|
Otoscope
An otoscope or auriscope is a medical device used by healthcare professionals to examine the ear canal and eardrum. This may be done as part of routine Physical examination, physical examinations, or for evaluating specific ear complaints, such as earaches, sense of fullness in the ear, or hearing loss. Usage Function An otoscope enables viewing and examination of the ear canal and tympanic membrane (eardrum). Otoscopic examination can help diagnose conditions such as acute otitis media (infection of the middle ear), traumatic Perforated eardrum, perforation of the eardrum, and cholesteatoma. The presence of cerumen (earwax), shed skin, pus, canal skin edema, Foreign body, foreign bodies, and various ear diseases, can obscure the view of the eardrum and thus compromise the value of otoscopy done with a common otoscope, but can confirm the presence of obstructing symptoms. Otoscopes can also be used to examine patients' noses (avoiding the need for a separate Specu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otoscope Spengler SMARTLED 5500
An otoscope or auriscope is a medical device used by healthcare professionals to examine the ear canal and eardrum. This may be done as part of routine physical examinations, or for evaluating specific ear complaints, such as earaches, sense of fullness in the ear, or hearing loss. Usage Function An otoscope enables viewing and examination of the ear canal and tympanic membrane (eardrum). Otoscopic examination can help diagnose conditions such as acute otitis media (infection of the middle ear), traumatic perforation of the eardrum, and cholesteatoma. The presence of cerumen (earwax), shed skin, pus, canal skin edema, foreign bodies, and various ear diseases, can obscure the view of the eardrum and thus compromise the value of otoscopy done with a common otoscope, but can confirm the presence of obstructing symptoms. Otoscopes can also be used to examine patients' noses (avoiding the need for a separate nasal speculum) and upper throats (by removing the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmoscope
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part of a routine physical examination. It is crucial in determining the health of the retina, optic disc, and vitreous humor. The pupil is a hole through which the eye's interior can be viewed. For better viewing, the pupil can be opened wider (dilated; mydriasis) before ophthalmoscopy using medicated eye drops ( dilated fundus examination). However, undilated examination is more convenient (albeit not as comprehensive), and is the most common type in primary care. An alternative or complement to ophthalmoscopy is to perform a fundus photography, where the image can be analysed later by a professional. Types There are two major types of ophthalmoscopy: * direct ophthalmoscopy, which produces an upright (unreversed) image of approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerumen
Earwax, also known by the medical term cerumen, is a waxy substance secreted in the ear canal of humans and other mammals. Earwax can be many colors, including brown, orange, red, yellowish, and gray. Earwax protects the skin of the human ear canal, assists in cleaning and lubrication, and provides protection against bacteria, fungus, fungi, particulate matter, and water. Major components of earwax include Ceruminous gland, cerumen, produced by a type of Ceruminous gland, modified sweat gland, and Sebaceous gland, sebum, an oily substance. Both components are made by glands located in the ear canal, outer ear canal. The chemical composition of earwax includes Saturated fat, saturated and Unsaturated fat, unsaturated Fatty acid#Length of free fatty acid chains, long chain fatty acids, alcohols, squalene, and cholesterol. Earwax also contains Desquamation, dead Keratinocyte, skin cells and hair. Excess or compacted cerumen is the buildup of ear wax causing a blockage in the ear c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internists
Internal medicine, also known as general medicine in Commonwealth nations, is a medical specialty for medical doctors focused on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases in adults. Its namesake stems from "treatment of diseases of the internal organs". Medical practitioners of internal medicine are referred to as internists, or physicians in Commonwealth nations. Internists possess specialized skills in managing patients with undifferentiated or multi-system disease processes. They provide care to both hospitalized (inpatient) and ambulatory (outpatient) patients and often contribute significantly to teaching and research. Internists are qualified physicians who have undergone postgraduate training in internal medicine, and should not be confused with " interns", a term commonly used for a medical doctor who has obtained a medical degree but does not yet have a license to practice medicine unsupervised. In the United States and Commonwealth nations, there is often co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Practice
General practice is personal, family, and community-orientated comprehensive primary care that includes diagnosis, continues over time and is anticipatory as well as responsive. Definitions A general practitioner (GP) is a doctor who is a consultant in the discipline of general practice. GPs have distinct expertise and experience in providing whole person medical care whilst managing the complexity, uncertainty and risk associated with the continuous care they provide. GPs work at the heart of their communities, striving to provide comprehensive and equitable care for everyone, taking into account their health care needs, stage of life and background. GPs work in, connect with and lead multidisciplinary teams that care for people and their families, respecting the context in which they live, aiming to ensure all of their physical health and mental health needs are met. General practice is an academic and scientific discipline with its own educational content, research, evidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
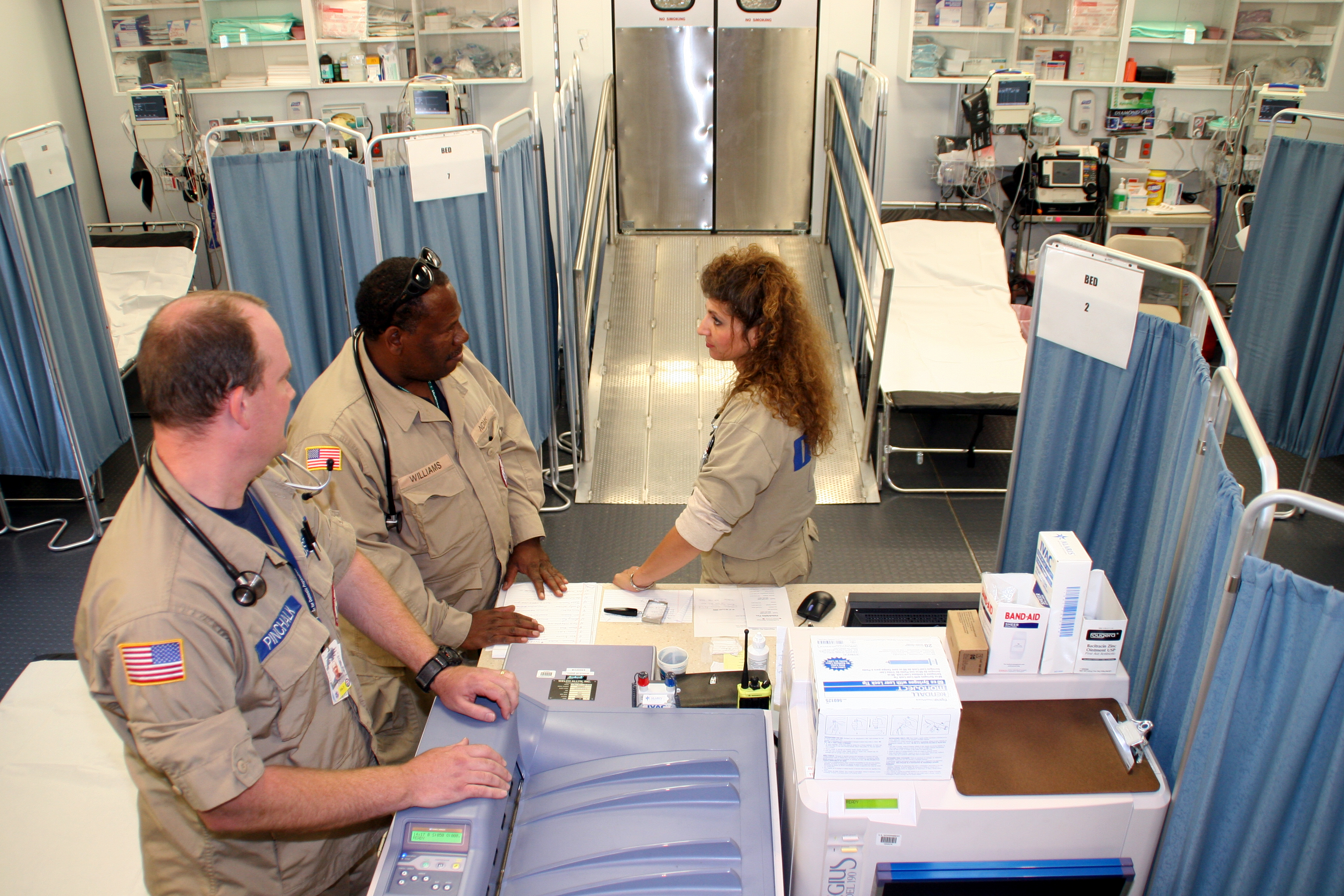
Emergency Department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the Acute (medicine), acute care of patients who present without prior appointment; either by their own means or by that of an ambulance. The emergency department is usually found in a hospital or other primary care center. Due to the unplanned nature of patient attendance, the department must provide initial treatment for a broad spectrum of illnesses and injuries, some of which may be Medical emergency, life-threatening and require immediate attention. In some countries, emergency departments have become important entry points for those without other means of access to medical care. The emergency departments of most hospitals operate 24 hours a day, although staffing levels may be varied in an attempt to reflect patient volume. History Accident services wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinna (anatomy)
The auricle or auricula is the visible part of the ear that is outside the head. It is also called the pinna (Latin for 'wing' or ' fin', : pinnae), a term that is used more in zoology. Structure The diagram shows the shape and location of most of these components: * '' antihelix'' forms a 'Y' shape where the upper parts are: ** ''Superior crus'' (to the left of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) ** ''Inferior crus'' (to the right of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) * ''Antitragus'' is below the ''tragus'' * ''Aperture'' is the entrance to the ear canal * ''Auricular sulcus'' is the depression behind the ear next to the head * ''Concha'' is the hollow next to the ear canal * Conchal angle is the angle that the back of the ''concha'' makes with the side of the head * ''Crus'' of the helix is just above the ''tragus'' * ''Cymba conchae'' is the narrowest end of the ''concha'' * External auditory meatus is the ear canal * ''Fossa triangularis'' is the depression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculum (medical)
A speculum (Latin for 'mirror'; : specula or speculums) is a medical tool for investigating body orifices, with a form dependent on the orifice for which it is designed. In old texts, the speculum may also be referred to as a diopter or dioptra. Like an endoscope, a speculum allows a view inside the body; endoscopes, however, tend to have optics while a speculum is intended for direct vision. History Vaginal and anal specula were used by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans, and speculum Artifact (archaeology), artifacts have been found in Pompeii. The modern vaginal speculum, developed by J. Marion Sims, consists of a hollow cylinder with a rounded end that is divided into two hinged parts, somewhat like the beak of a duck. This speculum is inserted into the vagina to dilate it for examination of the vagina and cervix. A more modern vaginal speculum was developed by Marie Boivin (1773–1841), a French midwife, inventor, and obstetrics writer who has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioptre
A dioptre ( British spelling) or (American spelling), symbol dpt or D, is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, . It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or curved mirror, which is a physical quantity equal to the reciprocal of the focal length, expressed in metres. For example, a 3-dioptre lens brings parallel rays of light to focus at metre. A flat window has an optical power of zero dioptres, as it does not cause light to converge or diverge. Dioptres are also sometimes used for other reciprocals of distance, particularly radii of curvature and the vergence of optical beams. The main benefit of using optical power rather than focal length is that the thin lens formula has the object distance, image distance, and focal length all as reciprocals. Additionally, when relatively thin lenses are placed close together their powers approximately add. Thus, a thin 2.0-dioptre lens placed close to a th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnifying Glass
A magnifying glass is a convex lens—usually mounted in a frame with a handle—that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. A magnifying glass can also be used to focus light, such as to concentrate the Sun's radiation to create a hot spot at the focus for fire starting. Evidence of magnifying glasses exists from antiquity. The magnifying glass is an icon of detective fiction, particularly that of Sherlock Holmes. An alternative to a magnifying glass is a sheet magnifier, which comprises many very narrow concentric ring-shaped lenses, such that the combination acts as a single lens but is much thinner. Use The convex lens of a magnifying glass can be used to produce a magnified image An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be di ... of an object. A magnify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |