|
Osteopetrosis
Osteopetrosis, literally , also known as marble bone disease or Albers-Schönberg disease, is an extremely rare inherited disorder whereby the bones harden, becoming denser, in contrast to more prevalent conditions like osteoporosis, in which the bones become less dense and more brittle, or osteomalacia, in which the bones soften. Osteopetrosis can cause bones to dissolve and break. It is one of the hereditary causes of osteosclerosis. It is considered to be the prototype of osteosclerosing dysplasias. The cause of the disease is understood to be malfunctioning osteoclasts and their inability to resorb bone. Although human osteopetrosis is a heterogeneous disorder encompassing different molecular lesions and a range of clinical features, all forms share a single pathogenic nexus in the osteoclast. The exact molecular defects or location of the mutations taking place are unknown. Osteopetrosis was first described in 1903 by German radiologist Albers-Schönberg. Signs and sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteopetrosis Tarda2
Osteopetrosis, literally , also known as marble bone disease or Albers-Schönberg disease, is an extremely rare inherited disorder whereby the bones harden, becoming denser, in contrast to more prevalent conditions like osteoporosis, in which the bones become less dense and more brittle, or osteomalacia, in which the bones soften. Osteopetrosis can cause bones to dissolve and break. It is one of the hereditary causes of osteosclerosis. It is considered to be the prototype of osteosclerosing dysplasias. The cause of the disease is understood to be malfunctioning osteoclasts and their inability to resorb bone. Although human osteopetrosis is a heterogeneous disorder encompassing different molecular lesions and a range of clinical features, all forms share a single pathogenic nexus in the osteoclast. The exact molecular defects or location of the mutations taking place are unknown. Osteopetrosis was first described in 1903 by German radiologist Albers-Schönberg. Signs and sympto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteosclerosis
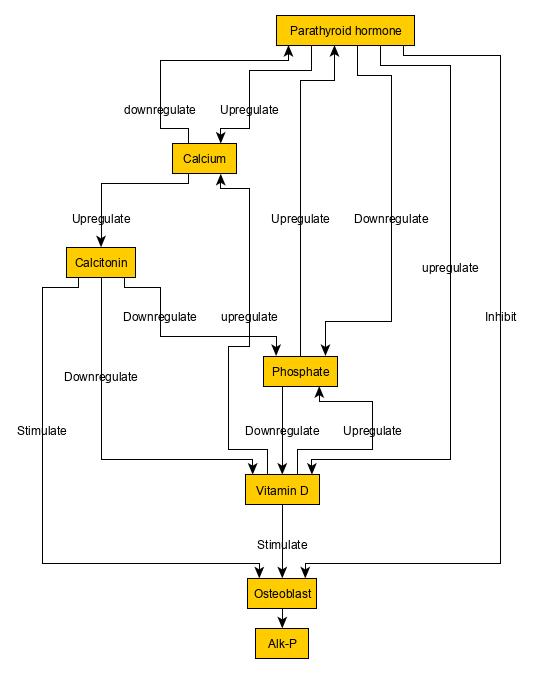
Osteosclerosis is a disorder characterized by abnormal hardening of bone and an elevation in bone density. It may predominantly affect the medullary portion and/or cortex of bone. Plain radiographs are a valuable tool for detecting and classifying osteosclerotic disorders. It can manifest in localized or generalized osteosclerosis. Localized osteosclerosis can be caused by Legg–Calvé–Perthes disease, sickle-cell disease and osteoarthritis among others. Osteosclerosis can be classified in accordance with the causative factor into acquired and hereditary. Types Acquired osteosclerosis * Osteogenic bone metastasis caused by carcinoma of prostate and breast * Paget's disease of bone * Myelofibrosis (primary disorder or secondary to intoxication or malignancy) * Osteosclerosing types of chronic osteomyelitis * Hypervitaminosis D * Hyperparathyroidism * Schnitzler syndrome * Mastocytosis * Skeletal fluorosis * Monoclonal IgM Kappa cryoglobulinemia * Hepatitis C. Here ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoclasts
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated protein and mineral at a molecular level by secreting acid and a collagenase, a process known as '' bone resorption''. This process also helps regulate the level of blood calcium. Osteoclasts are found on those surfaces of bone that are undergoing resorption. On such surfaces, the osteoclasts are seen to be located in shallow depressions called ''resorption bays (Howship's lacunae)''. The resorption bays are created by the erosive action of osteoclasts on the underlying bone. The border of the lower part of an osteoclast exhibits finger-like processes due to the presence of deep infoldings of the cell membrane; this border is called ''ruffled border''. The ruffled border lies in contact with the bone surface within a resorption bay. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Albers-Schönberg
Heinrich Ernst Albers-Schönberg (21 January 1865 – 4 June 1921) was a German gynecologist and radiologist. He was a native of Hamburg. He studied medicine at the Universities of Tübingen and Leipzig, where in 1891 he earned his medical doctorate under the guidance of Heinrich Curschmann (1846-1910). From 1892 to 1894 he was an assistant at Hamburg-Eppendorf Hospital, afterwards working as an assistant to gynecologist Paul Zweifel (1848–1927) at the University of Leipzig. Soon afterwards, he settled in Hamburg as a medical practitioner. In 1897, with internist (1865–1938), he established an X-ray clinic and laboratory in Hamburg. Later, he was appointed head of the radiology department at St Georg Hospital. In 1919 he became a full professor and chair of radiology at the newly established University of Hamburg. Albers-Schönberg is credited with providing a description of osteopetrosis, a condition sometimes referred to as "Albers-Schönberg disease". It is described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Bodies
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature as its own body temperature, thus avoiding the need for internal thermoregulation. The internal thermoregulation process is one aspect of homeostasis: a state of dynamic stability in an organism's internal conditions, maintained far from thermal equilibrium with its environment (the study of such processes in zoology has been called physiological ecology). If the body is unable to maintain a normal human body temperature, normal temperature and it increases significantly above normal, a condition known as hyperthermia occurs. Humans may also experience lethal hyperthermia when the wet bulb temperature is sustained above for six hours. Work in 2022 established by experiment that a wet-bulb temperature exceeding 30.55°C caused uncompensab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
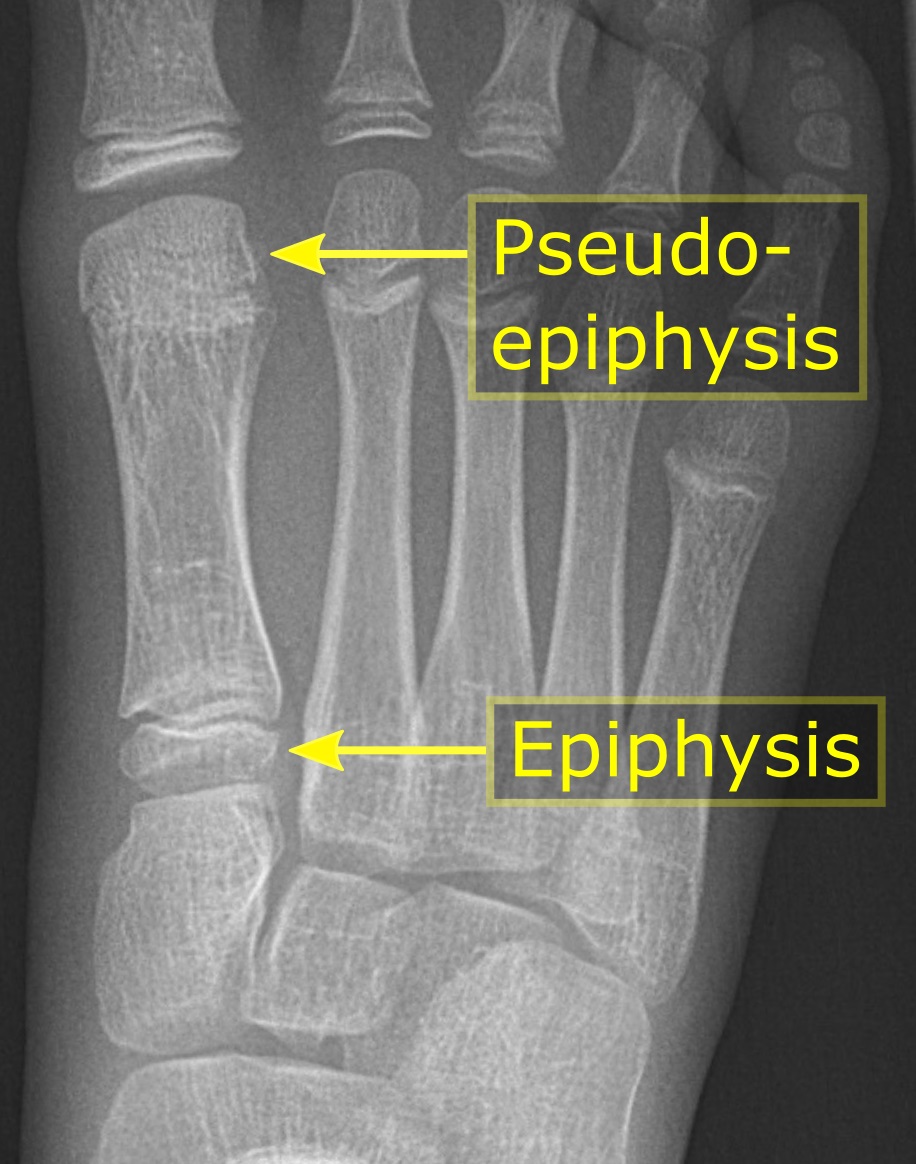
Epiphysis
An epiphysis (; : epiphyses) is one of the rounded ends or tips of a long bone that ossify from one or more secondary centers of ossification. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth plate). During formation of the secondary ossification center, vascular canals (epiphysial canals) stemming from the perichondrium invade the epiphysis, supplying nutrients to the developing secondary centers of ossification. At the joint, the epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage; below that covering is a zone similar to the epiphyseal plate, known as Wikt:subchondral, subchondral bone. The epiphysis is mostly found in mammals but it is also present in some lizards. However, the secondary center of ossification may have evolved multiple times, having been found in the Jurassic sphenodont ''Sapheosaurus'' as well as in the therapsid ''Niassodon, Niassodon mfumukasi.'' The epiphysis is filled wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Pain
Bone pain (also known medically by several other names) is pain coming from a bone, and is caused by damaging stimuli. It occurs as a result of a wide range of diseases or physical conditions or both, and may severely impair the quality of life.Luger, N. Mach, D. Sevcik, M. Mantyh, P. (2005). Bone cancer pain: From mechanism to model to therapy. ''Journal of Pain and Symptom Management''. 29(5): 32-46. Bone pain belongs to the class of deep somatic pain, often experienced as a dull pain that cannot be localized accurately by the patient. This is in contrast with the pain which is mediated by superficial receptors in, e.g., the skin. Bone pain can have several possible causes ranging from extensive physical stress to serious diseases such as cancer.Zwas, T. Elkanovitch, R. George, F. (1987). Interpretation and Classification of Bone Scintigraphic Findings in Stress Fractures. ''Journal of Nuclear Medicine''. 28: 452-457.Mantyh, P. Clohisy, D. Koltzenburg, M. Hunt, S. (2002). Mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Nanometre, nanometers to 10 Picometre, picometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range of 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 electronvolt, eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 in science, 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken language, and in adults it can create difficulties with social interaction and at work. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. Hearing loss related to age usually affects both ears and is due to cochlear hair cell loss. In some people, particularly older people, hearing loss can result in loneliness. Hearing loss may be caused by a number of factors, including: genetics, ageing, exposure to noise, some infections, birth complications, trauma to the ear, and certain medications or toxins. A common condition that results in hearing loss is chronic ear infections. Certain infections during pregnancy, such as cytomegalovirus, syphilis and rubella, may also cause hearing loss in the child. Hearing loss is diagnosed when hearing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of Visual perception, vision, taste, Olfaction, smell, and hearing. The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system above the level of the Atlas (anatomy), first vertebra of the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including the non-paired cranial nerve zero. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back. The terminal nerves (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) emerge f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralysis
Paralysis (: paralyses; also known as plegia) is a loss of Motor skill, motor function in one or more Skeletal muscle, muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 people have been diagnosed with some form of permanent or transient paralysis. The word "paralysis" derives from the Greek language, Greek παράλυσις, meaning "disabling of the nerves" from παρά (''para'') meaning "beside, by" and λύσις (''lysis'') meaning "making loose". A paralysis accompanied by involuntary tremors is usually called "palsy". Causes Paralysis is most often caused by damage in the nervous system, especially the spinal cord. Other major causes are stroke, Physical trauma, trauma with nerve injury, poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson's disease, ALS, botulism, spina bifida, multiple sclerosis and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Incidents th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |