|
Os Clitoridis
The os clitoridis (also called the os clitoris, clitoral bone or baubellum; : baubella) is a bone inside the clitoris of many placental mammals. It is absent from the human clitoris, but present in clitoris#Non-human primates, the clitoris of some primates, such as ring-tailed lemurs and non-human great apes. However, in the latter case, the bone is greatly reduced in size. It is homologous to the baculum in male mammals. The structure is more evolutionarily labile than the baculum, exhibiting both more inherent variability and more gains and losses over time, which has been interpreted as evidence for its non-functionality. Other work posits that the variation in the os clitoridis could be driven by intersexual conflict, lock-and-key genital evolution, and cryptic female choice, especially given the high level of variation within species as well as between them. History The os clitoridis was described in 1666 by Claude Perrault in otters and in the lioness. The term ''os clit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomischer Anzeiger (1914) (18190549982)
''Annals of Anatomy'' is a Peer review, peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of anatomy, published by Elsevier under its "Urban and Fischer" imprint. It was established in 1886 by Karl von Bardeleben and until 1991 was published under the title ''Anatomischer Anzeiger'' () by Gustav Fischer Verlag. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor of 2.2, ranking it 9th out of 20 journals in the category "Anatomy & Morphology". References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Annals Of Anatomy Publications established in 1886 Elsevier academic journals Anatomy journals English-language journals Bimonthly journals 1886 establishments in Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include Mouse, mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, Cavia, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) phenotypic variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copulation (zoology)
In zoology, copulation is animal sexual behavior in which a male introduces sperm into the female's body, especially directly into her reproductive tract. This is an aspect of mating. Many aquatic animals use external fertilization, whereas internal fertilization may have developed from a need to maintain gametes in a liquid medium in the Late Ordovician epoch. Internal fertilization with many vertebrates (such as all reptiles, some fish, and most birds) occurs via cloacal copulation, known as cloacal kiss (see also hemipenis), while most mammals copulate vaginally, and many basal vertebrates reproduce sexually with external fertilization. In spiders and insects Spiders are often confused with insects, but they are not insects; instead, they are arachnids. Spiders have separate male and female sexes. Before mating and copulation, the male spider spins a small web and ejaculates on to it. He then stores the sperm in reservoirs on his large pedipalps, from which he tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large pinniped marine mammal with discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. It is the only extant species in the family Odobenidae and genus ''Odobenus''. This species is subdivided into two subspecies: the Atlantic walrus (''O. r. rosmarus''), which lives in the Atlantic Ocean, and the Pacific walrus (''O. r. divergens''), which lives in the Pacific Ocean. Adult walrus are characterised by prominent tusks and whiskers, and considerable bulk: adult males in the Pacific can weigh more than and, among pinnipeds, are exceeded in size only by the two species of elephant seals. Walrus live mostly in shallow waters above the continental shelves, spending significant amounts of their lives on the sea ice looking for benthic bivalve molluscs. Walruses are relatively long-lived, social animals, and are considered to be a " keystone species" in the Arctic marine regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Beaver
The mountain beaver (''Aplodontia rufa'')Other names include boomer, mountain boomer, ground bear, giant mole, gehalis, sewellel, suwellel, showhurll, showtl, and showte, as well as a number of other Native American terms. "Mountain beaver" is a misnomer as the animal is not a true beaver (''Castor'') and it is not restricted to mountains. "Boomer" refers to the loud vocalizations that these usually-solitary animals make when in social situations, but this has not been recorded nor verified. Lewis and Clark originally called the animal "sewellel", a misunderstanding of the Chinook word "she-wal-lal", the name for garments made from the skin of the creature. See Borrecco and Anderson, 1980. is a North American rodent. It is the only living member of its genus, ''Aplodontia'', and Family (biology), family, Aplodontiidae. It should not be confused with true North American beaver, North American and Eurasian beavers, to which it is not closely related; the mountain beaver is instead m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Shorthaired Pointer
The German Shorthaired Pointer or is a German breed of continental pointing dog of Braque type. It originated in the nineteenth century in what is now Germany. It is of medium size, and is an all-purpose gun dog suitable for hunting and retrieving on both land and water. It may also be kept as a companion dog. History The pointing dog breeds of Europe all derive from the now-extinct Old Spanish Pointer, which spread through France and the Low Countries and reached the princely houses of the German-speaking world, where at first they were used in bird-hunting with nets or falcons, and later by huntsmen with guns. Bird dogs were also brought from England; , in his ''Aufrichtiger Lehrprinz'' of 1751, describes these as taller and stronger than the local type. In the nineteenth century large numbers of dogs of Burgos Pointing Dog type were brought to Germany. In the early part of that century the resulting mixed population had no specific name – the dogs were called ('bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Cocker Spaniel
The American Cocker Spaniel is a breed of sporting dog. It is a spaniel type dog that is closely related to the English Cocker Spaniel; the two breeds diverged during the 20th century due to differing breed standards in the US and the UK. In the United States, the breed is usually called a Cocker Spaniel, while elsewhere in the world, it is called an American Cocker Spaniel to distinguish it from its older English cousin. The word ''cocker'' is commonly held to stem from their use to hunt woodcock in England, while ''spaniel'' is thought to be derived from the breed's origins in Spain. The first spaniel in America came across with the ''Mayflower'' in 1620, but it was not until 1878 that the first Cocker Spaniel was registered with the American Kennel Club (AKC). A national breed club was set up three years later and the dog considered to be the father of the modern breed, Ch. Obo II, was born around this time. By the 1920s the English and American varieties of Cocker had become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
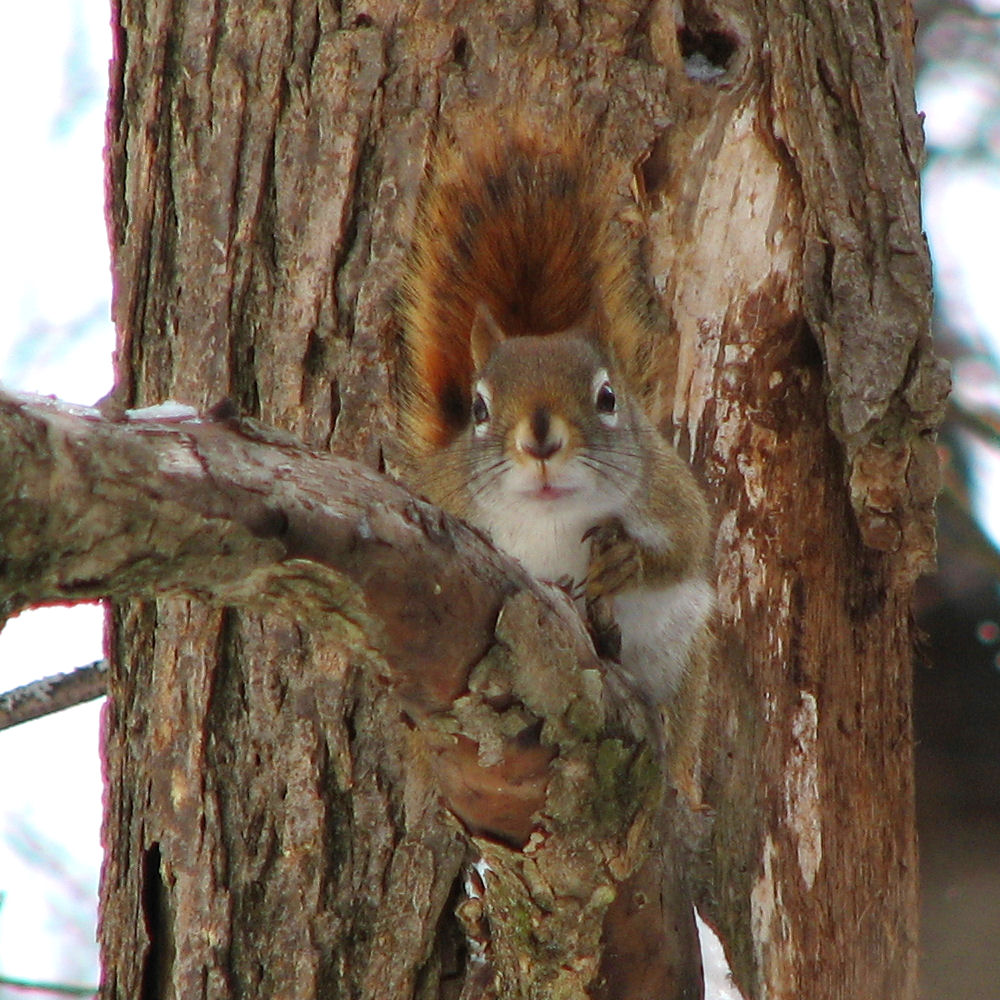
American Red Squirrel
The American red squirrel (''Tamiasciurus hudsonicus'') is one of three species of tree squirrels currently classified in the genus ''Tamiasciurus'', known as the pine squirrels (the others are the Douglas squirrel, ''T. douglasii'', and the southwestern red squirrel, ''T. fremonti''). The American red squirrel is variously known as the pine squirrel or piney squirrel, North American red squirrel, chickaree, boomer, or simply red squirrel. The squirrel is a small, , Diurnal animal, diurnal mammal that defends a year-round exclusive territory. It feeds primarily on the seeds of conifer cones, and is widely distributed across much of the United States and Canada wherever conifers are common, except in the southwestern United States, where it is replaced by the formerly conspecific southwestern red squirrel, and along the Pacific coast of the United States, where its cousin the Douglas squirrel is found instead. The squirrel has been expanding its range into hardwood forests. Taxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |