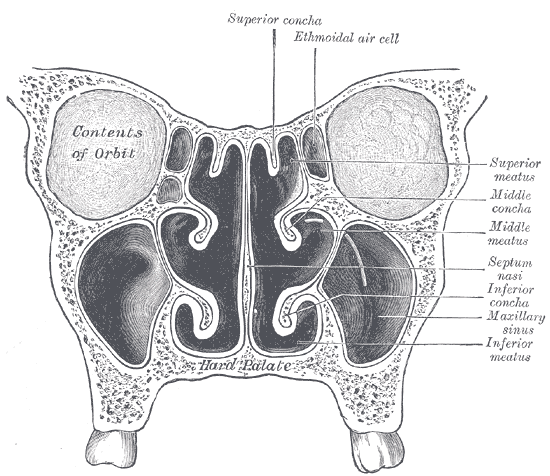
|
Ostium Maxillare
The maxillary hiatus (also known as maxillary sinus ostium, maxillary ostium, or opening from the maxillary sinus) is the opening of a maxillary sinus into the middle nasal meatus of the nasal cavity. It is situated superoposteriorly upon the lateral nasal wall, opening into the nasal cavity at the posterior portion of the ethmoidal infundibulum. Its opening in the maxillary sinus is present upon the superior part of the medial wall of the sinusHuman Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209-210Bell, G.W., et al. Maxillary sinus disease: diagnosis and treatment, ''British Dental Journal'' 210, 113 - 118 (2011) at http://www.nature.com/bdj/journal/v210/n3/full/sj.bdj.2011.47.html near the roof of the sinus; because of the position, gravity cannot drain the maxillary sinus contents when the head is erect. An accessory maxillary hiatus may be present either anterior or posterior to the inferior portion of the uncinate process of ethmoid bone. Anatomy It measures 2–4 mm in diamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillary Sinus
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Nathaniel Highmore (surgeon), Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, located in the maxilla. It drains into the middle meatus of the noseHuman Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209-210 through the semilunar hiatus. It is located to the side of the nasal cavity, and below the orbit. Structure It is the largest air sinus in the body. It has a mean volume of about 10 ml. It is situated within the body of the maxilla, but may extend into its Maxilla, zygomatic and Maxilla, alveolar processes when large. It is pyramid-shaped, with the apex at the maxillary zygomatic process, and the base represented by the lateral nasal wall. It has three recesses: an alveolar recess pointed inferiorly, bounded by the alveolar process of the maxilla; a zygomatic recess pointed laterally, bounded by the zygomatic bone; and an infraorbital recess pointed superiorly, bounded by the inferior Orbital surface of the body of the maxilla, orbita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Nasal Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are the spaces beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus in the Body of sphenoid bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoidal Infundibulum
The ethmoidal infundibulum is a funnel-shaped/slit-like/curved opening/passage/space/cleft upon the anterosuperior portion of the middle nasal meatus (and thus of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity) at the hiatus semilunaris (which represents the medial extremity of the infundibulum). The anterior ethmoidal air cells, and (usually) the frontonasal duct (which drains the frontal sinus) open into the ethmoidal infundibulum. The ethmoidal infundibulum extends anterosuperiorly from its opening into the nasal cavity. Anatomy The ethmoidal infundibulum is bordered medially by the uncinate process of the ethmoid bone, and laterally by the orbital plate of the ethmoid bone. The ethmoid infundibulum leads towards the maxillary hiatus.The anterior ethmoidal cells The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paranasal Sinus
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired skeletal pneumaticity, air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the Ethmoid sinus, ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes. The sinus (anatomy), sinuses are named for the Facial skeleton, facial bones and sphenoid bone in which they are located. Their role is disputed. Structure Humans possess four pairs of paranasal sinuses, divided into subgroups that are named according to the bones within which the sinuses lie. They are all innervated by branches of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). * The maxillary sinuses, the largest of the paranasal sinuses, are under the Human eye, eyes, in the maxillary bones (open in the back of the semilunar hiatus of the nose). They are innervated by the maxillary nerve (CN V2). * The frontal sinuses, superior to the eyes, in the frontal bone, which forms the hard part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncinate Process Of Ethmoid Bone
In the ethmoid bone, a sickle shaped projection, the uncinate process, projects posteroinferiorly from the ethmoid labyrinth. Between the posterior edge of this process and the anterior surface of the ethmoid bulla, there is a two-dimensional space, resembling a crescent shape. This space continues laterally as a three-dimensional slit-like space - the ethmoidal infundibulum. This is bounded by the uncinate process, medially, the orbital lamina of ethmoid bone The orbital lamina of ethmoid bone (or lamina papyracea or orbital lamina) is a smooth, oblong, paper-thin bone plate which forms the lateral wall of the labyrinth of the ethmoid bone. It covers the middle and posterior ethmoidal cells, and forms ... (lamina papyracea), laterally, and the ethmoidal bulla, posterosuperiorly. This concept is easier to understand if one imagine the infundibulum as a prism so that its medial face is the hiatus semilunaris. The "lateral face" of this infundibulum contains the ostium of the max ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulla Ethmoidalis
The ethmoid bulla (or ethmoidal bulla) is a rounded elevation upon the lateral wall of the middle nasal meatus (nasal cavity inferior to the middle nasal concha) produced by one or more of the underlying middle ethmoidal air cells (which open into the nasal cavity upon or superior to the ethmoidal bulla). It varies significantly based on the size of the underlying air cells. Structure The ethmoid bulla is formed by is the largest and least variable of the middle ethmoidal air cells. The size of the bulla varies with that of its contained cells. The bulla may be a pneumatised cell or a bony prominence found in middle meatus. Relations The hiatus semilunaris is situated (sources differ) inferior/anterior to the ethmoid bulla. The maxillary sinus also opens below the bulla. Development The ethmoid bulla begins to develop between 8 weeks and 12 weeks of gestation Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoidal Process Of Inferior Nasal Concha
Behind the lacrimal process of the inferior nasal conchae lies a broad, thin plate, the ethmoidal process, which ascends to join the uncinate process of the ethmoid; from its lower border a thin lamina, the maxillary process, curves downward and lateralward; it articulates with the maxilla and forms a part of the medial wall of the maxillary sinus The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Nathaniel Highmore (surgeon), Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, located in the maxilla. It drains into the middle meatus of the noseHuman Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209- .... References Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular Plate Of Palatine Bone
The perpendicular plate of palatine bone is the vertical part of the palatine bone, and is thin, of an oblong form, and presents two surfaces and four borders. Surfaces The nasal surface exhibits at its lower part a broad, shallow depression, which forms part of the inferior meatus of the nose. Immediately above this is a well-marked horizontal ridge, the conchal crest, for articulation with the inferior nasal concha; still higher is a second broad, shallow depression, which forms part of the middle meatus, and is limited above by a horizontal crest less prominent than the inferior, the ethmoidal crest, for articulation with the middle nasal concha. Above the ethmoidal crest is a narrow, horizontal groove, which forms part of the superior meatus. The maxillary surface is rough and irregular throughout the greater part of its extent, for articulation with the nasal surface of the maxilla; its upper and back part is smooth where it enters into the formation of the pterygopalatine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nose
A nose is a sensory organ and respiratory structure in vertebrates. It consists of a nasal cavity inside the head, and an external nose on the face. The external nose houses the nostrils, or nares, a pair of tubes providing airflow through the nose for Respiration (physiology), respiration. Where the nostrils pass through the nasal cavity they widen, are known as nasal fossae, and contain nasal concha, turbinates and olfactory mucosa. The nasal cavity also connects to the paranasal sinuses (dead-end air cavities for pressure buffering and humidification). From the nasal cavity, the nostrils continue into the pharynx, a switch track valve connecting the respiratory system, respiratory and digestive systems. In humans, the nose is located centrally on the face and serves as an alternative respiratory passage especially during suckling for infants. The protruding nose that is completely separate from the mouth part is a characteristic found only in theria, therian mammals. It has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |