|
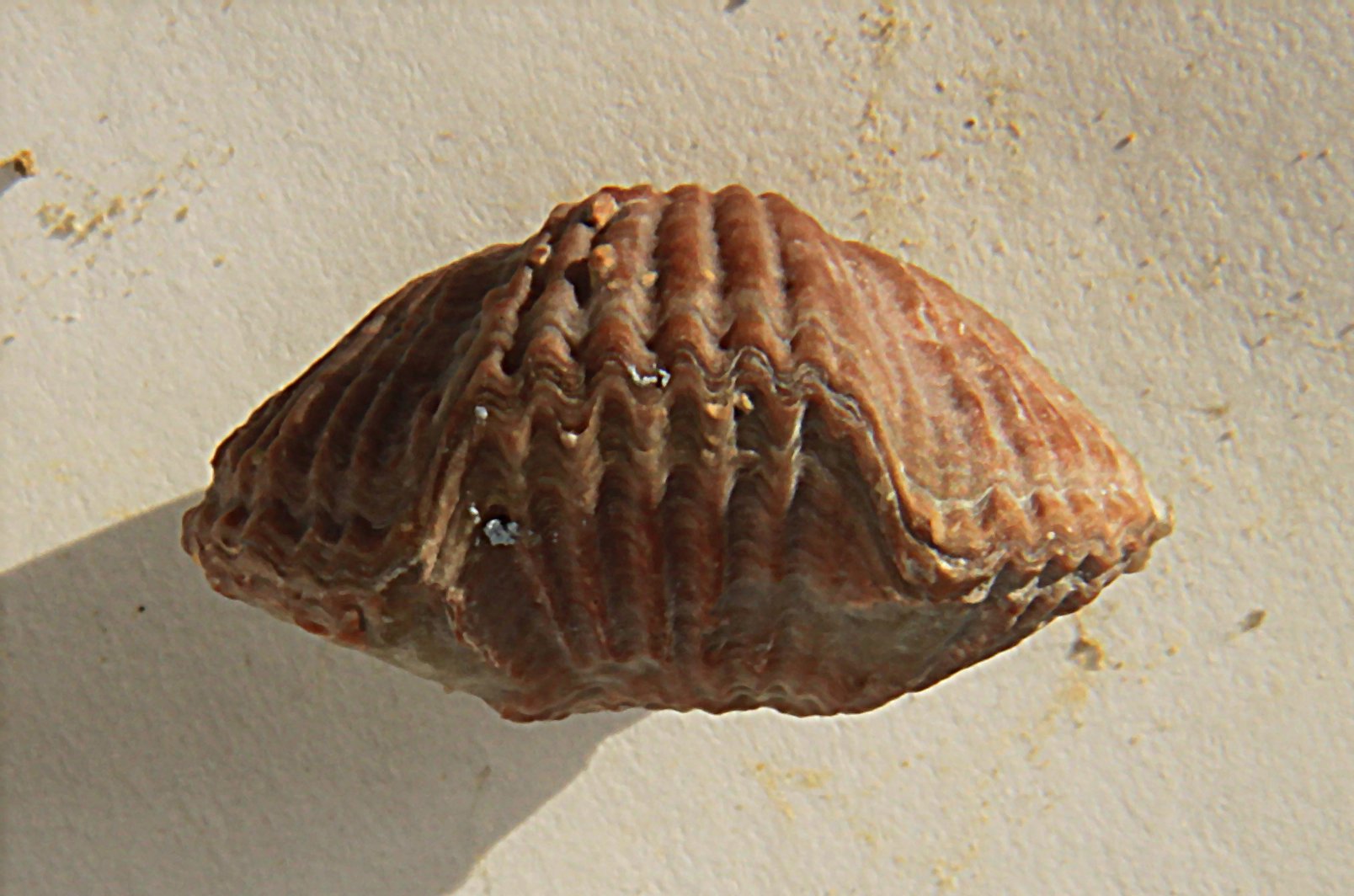
Orthotetida
The orthotetides (Orthotetida) are an extinct order of brachiopods in the class Strophomenata. Though not particularly diverse or abundant relative to strophomenides (Strophomenida) or productides (Productida), orthotetides were nevertheless the longest-lasting order of strophomenates, surviving from the Middle Ordovician (“Darriwilian, Llanvirn”) up until the Late Permian. Externally, many orthotetides are difficult to distinguish from strophomenides. Most fundamental differences between the two orders are internal: orthotetides have more elaborate cardinal processes and a greater diversity of shell microstructure. Anatomy All orthotetides have a strophic (straight) hinge line, and a shell profile ranging from biconvex (both valves convex) to concavoconvex (concave dorsal valve, convex ventral valve). In most other regards, the shell profile, ornamentation, and microstructure are strongly variable between orthotetide subgroups. Shell form Internally, the ventral valve ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilidiopsidae
Strophomenata is an extinct class of brachiopods in the subphylum Rhynchonelliformea. They originated in the Cambrian period, hugely diversified during the Ordovician, and faced near extinction from the Permian-Triassic extinction. Only a few lingered around in the Triassic until eventually going extinct. They were an exceptionally diverse group of brachiopods, and within the group the Strophomenids of the early Paleozoic and Productids of the late Paleozoic hugely contributed to the immense diversity. Common Features In ''The phylogeny and classification of Rhynchonelliformea'', Strophomenates are described as having "no definite synapomorphies In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to ...". A number of common features appear throughout the group, but there are many excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal Processes
Rhynchonelliformea is a major subphylum and clade of brachiopods. It is roughly equivalent to the former class Articulata, which was used previously in brachiopod taxonomy up until the 1990s. These so-called articulated brachiopods have many anatomical differences relative to "inarticulate" brachiopods of the subphyla Linguliformea and Craniformea. Articulates have hard calcium carbonate shells with tongue-and-groove hinge articulations (hence the name) and separate sets of simple opening and closing muscles. The Rhynchonelliformea (as described in the Treatise Part H, revised 1997–2007) is divided into five classes: Obolellata, Kutorginata, Chileata, Strophomenata, and Rhynchonellata. The Rhynchonellata are found living today, as the major constituent of modern brachiopod faunas. The other classes are all extinct: the Obolellata and Kutorginata are restricted to the Cambrian, while the Chileata and Strophomenata range through most of the Paleozoic. Anatomy Like all brach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
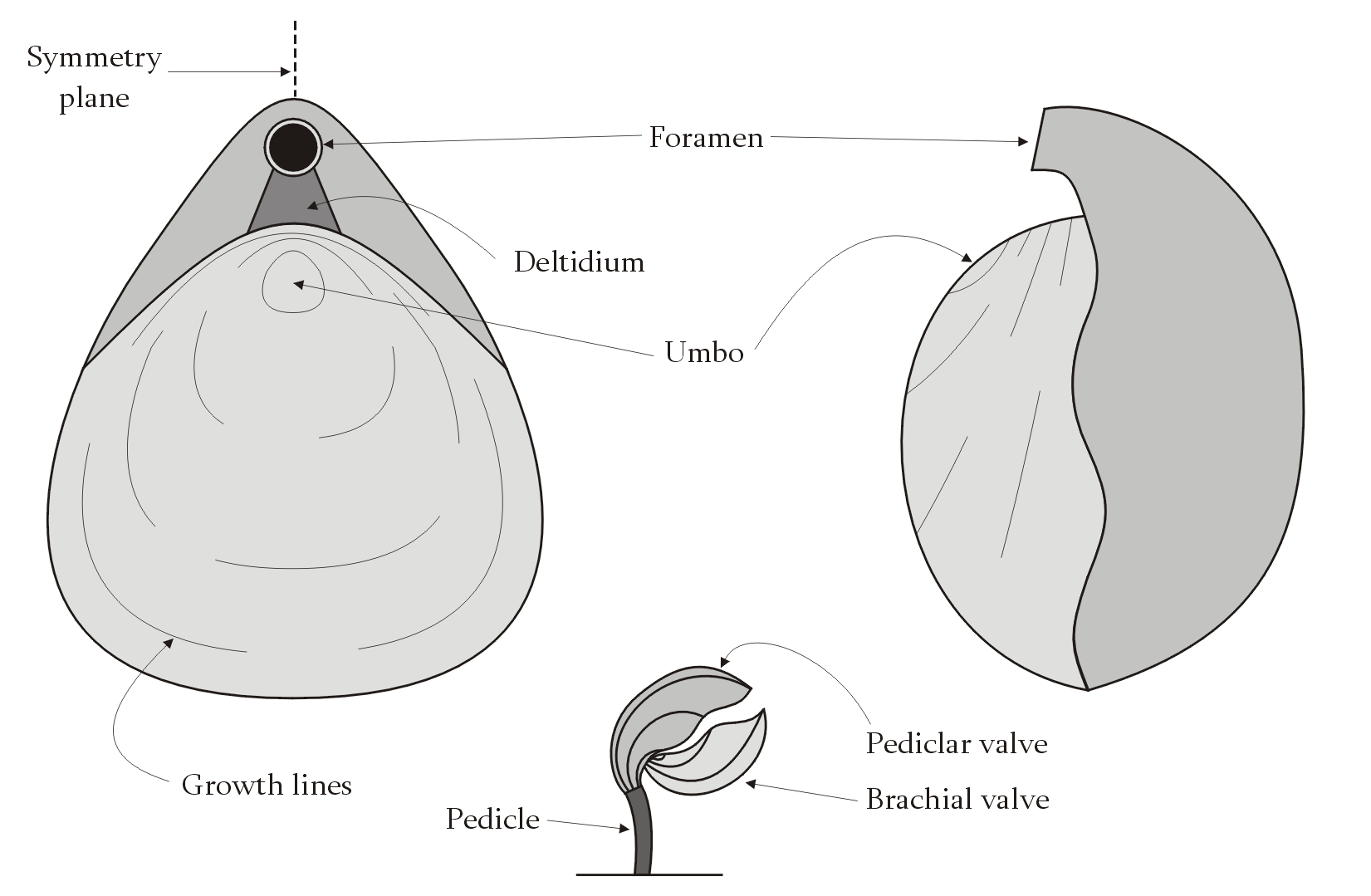
Pedicle (brachiopod)
Brachiopods (), phylum (biology), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiophore
Rhynchonelliformea is a major subphylum and clade of brachiopods. It is roughly equivalent to the former class Articulata, which was used previously in brachiopod taxonomy up until the 1990s. These so-called articulated brachiopods have many anatomical differences relative to "inarticulate" brachiopods of the subphyla Linguliformea and Craniformea. Articulates have hard calcium carbonate shells with tongue-and-groove hinge articulations (hence the name) and separate sets of simple opening and closing muscles. The Rhynchonelliformea (as described in the Treatise Part H, revised 1997–2007) is divided into five classes: Obolellata, Kutorginata, Chileata, Strophomenata, and Rhynchonellata. The Rhynchonellata are found living today, as the major constituent of modern brachiopod faunas. The other classes are all extinct: the Obolellata and Kutorginata are restricted to the Cambrian, while the Chileata and Strophomenata range through most of the Paleozoic. Anatomy Like all brachio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |