|
Outline Of Archaeology
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to archaeology: Archaeology – study of cultures through the recovery, documentation, and analysis of material remains and environmental data, including architecture, artifacts, biofacts, human remains, and landscapes. What type of thing is archaeology? Archaeology can be described as all of the following: * Academic discipline * Science ** Social science Essence of archaeology * Archaeological ethics * Archaeological excavation * Archaeological record * Archaeological science * Archaeological site * Archaeological theory * Artifacts * Biofacts * Excavation Branches of archaeology Archaeological practice * Cultural Resources Management * Archaeological ethics * Urban archaeology Archaeological science Archaeological science * Archaeometry * Dendrochronology * Isotope analysis * Palynology * Radiocarbon dating * Zooarchaeology * Geoarchaeology * Bioarchaeology * Archaeogenetics * Computatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or recorded history, historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort, although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition, such as a hoard or burial, can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
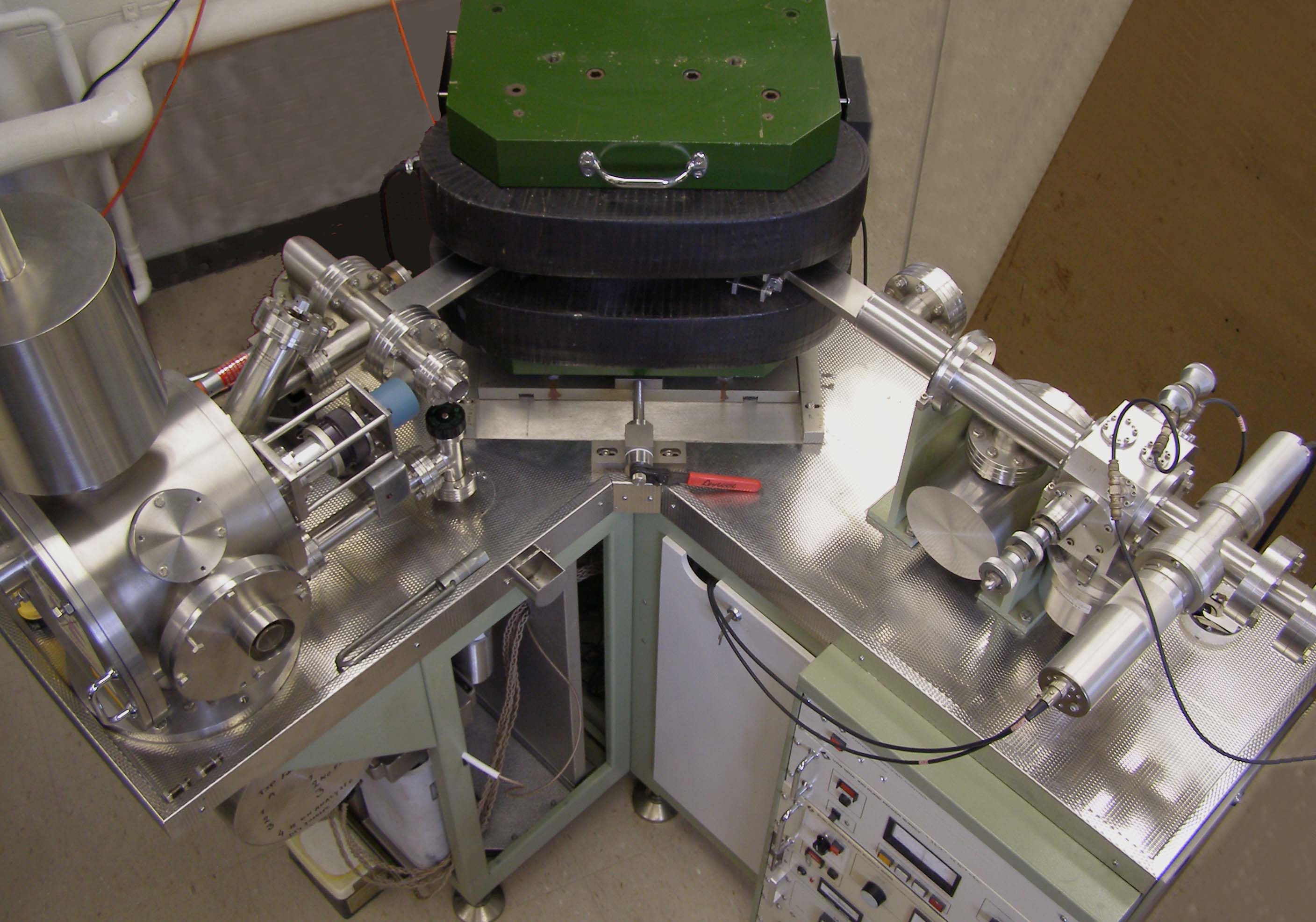
Archaeogenetics
Archaeogenetics is the study of ancient DNA using various molecular genetic methods and DNA resources. This form of genetic analysis can be applied to human, animal, and plant specimens. Ancient DNA can be extracted from various fossilized specimens including bones, eggshells, and artificially preserved tissues in human and animal specimens. In plants, ancient DNA can be extracted from seeds and tissue. Archaeogenetics provides us with genetic evidence of ancient population group migrations, domestication events, and plant and animal evolution. The ancient DNA cross referenced with the DNA of relative modern genetic populations allows researchers to run comparison studies that provide a more complete analysis when ancient DNA is compromised. Archaeogenetics receives its name from the Greek word ''arkhaios'', meaning "ancient", and the term ''genetics'', meaning "the study of heredity". The term archaeogenetics was conceived by archaeologist Colin Renfrew. In February 2021, sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioarchaeology
Bioarchaeology (osteoarchaeology, osteology or palaeo-osteology) in Europe describes the study of biological remains from archaeological sites. In the United States it is the scientific study of human remains from archaeological sites. The term was minted by British archaeologist Grahame Clark who, in 1972, defined it as the study of animal and human bones from archaeological sites. Jane Buikstra came up with the current US definition in 1977. Human remains can inform about health, lifestyle, diet, mortality and physique of the past. Although Clark used it to describe just human remains and animal remains, increasingly archaeologists include botanical remains. Bioarchaeology was largely born from the practices of New Archaeology, which developed in the United States in the 1970s as a reaction to a mainly cultural-historical approach to understanding the past. Proponents of New Archaeology advocate testing hypotheses about the interaction between culture and biology, or a bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoarchaeology
Geoarchaeology is a multi-disciplinary approach which uses the techniques and subject matter of geography, geology, geophysics and other Earth sciences to examine topics which inform archaeological and chronological knowledge and thought. Geoarchaeologists study the natural physical processes that affect archaeological sites such as geomorphology, the formation of sites through geological processes and the effects on buried sites and artifacts post-deposition. Geoarchaeologists' work frequently involves studying soil and sediments as well as other geographical concepts to contribute an archaeological study. Geoarchaeologists may also use computer cartography, geographic information systems (GIS) and digital elevation models (DEM) in combination with disciplines from human and social sciences and earth sciences. Geoarchaeology is important to society because it informs archaeologists about the geomorphology of the soil, sediment, and rocks on the buried sites and artifacts they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooarchaeology
Zooarchaeology or archaeozoology merges the disciplines of zoology and archaeology, focusing on the analysis of animal remains within archaeological sites. This field, managed by specialists known as zooarchaeologists or faunal analysts, examines remnants such as bones, shells, hair, chitin, scales, hides, and proteins, such as DNA, to derive insights into historical human-animal interactions and environmental conditions. While bones and shells tend to be relatively more preserved in archaeological contexts, the survival of faunal remains is generally infrequent. The degradation or fragmentation of faunal remains presents challenges in the accurate analysis and interpretation of data. Characterized by its interdisciplinary nature, zooarchaeology bridges the studies of ancient human societies and the animal kingdom. Practitioners, from various scientific backgrounds including anthropology, paleontology, and ecology, aim primarily to identify and understand human interactions with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotopes of carbon, isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palynology
Palynology is the study of microorganisms and microscopic fragments of mega-organisms that are composed of acid-resistant organic material and occur in sediments, sedimentary rocks, and even some metasedimentary rocks. Palynomorphs are the microscopic, acid-resistant organic remains and debris produced by a wide variety of plants, animals, and Protista that have existed since the late Proterozoic.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds., 2005, ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. It is the science that studies contemporary and fossil palynomorphs (paleopalynology), including pollen, spores, orbicules, dinocysts, acritarchs, chitinozoans and scolecodonts, together with particulate organic matter (POM) and kerogen found in sedimentary rocks and sediments. Palynology does not include diatoms, foraminiferans or other organisms with siliceous or calcareous tests. The name of the science and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, abundance of certain stable isotopes of chemical elements within organic and inorganic compounds. Isotopic analysis can be used to understand the flow of energy through a food web, to reconstruct past environmental and climatic conditions, to investigate human and animal diets, for food authentification, and a variety of other physical, geological, palaeontological and chemical processes. Stable isotope ratios are measured using mass spectrometry, which separates the different isotopes of an element on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio. Tissues affected Isotopic oxygen is incorporated into the body primarily through ingestion at which point it is used in the formation of, for archaeological purposes, bones and teeth. The oxygen is incorporated into the hydroxylcarbonic apatite of bone and tooth enamel. Bone is continually remodelled throughout the lifetime of an individual. Although the rate of tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrochronology
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of chronological dating, dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed in a tree. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, the study of climate and atmospheric conditions during different periods in history from the wood of old trees. Dendrochronology derives from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "tree", (), meaning "time", and (), "the study of". Dendrochronology is useful for determining the precise age of samples, especially those that are too recent for radiocarbon dating, which always produces a range rather than an exact date. However, for a precise date of the death of the tree a full sample to the edge is needed, which most trimmed timber will not provide. It also gives data on the timing of events and rates of change in the environment (most prominently climate) and also in wood found in archaeology or works of art and architecture, such as old pane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeometry
Archaeological science consists of the application of scientific techniques to the analysis of archaeological materials and sites. It is related to methodologies of archaeology. Martinón-Torres and Killick distinguish ‘scientific archaeology’ (as an epistemology) from ‘archaeological science’ (the application of specific techniques to archaeological materials). Martinón-Torres and Killick claim that ‘archaeological science’ has promoted the development of high-level theory in archaeology. However, Smith rejects both concepts of archaeological science because neither emphasize falsification or a search for causality. In the United Kingdom, the Natural and Environmental Research Council provides funding for archaeometry separate from the funding provided for archaeology. Types of archaeological science Archaeological science can be divided into the following areas: * physical and chemical dating methods which provide archaeologists with absolute and relative c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Archaeology
Urban archaeology is a sub discipline of archaeology specializing in the material past of towns and cities where long-term human habitation has often left a rich record of the past. In modern times, when someone talks about living in a city, they are in an area with many surrounding people and buildings, generally quite tall ones. In archaeological terms, cities give great information because of the infrastructure they have and amounts of people that were around one another. Through the years there has been one big method used for urban archaeology along with significant historic developments. Large concentrations of humans produce large concentrations of waste. Kitchen waste, broken objects, and similar material all need to be disposed of, while small numbers of people can dispose of their waste locally without encouraging vermin or endangering their health. Once people began to live together in large numbers, around five thousand years ago, such methods began to become impracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |