|
Otto Ernst Remer
Otto Ernst Remer (18 August 1912 – 4 October 1997) was a German ''Wehrmacht'' German Army officer in World War II who played a major role in stopping the 20 July plot in 1944 against Adolf Hitler. He was a Captain and Major (1943-1944) and finally a Colonel and a General in 1945. In his later years, he became a politician and far-right activist. He co-founded the Socialist Reich Party in West Germany in the 1950s and is considered an influential figure in postwar neo-fascist politics in Germany.Atkins 2004, pp. 273–274. Early life Otto Ernest Remer was born at Neubrandenburg, Mecklenburg-Strelitz, in the German Empire on 18 August 1912. He attended a military academy and was commissioned as an officer in the German Army 1932 at the age of 20, a few months before Adolf Hitler rose to power in Germany, initiating a series of laws in the Weimar Republic which made him the sole leader in the country. Military career Remer began his career in April 1933 as an ensign in the 4th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neubrandenburg
Neubrandenburg (, Low German ''Niegenbramborg'', both lit. ''New Brandenburg an der Havel, Brandenburg'') is a city in the southeast of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is located on the shore of a lake called Tollensesee and forms the urban centre of the Mecklenburg Lake District, Mecklenburg Lakeland. The city is famous for its rich medieval heritage of Brick Gothic architecture, including the world's best preserved defensive wall of this style as well as a Marienkirche, Neubrandenburg, Concert Church (Saint Mary), the home venue of the Neubrandenburg Philharmonic. It is part of the European Route of Brick Gothic, a route which leads through seven countries along the Baltic Sea coast. Neubrandenburg is nicknamed for its four medieval city gates - ''Stadt der Vier Tore'' ("City of Four Gates"). Since 2011, Neubrandenburg has been the capital of the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte (district), Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district. It is the List of cities in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming Chancellor of Germany#Nazi Germany (1933–1945), the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. His invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 marked the start of the Second World War. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of Holocaust victims, about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and moved to German Empire, Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his service in the German Army in the First World War, receiving the Iron Cross. In 1919 he joined the German Workers' Party (DAP), the precursor of the Nazi Party, and in 1921 was app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
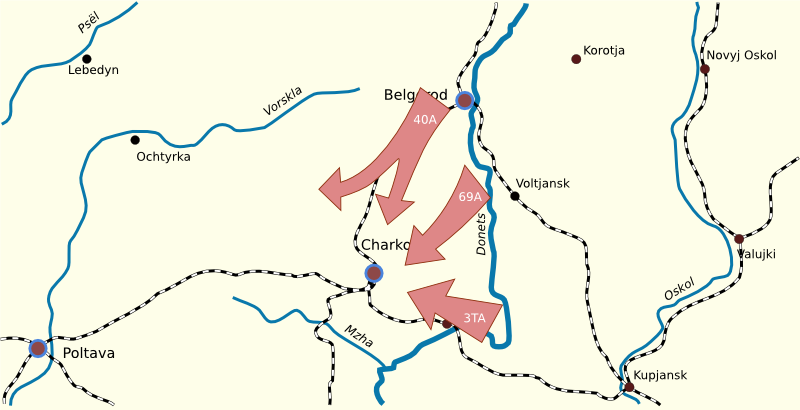
Third Battle Of Kharkov
The Third Battle of Kharkov was a series of battles on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, undertaken by Nazi Germany's Army Group South against the Soviet Red Army, around the city of Kharkov between 19 February and 15 March 1943. Known to the German side as the Donets Campaign, and in the Soviet Union as the Donbass and Kharkov operations, the German counterstrike led to the recapture of the cities of Kharkov and Belgorod. As the German 6th Army (Wehrmacht), 6th Army was encircled in the Battle of Stalingrad, the Red Army undertook a series of wider attacks against the rest of Army Group South. These culminated on 2 January 1943 when the Red Army launched Operation Star and Operation Gallop, which between January and early February broke German defenses and led to the Soviet recapture of Kharkov, Belgorod, Kursk, as well as Voroshilovgrad and Izium. These victories caused participating Soviet units to over-extend themselves. Freed on 2 February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waffen-SS
The (; ) was the military branch, combat branch of the Nazi Party's paramilitary ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both German-occupied Europe and unoccupied lands. With the start of World War II, tactical control was exercised by the (OKW, "High Command of the Armed Forces"), with some units being subordinated to the (Command Staff ''Reichsführer-SS'') directly under Himmler's control. It was disbanded in May 1945. The grew from three regiments to over 38 division (military), divisions during World War II. Combining combat and police functions, it served alongside the German Army (1935–1945), German Army (''Heer''), ''Ordnungspolizei'' (Order Police), and other security units. Originally, it was under the control of the (SS operational command office) beneath Heinrich Himmler, the head of the SS. Initially, in keeping with the raci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Großdeutschland Division
Pan-Germanism ( or '), also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanism seeks to unify all ethnic Germans, German-speaking people, and possibly also non-German Germanic peoples – into a single nation-state known as Greater Germany. Pan-Germanism was highly influential in German politics in the 19th century during the unification of Germany when the German Empire was proclaimed as a nation-state in 1871 but without Habsburg Austria, Luxembourg and Liechtenstein (Kleindeutsche Lösung/Lesser Germany) and the first half of the 20th century in the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the German Empire. From the late 19th century, many Pan-Germanist thinkers, since 1891 organized in the Pan-German League, had adopted openly ethnocentric and racist ideologies, and ultimately gave rise to the foreign policy ''Heim ins Reich'' pursued by Nazi Germany under Austrian-born Adolf Hitler from 1938, one of the primary factors leading to the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along a front, with the main goal of capturing territory up to a line between Arkhangelsk and Astrakhan, known as the A-A line. The attack became the largest and costliest military offensive in history, with around 10 million combatants taking part in the opening phase and over 8 million casualties by the end of the operation on 5 December 1941. It marked a major escalation of World War II, opened the Eastern Front—the largest and deadliest land war in history—and brought the Soviet Union into the Allied powers. The operation, code-named after the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa ("red beard"), put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goals of eradicating communism and conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberleutnant
(English: First Lieutenant) is a senior lieutenant Officer (armed forces), officer rank in the German (language), German-speaking armed forces of Germany (Bundeswehr), the Austrian Armed Forces, and the Swiss Armed Forces. In Austria, ''Oberleutnant'' is also a designation for certain positions in the federal police and prison guards. In the former West Germany, it was also a rank in the Federal Border Guard (''Bundesgrenzschutz''). Occupied Austria Germany In the German Army, it dates from the early 19th century. Translated as "first lieutenant", the rank is typically bestowed upon commissioned officers after five to six years of active-duty service. is used by both the German Army and the German Air Force. In the NATO military comparison system, a German is the equivalent of a first lieutenant in the Army/Air Forces of Allied nations. ;Other uses The equivalent naval rank is ''Oberleutnant zur See''. In Nazi Germany, within the SS, Sturmabteilung, SA and Waffen-SS, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, and the Soviet Union, which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviet invasion of Poland, Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The aim of the invasion was to disestablish Poland as a sovereign country, with its citizens destined for The Holocaust, extermination. German and Field Army Bernolák, Slovak forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclaimed itself, as the German Republic. The period's informal name is derived from the city of Weimar, which hosted the constituent assembly that established its government. In English, the republic was usually simply called "Germany", with "Weimar Republic" (a term introduced by Adolf Hitler in 1929) not commonly used until the 1930s. The Weimar Republic had a semi-presidential system. Toward the end of the First World War (1914–1918), Germany was exhausted and suing for peace, sued for peace in desperate circumstances. Awareness of imminent defeat sparked a German Revolution of 1918–1919, revolution, Abdication of Wilhelm II, the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II, the proclamation of the Weimar Republic on 9 November 1918, and formal cessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enabling Act Of 1933
The Enabling Act of 1933 ( German: ', officially titled ' ), was a law that gave the German Cabinet—most importantly, the chancellor, Adolf Hitler—the power to make and enforce laws without the involvement of the Reichstag or President Paul von Hindenburg. By allowing the Chancellor to override the checks and balances in the constitution, the Enabling Act was a pivotal step in the transition from the democratic Weimar Republic to the totalitarian dictatorship of Nazi Germany. Background On 30 January 1933, Adolf Hitler, leader of the Nazi Party (NSDAP), was appointed as Chancellor, the head of the German government. Hitler immediately asked President von Hindenburg to dissolve the Reichstag. A general election was scheduled for 5 March 1933. Reichstag fire On 27 February 1933, the Reichstag building of the German parliament caught fire. Acting as chancellor, Hitler immediately accused the Communists of perpetrating the arson as part of a larger effort to overthrow th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecklenburg-Strelitz
The Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz was a duchy in Northern Germany consisting of the eastern fifth of the historic Mecklenburg region, roughly corresponding with the present-day Mecklenburg-Strelitz district (the former Lordship of Stargard), and the western Principality of Ratzeburg exclave (the former Prince-Bishopric of Ratzeburg), which lay mostly in the west of the modern district. At the time of its establishment, the main part of the duchy bordered on the territory of Swedish Pomerania in the north and of Brandenburg in the south; Ratzeburg bordered Saxe-Lauenburg and the Free City of Lübeck. History After more than five years of dispute over succession to the House of Mecklenburg, the duchy was established in 1701 in the territory of the former duchy of Mecklenburg-Güstrow. The Güstrow branch of the House of Mecklenburg had died out with the death of Duke Gustav Adolph in 1695. Duke Frederick William of Mecklenburg-Schwerin claimed heirship, but he had to deal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |