|
Oudaya
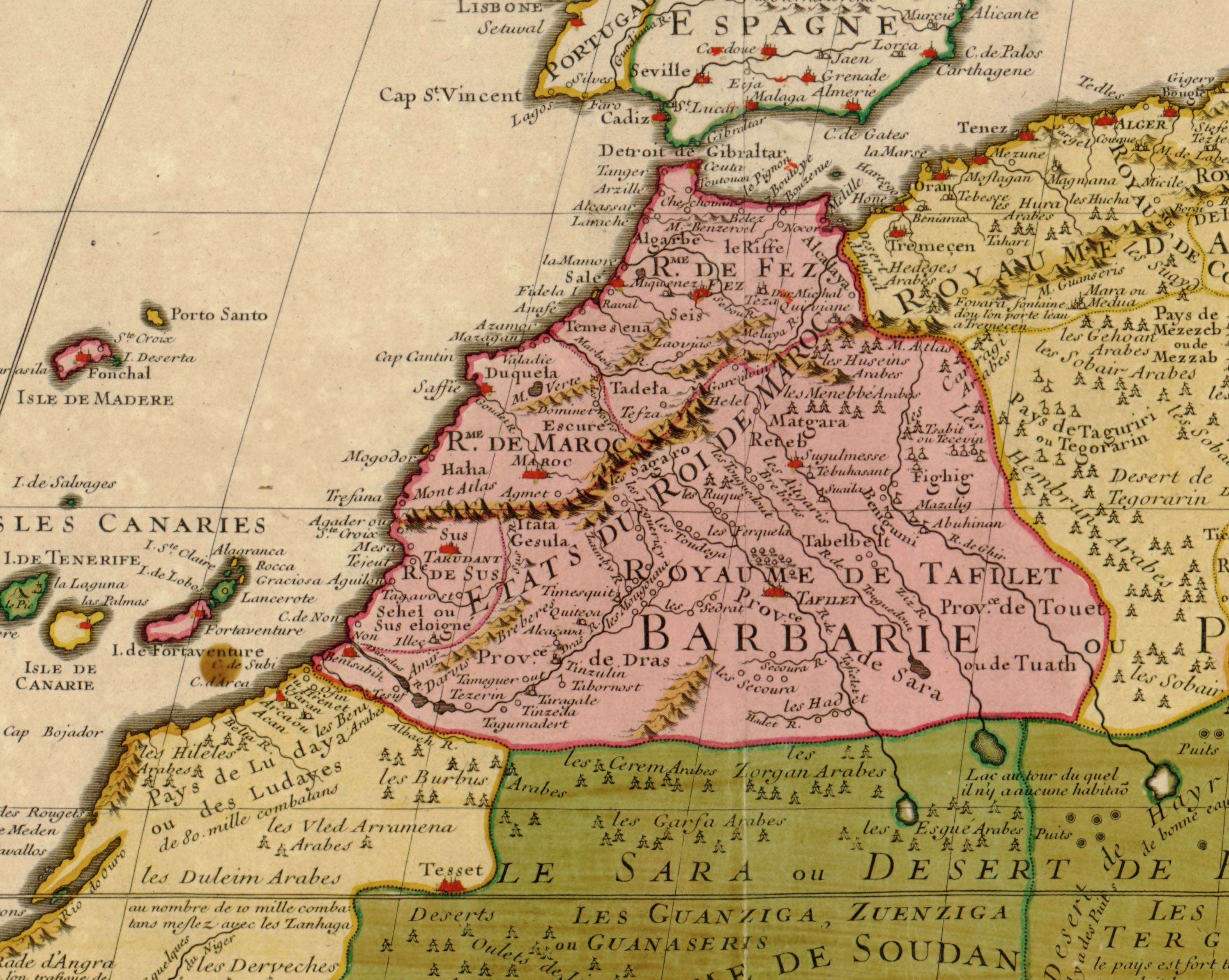
The Oudaya () also written as Udaya, Oudaia and sometimes referred to as Wadaya () is an Arabs, Arab tribe in Morocco of Maqil origin. They are situated around Fez, Morocco, Fez and Meknes, Marrakesh and in Rabat. They were recruited by Ismail Ibn Sharif as one of the guich tribes that formed an integral component of the pre-colonial Moroccan military. The Mghafra (), a sub-tribe of the Oudaya, founded several emirates in Mauritania, for example the Emirate of Trarza, as a result of the Char Bouba war, Char Bouba War. Etymology The name Oudaya is the plural of the Arabic word Wadi, oued () which means river as well as the words ''awdāʾ'' (اوداء), ''awdiya'' (أودية) and ''awdāh'' (أوداه; in the dialect of Tayy). This was corrupted into ''awādiya'' (أوادية). Ibn Sidah said the correct form is ''awdāya'' (الاوداية) and said: History Origins According to historical authors Leo Africanus and Luis del Mármol Carvajal, Marmol Carvajal, the Ouda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabat
Rabat (, also , ; ) is the Capital (political), capital city of Morocco and the List of cities in Morocco, country's seventh-largest city with an urban population of approximately 580,000 (2014) and a metropolitan population of over 1.2 million. It is also the capital city of the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra administrative region. Rabat is located on the Atlantic Ocean at the mouth of the river Bou Regreg, opposite Salé, the city's main commuter town. Rabat was founded in the 12th century by the Almohad Caliphate, Almohads. After a period of growth, the city fell into a long period of decline. In the 17th century, Rabat became a haven for Barbary pirates. When the French established a French protectorate in Morocco, protectorate over Morocco in 1912, Rabat became its administrative center. When Morocco achieved independence in 1955, Rabat became its capital. Rabat, Temara, and Salé form a conurbation of over 1.8 million people. Rabat is one of four Imperial cities of Morocco, and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
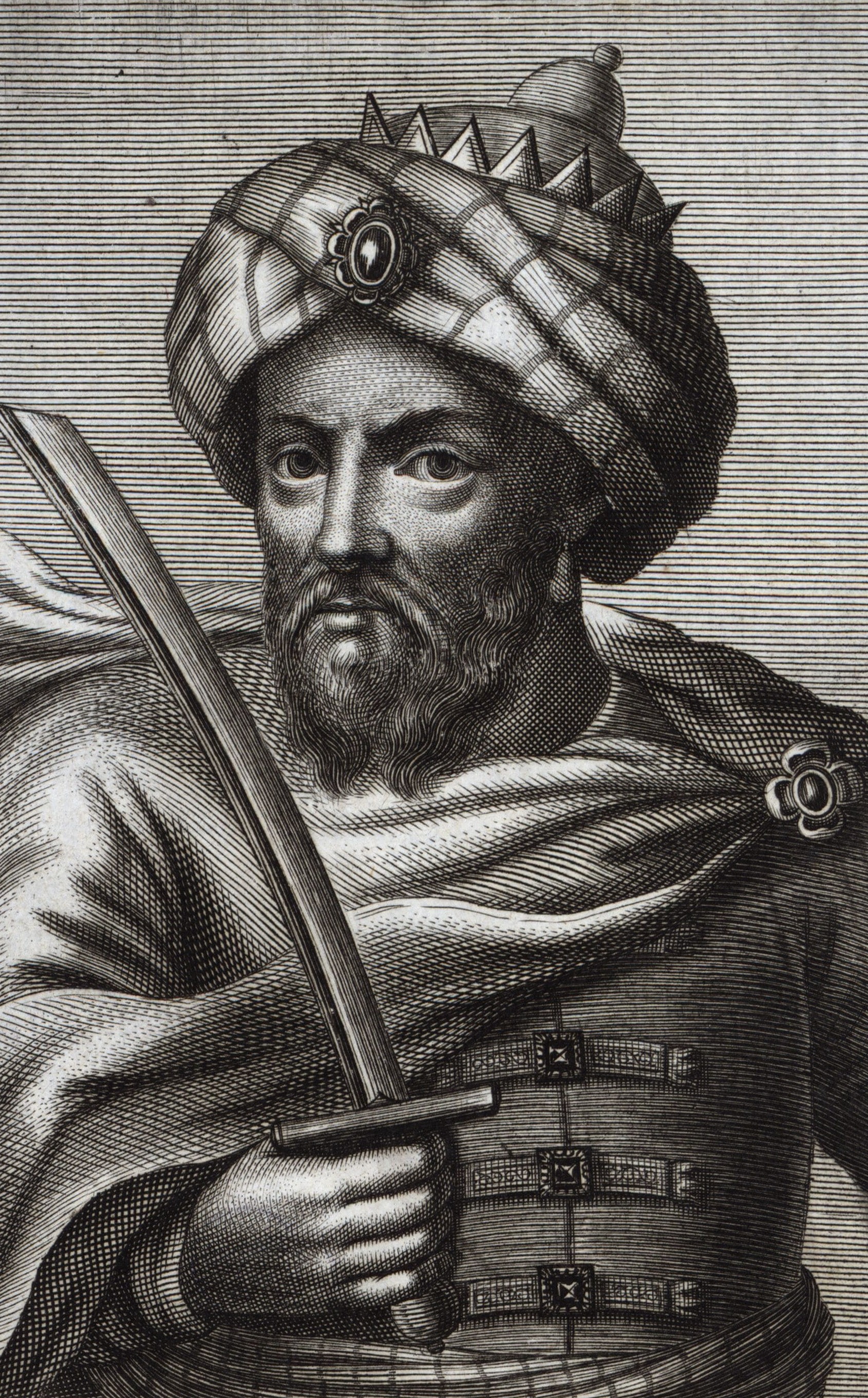
Ismail Ibn Sharif
Moulay Ismail Ibn Sharif (, – 22 March 1727) was a Sultan of Morocco from 1672 to 1727, as the second ruler of the 'Alawi dynasty. He was the seventh son of Sharif ibn Ali, Moulay Sharif and was governor of the province of Fez and the north of Morocco from 1667 until the death of his half-brother, Sultan Al-Rashid of Morocco, Moulay Rashid in 1672. He was proclaimed sultan at Fez, Morocco, Fez, but spent several years in conflict with his nephew Ahmed ben Mehrez, Moulay Ahmed ben Mehrez, who also claimed the throne, until the latter's death in 1687. Moulay Ismail's 55-year reign is the longest of any sultan of Morocco. During his lifetime, Isma’il amassed a harem of over 500 women with more than 800 confirmed biological children, making him one of the List of people with the most children, most prodigious fathers in recorded history. The reign of Moulay Ismail marked a high watermark for Moroccan power. His military successes are explained by the creation of a strong army, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fez, Morocco
Fez () or Fes (; ) is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the Fez-Meknes, Fez-Meknes administrative region. It is one of the List of cities in Morocco, largest cities in Morocco, with a population of 1.256 million, according to the 2024 Moroccan census, census. Located to the northwest of the Atlas Mountains, it is surrounded by hills and the old city is centered around the Oued Fes, Fez River (''Oued Fes'') flowing from west to east. Fez has been called the "Mecca of the West" and the "Athens of Africa". It is also considered the spiritual and cultural capital of Morocco. Founded under Idrisid dynasty, Idrisid rule during the 8th century Common Era, CE, Fez initially consisted of two autonomous and competing settlements. Successive waves of mainly Arab immigrants from Ifriqiya (Tunisia) and al-Andalus (Spain/Portugal) in the early 9th century gave the nascent city its Arab character. After the downfall of the Idrisid dynasty, other empires came and went until t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guich
''Guich'' tribes, ''Gish'' tribes, or ''Jaysh'' tribes ( or ), or sometimes ''Makhzen'' tribes, were tribes of usually Arab origin organized by the sultans of Moroccan dynasties under the pre-colonial Makhzen regime to serve as troops and military garrisons, as well as to protect the outskirts of the capital and suppress rebellions. They were usually cantoned in their own lands and maintained a state of perpetual military mobilization. The contingents were formed in order to be loyal to the sultan only instead of to other local interests, but they often maintained a coherent group identity long after the death of the sultan and were sometimes the source of political instability. The historical ''guich'' system took shape primarily under the reign of the 'Alawid sultan Mawlay Isma'il, although variations of similar military organisations were used by prior rulers and dynasties. The major historical ''guich'' tribes were the Cheraga, the Udayas, the Cherarda, and the Bwakher. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Rahman Of Morocco
''Moulay'' Abd al-Rahman bin Hisham (; 19 February 1778 – 28 August 1859) was List of rulers of Morocco, Sultan of Morocco from 30 November 1822 to 28 August 1859, as a ruler of the 'Alawi dynasty. He was a son of Hisham bin Mohammed, Moulay Hisham. He was proclaimed sultan in Fez, Morocco, Fes after the death of Sulayman of Morocco, Moulay Sulayman. During his long reign he proved himself competent in an age where Africa was being Scramble for Africa, colonized by stronger European nations, such as neighbouring Ottoman Algeria which was Invasion of Algiers in 1830, invaded by France. He was able to preserve Moroccan independence and maintain Moroccan borders without ceding any land, while also supporting Emirate of Abdelkader, Emir Abd al-Qadir's resistance in Algeria against France. He also signed the necessary treaties to enforce his beliefs, and fought numerous conflicts with European nations, especially July Monarchy, France. Biography Abd al-Rahman bin Hisham was born i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Guard
The Black Guard or ''‘Abid al-Bukhari'' (; also known as ''‘Abīd ad-Dīwān'' "slaves of the diwan", ''Jaysh al-‘Abīd'' "the slave army", and ''‘Abid as-Sultan'' "the sultan’s slaves") were the corps of black-African slaves and ''Haratin'' slave-soldiers assembled by the 'Alawi sultan of Morocco, Isma‘il ibn Sharif (reigned 1672–1727). They were called the "Slaves of Bukhari" because Sultan Isma‘il emphasized the importance of the teachings of the famous imam Muhammad al-Bukhari, going so far as to give the leaders of the army copies of his book. This military corps, which was loyal only to the sultan, was one of the pillars of Isma'il's power as he sought to establish a more stable and more absolute authority over Morocco. After Isma'il's death, the Black Guard became one of the most powerful factions in Moroccan politics and played the role of kingmakers during the period of turmoil that followed. Over the course of the later 18th century and the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beni Ḥassān
Beni Ḥassan ( "sons of Ḥassān") is a Bedouin Arab tribe which inhabits Western Sahara, Mauritania, Morocco and Algeria. It is one of the four sub-tribes of the Banu Maqil who emigrated in the 11th century from South Arabia to the Maghreb with the Banu Hilal and Banu Sulaym Arab tribes. In the 13th century, they took the Sanhaja territories in the southwest of the Sahara. In Morocco, they first settled, alongside their Maqil relatives, in the area between Tadla and the Moulouya River. The Sous Almohad governor called upon them for help against a rebellion in the Sous, and they resettled in and around that region. They later moved to what is today Mauritania, and from the 16th century onwards, they managed to push back all black peoples southwards to the Senegal Valley river. The Beni Hassan and other warrior Arab tribes dominated the Sanhaja Berber tribes of the area after the Char Bouba war of the 17th century. As a result, Arabs became the dominant ethnic group in West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouadane
Ouadane or Wādān () is a small town in the desert region of central Mauritania, situated on the southern edge of the Adrar Plateau, northeast of Chinguetti. The town was a staging post in the trans-Saharan trade and for caravans transporting slabs of salt from the mines at Idjil. The old town, a World Heritage Site, though in ruins, is still substantially intact, while a small modern settlement lies outside its gate. Ouadane is the closest town to the Richat Structure, a massive circular landmark visible from space. The whole Ouadane commune has a total size of , mostly consisting of desert. The main town is located in the south-west of the commune. History The early history of Ouadane is uncertain but it is possible that the town prospered from the trans-Saharan gold trade. In the middle of the 11th century, the Arabic geographer al-Bakri described a trans-Saharan route that ran between Tamdoult near Akka in Morocco Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oualata
Oualata or Walāta () (also Biru in 17th century chronicles) is a small oasis town in southeast Mauritania, located at the eastern end of the Aoukar basin. Oualata was important as a caravan city in the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries as the southern terminus of a trans-Saharan trade route and now it is a World Heritage Site. The whole Oualata commune has a total size of , mostly consisting of desert. The main town is located in the south of the commune. History The Oualata area is believed to have been first settled by an agro-pastoral people akin to the Mandé Soninke people who lived along the rocky promontories of the Tichitt-Oualata and Tagant cliffs of Mauritania facing the Aoukar basin. There, they built what are among the oldest stone settlements on the African continent. The town formed part of the Ghana Empire and grew wealthy through trade. At the beginning of the thirteenth century Oualata replaced Aoudaghost as the principal southern terminus of the tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmad Ibn Khalid An-Nasiri
Abu al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Khālid al-Nāṣirī al-Slāwī, (; 1835–1897) was born in Salé, Morocco and is considered to be the greatest Moroccan historian of the 19th century. He was a prominent scholar and a member of the family that founded the Nasiriyya Sufi order in the 17th century. He wrote an important multivolume history of Morocco Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...: '' Kitab al-Istiqsa li-Akhbar duwal al-Maghrib al-Aqsa''. The work is a general history of Morocco and the Islamic west from the Islamic conquest to the end of the 19th century. He died in 1897 shortly after having put the finishing touches to his chronicle.C.R. Pennell ''Morocco Since 1830: A History'', p. 109, Notes External links *M. Th. Houtsma, ''E.J. Brill's first encyclopaedia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaanite and Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful kingdoms emerged such as Saba, Lihyan, Minaean, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alawi Dynasty
The Alawi dynasty () – also rendered in English as Alaouite, Alawid, or Alawite – is the current Moroccan royal family and reigning dynasty. They are an Arab Sharifian dynasty and claim descent from the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his grandson, Hasan ibn Ali. Their ancestors originally migrated to the Tafilalt region, in present-day Morocco, from Yanbu on the coast of the Hejaz in the 12th or 13th century. The dynasty rose to power in the 17th century, beginning with Mawlay al-Sharif who was declared sultan of the Tafilalt in 1631. His son Al-Rashid, ruling from 1664 to 1672, was able to unite and pacify the country after a long period of regional divisions caused by the weakening of the Saadi Sultanate, establishing the Alawi Sultanate that succeeded it. His brother Isma'il presided over a period of strong central rule between 1672 and 1727, one of the longest reigns of any Moroccan sultan. After Isma'il's death, the country was plunged into disarray as his sons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |