Cannabinodiol (CBDL) *** Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) *** Tetrahydrocannabinol-C4 (THC-C4) *** Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV, THV) ***Synthetic cannabinoids ** Terpenes *** Humulene *** Limonene *** Linalool *** Myrcene *** alpha-Pinene *No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabis Edible
A cannabis edible, also known as a cannabis-infused food or simply an edible, is a food product (either homemade or produced commercially) that contains decarboxylated cannabinoids (cannabinoid acids converted to their orally bioactive form) from cannabis extract as an active ingredient. Although ''edible'' may refer to either a food or a drink, a cannabis-infused drink may be referred to more specifically as a liquid edible or drinkable. Edibles are a way to consume cannabis. Unlike smoking, in which cannabinoids are inhaled into the lungs and pass rapidly into the bloodstream, peaking in about ten minutes and wearing off in a couple of hours, cannabis edibles may take hours to digest, and their effects may peak two to three hours after consumption and persist for around six hours. The food or drink used may affect both the timing and potency of the dose ingested. Most edibles contain a significant amount of THC, which can induce a wide range of effects, including: height ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' usually refers to the Delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-''trans''-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. THC is a lipid found in cannabis and, like most pharmacologically active secondary metabolites of plants, it is assumed to be involved in the plant's evolutionary adaptation, putatively against insect predation, ultraviolet light, and environmental stress. THC was first discovered and isolated by Israeli chemist Raphael Mechoulam in Israel in 1964. It was found that, when smoked, THC is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain, attaching itself to endocannabinoid receptors located in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. These are the parts of the brain responsible for thinking, memory, pleasure, coordina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinodiol
Cannabinodiol (CBND), also known as cannabidinodiol, cannabinoid that is present in the plant '' Cannabis sativa'' at low concentrations. It is the fully aromatized derivative of cannabidiol (CBD) and can occur as a product of the photochemical conversion of cannabinol (CBN). See also * Cannabidiol * Cannabinol * Cannabichromene * Cannabimovone * Delta-6-CBD Delta-6-cannabidiol (∆6-CBD) is a positional isomer of cannabidiol, found in only trace amounts in natural cannabis plants but readily synthesised from cannabidiol by base-catalysed migration of the double bond. See also * 4'-Fluorocannabidio ... * Dimethylheptylpyran * HU-210 * Nabilone * Parahexyl * Tetrahydrocannabivarin References Cannabinoids Natural phenols 2,6-Dihydroxybiphenyls Alkyl-substituted benzenes {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabidivarin
Cannabidivarin (CBDV, GWP42006) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in ''Cannabis''. It is a homolog (chemistry) of cannabidiol (CBD), with the side-chain shortened by two methylene bridges (CH2 units). Although cannabidivarin (CBDV) is usually a minor constituent of the cannabinoid profile, enhanced levels of CBDV have been reported in feral populations of ''C. indica'' ( = ''C. sativa'' ssp. ''indica'' var. ''kafiristanica'') from northwest India, and in hashish from Nepal. CBDV has anticonvulsant effects. It was identified for the first time in 1969 by Vollner et al. Similarly to CBD, it has seven double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers (see: Cannabidiol#Isomerism). It is not scheduled by Convention on Psychotropic Substances The Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 is a United Nations treaty designed to control psychoactive drugs such as amphetamine-type stimulants, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and psychedelics signed in Vienna, Austria on 21 Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinol
Cannabinol (CBN) is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid that acts as a low affinity partial agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors. This activity at CB1 and CB2 receptors constitutes interaction of CBN with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). CBN was the first cannabis compound to be isolated from cannabis extract in the late 1800s. Its structure and chemical synthesis were achieved by 1940, followed by some of the first basic research studies to determine the effects of individual cannabis-derived compounds in vivo. Although CBN shares the same mechanism of action as other phytocannabinoids (e.g., delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol or D9THC), it has a lower affinity for CB1 receptors, meaning that much higher doses of CBN are required in order to experience effects, such as mild sedation. Chemical structure Cannabinoid receptor agonists are categorized into four groups based on chemical structure. CBN, as one of the many phytocannabinoids derived from Cannabis Sativa L, is considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabicyclol
Cannabicyclol (CBL) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in '' Cannabis''. CBL is a degradative product like cannabinol, with cannabichromene degrading into CBL through natural irradiation or under acid conditions. CBL is not scheduled under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. See also * Cannabis * Medical cannabis Medical cannabis, or medical marijuana (MMJ), is cannabis and cannabinoids that are prescribed by physicians for their patients. The use of cannabis as medicine has not been rigorously tested due to production and governmental restrictions ... References External links CTD's Cannabicyclol pagefrom the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database Wiley-VCH list of chemicals Phytocannabinoids Phenols Benzopyrans Cyclobutanes Cyclopentanes Heterocyclic compounds with 4 rings {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabigerol
Cannabigerol (CBG) is one of more than 120 identified cannabinoid compounds found in the plant genus ''Cannabis''. Cannabigerol is the decarboxylated form of cannabigerolic acid, the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. Cannabigerol is normally a minor constituent of cannabis. During plant growth, most of the cannabigerol is converted into other cannabinoids, primarily tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD), leaving about 1% cannabigerol in the plant. Some strains, however, produce larger amounts of cannabigerol and cannabigerolic acid, while having low quantities of other cannabinoids, like THC and CBD. Although cannabigerol is sold as a dietary supplement, its effects and safety for human consumption are undefined. Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of cannabigerol begins by loading hexanoyl-CoA onto a polyketide synthase assembly protein and subsequent condensation with three molecules of malonyl-CoA. This polyketide is cyclized to olivetol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabidiol
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. , clinical research on CBD included studies related to anxiety, cognition, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that cannabidiol is effective for these conditions. Nevertheless, CBD is an herbal dietary supplement promoted with unproven claims of particular therapeutic effects. The global market size for CBD was predicted to exceed billion by 2028. Cannabidiol can be taken internally in multiple ways, including by inhaling cannabis smoke or vapor, oral, and as an aerosol spray into the cheek. It may be supplied as CBD oil containing only CBD as the active ingredient (excluding tetrahydrocannabinol HCor terpenes), CBD-dominant hemp extract oil, capsules, dried cannabis, or prescription liquid solution. CBD does not have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
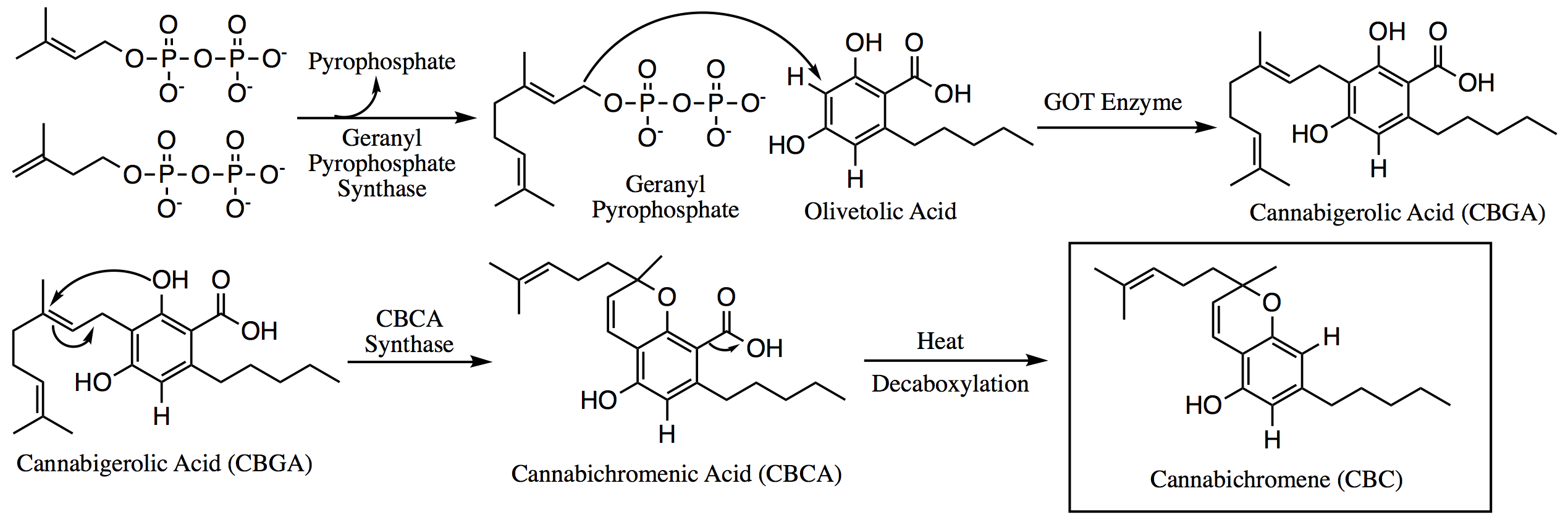
Cannabichromene
Cannabichromene (CBC), also called cannabichrome, cannanbichromene, pentylcannabichromene or cannabinochromene, is an anti-inflammatory which may contribute to the pain-killing effect of cannabis. It is one of the hundreds of cannabinoids found in the ''Cannabis'' plant, and is therefore a phytocannabinoid. It bears structural similarity to the other natural cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), cannabidiol (CBD), and cannabinol (CBN), among others. CBC and its derivatives are as abundant as cannabinols in cannabis. It is not scheduled by the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. It is more common in tropical cannabis varieties. Biosynthesis Within the ''Cannabis'' plant, CBC occurs mainly as cannabichromenic acid (CBCA, 2-COOH-CBC, CBC-COOH). Geranyl pyrophosphate and olivetolic acid combine to produce cannabigerolic acid (CBGA; the sole intermediate for all other phytocannabinoids), which is cyclized by the enzyme CBCA syntha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabis Smoking
Cannabis smoking (or colloquially smoking pot) is the inhalation of smoke or vapor released by heating the flowers, leaves, or extracts of cannabis and releasing the main psychoactive chemical, Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is absorbed into the bloodstream via the lungs. Archaeological evidence indicates cannabis with high levels of THC was being smoked at least 2,500 years ago. In addition to being smoked and vaporized, cannabis and its active cannabinoids may be ingested, placed under the tongue, or applied to the skin. The bioavailability characteristics and effects of smoking and vaporizing cannabis differ from other cannabis consumption methods in having a more rapid and predictable onset of effect. Methods Cannabis (marijuana) can be smoked in a variety of pipe-like implements made in different shapes and of different materials including hand pipes ( "bowls"), water pipes ("bongs"), cigarettes ("joints"), or blunts. Solar puffing (also called ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |