|
Orphics
Orphism is the name given to a set of religious beliefs and practices originating in the ancient Greek and Hellenistic world, associated with literature ascribed to the mythical poet Orpheus, who descended into the Greek underworld and returned. Orphism has been described as a reform of the earlier Dionysian religion, involving a re-interpretation or re-reading of the myth of Dionysus and a re-ordering of Hesiod's ''Theogony'', based in part on pre-Socratic philosophy. The suffering and death of the god Dionysus at the hands of the Titans has been considered the central myth of Orphism. According to this myth, the infant Dionysus is killed, torn apart, and consumed by the Titans. In retribution, Zeus strikes the Titans with a thunderbolt, turning them to ash. From these ashes, humanity is born. In Orphic belief, this myth describes humanity as having a dual nature: body (), inherited from the Titans, and a divine spark or soul (), inherited from Dionysus. In order to achieve sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
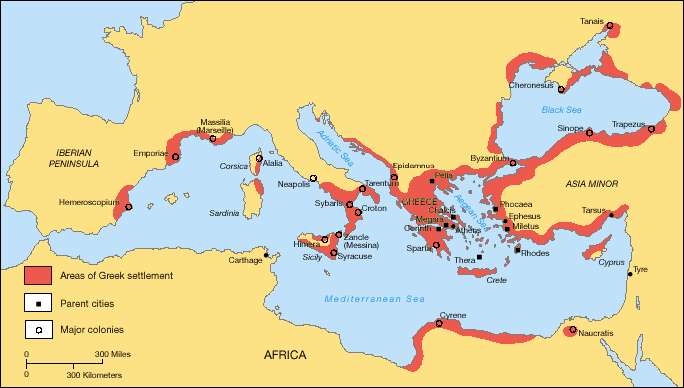
Pythagoreanism
Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek colony of Crotone, Kroton, in modern Calabria (Italy) circa 530 BC. Early Pythagorean communities spread throughout Magna Graecia. Already during Pythagoras' life it is likely that the distinction between the ''akousmatikoi'' ("those who listen"), who is conventionally regarded as more concerned with religious, and ritual elements, and associated with the oral tradition, and the ''mathematikoi'' ("those who learn") existed. The ancient biographers of Pythagoras, Iamblichus () and his master Porphyry (philosopher), Porphyry ( ) seem to make the distinction of the two as that of 'beginner' and 'advanced'. As the Pythagorean cenobites practiced an esoteric path, like the Greco-Roman mysteries, mystery schools of antiquity, the adherents, ''akou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Socratic Philosophy
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of these early philosophers spanned the workings of the natural world as well as human society, ethics, and religion. They sought explanations based on natural law rather than the actions of gods. Their work and writing has been almost entirely lost. Knowledge of their views comes from ''testimonia'', i.e. later authors' discussions of the work of pre-Socratics. Philosophy found fertile ground in the ancient Greek world because of the close ties with neighboring civilizations and the rise of autonomous civil entities, '' poleis''. Pre-Socratic philosophy began in the 6th century BC with the three Milesians: Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes. They all attributed the '' arche'' (a word that could take the meaning of "origin", "substance" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reincarnation
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the Philosophy, philosophical or Religion, religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new lifespan (other), lifespan in a different physical form or physical body, body after biological death. In most beliefs involving reincarnation, the soul of a human being is immortality, immortal and does not disperse after the physical body has perished. Upon death, the soul merely becomes transmigrated into a newborn baby or into an animal to continue its immortality. (The term "transmigration" means the passing of a soul from one body to another after death.) Reincarnation (''punarjanman'') is a central tenet of Indian religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. In various forms, it occurs as an esoteric belief in many streams of Judaism, in certain Paganism, pagan religions (including Wicca), and in some beliefs of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas and of Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theogony
The ''Theogony'' () is a poem by Hesiod (8th–7th century BC) describing the origins and genealogy, genealogies of the Greek gods, composed . It is written in the Homeric Greek, epic dialect of Ancient Greek and contains 1,022 lines. It is one of the most important sources for the understanding of early Greek cosmology. Descriptions Hesiod's ''Theogony'' is a large-scale synthesis of a vast variety of local Greece, Greek traditions concerning the gods, organized as a narrative that tells how they came to be and how they established permanent control over the cosmos. It is the first known Greece, Greek mythical cosmogony. The initial state of the universe is Chaos (mythology), chaos, a dark indefinite void considered a divine primordial condition from which everything else appeared. Theogonies are a part of Greek mythology which embodies the desire to articulate reality as a whole; this universalizing impulse was fundamental for the first later projects of speculative theorizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argonautica Orphica
__NOTOC__ The ''Orphic Argonautica'' or ''Argonautica Orphica'' () is a Greek epic poem dating from the 4th century CE.Meisnerp. 4 West, p. 37 states that "it can hardly be earlier and may well be later than the fourth century AD". It is narrated in the first person in the name of Orpheus and tells the story of Jason and the Argonauts. It is not known who the real author is. The poem is found in manuscripts either on its own or together with the '' Orphic Hymns'' and other hymns such as the ''Homeric Hymns'' and those of Proclus and Callimachus. The poem was lost, but in the fifteenth century it was found and copied in a manuscript (Codex Matritensis gr. 4562) by the Neoplatonic Greek scholar Constantine Lascaris, who is considered a Pythagorean Orpheus. Another related work is the '' Lithica'' (describing the properties and symbolism of different stones). The narrative is basically similar to that in other versions of the story, such as the ''Argonautica'' of Apollonius Rhodius, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of Plato, Aristotle, and, through them, Western philosophy. Modern scholars disagree regarding Pythagoras's education and influences, but most agree that he travelled to Croton in southern Italy around 530 BC, where he founded a school in which initiates were allegedly sworn to secrecy and lived a communal, ascetic lifestyle. In antiquity, Pythagoras was credited with mathematical and scientific discoveries, such as the Pythagorean theorem, Pythagorean tuning, the five regular solids, the theory of proportions, the sphericity of the Earth, the identity of the morning and evening stars as the planet Venus, and the division of the globe into five climatic zones. He was reputedly the first man to call himself a philosopher ("lover of wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proclus
Proclus Lycius (; 8 February 412 – 17 April 485), called Proclus the Successor (, ''Próklos ho Diádokhos''), was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, one of the last major classical philosophers of late antiquity. He set forth one of the most elaborate and fully developed systems of Neoplatonism and, through later interpreters and translators, exerted an influence on Byzantine philosophy, early Islamic philosophy, scholastic philosophy, and German idealism, especially G. W. F. Hegel, who called Proclus's ''Platonic Theology'' "the true turning point or transition from ancient to modern times, from ancient philosophy to Christianity." Biography The primary source for the life of Proclus is the eulogy ''Proclus'', ''or On Happiness'' that was written for him upon his death by his successor, Marinus, Marinus' biography set out to prove that Proclus reached the peak of virtue and attained eudaimonia. There are also a few details about the time in which he lived in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Lascaris
Constantine Lascaris ( ''Kostantinos Láskaris''; 1434 – 15 August 1501) was a Greek scholar and grammarian, one of the promoters of the revival of Greek learning in Italy during the Renaissance, born in Constantinople. Life Constantine Lascaris was born in Constantinople, where he was educated by the scholar John Argyropoulos, Gemistus Pletho's friend and pupil. After the fall of Constantinople in 1453, he took refuge in Rhodes and then in Italy, where Francesco Sforza, Duke of Milan, appointed him Greek tutor to his daughter Hippolyta. Here was published his ''Grammatica Graeca, sive compendium octo orationis partium'', remarkable as being probably the first book entirely in Greek issued from the printing press, in 1476. After leaving Milan in 1465, Lascaris taught in Rome and in Naples, to which he had been summoned by Ferdinand I to deliver a course of lectures on Greece. In the following year, on the invitation of the inhabitants, and especially of Ludovico Saccano, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSC00355 - Orfeo (epoca Romana) - Foto G
DSC or Dsc may refer to: Education * Doctor of Science (D.Sc.) * District Selection Committee, an entrance exam in India * Doctor of Surgical Chiropody, superseded in the 1960s by Doctor of Podiatric Medicine Educational institutions * Dyal Singh College, Delhi, India * DSC International School, Hong Kong, China United States * Dalton State College, Georgia * Daytona State College, Florida * Deep Springs College, California * Dixie State College, now Utah Tech University, Utah Science and technology * Dice similarity coefficient, a statistical measure * Differential scanning calorimetry, or the differential scanning calorimeter * Digital setting circles, on telescopes * Digital still camera, a type of camera * Doppler shift compensation, in bat echolocation * Dye-sensitized solar cell, a low-cost solar cell * Dynamic stability control, computerized technology that improves a vehicle's stability * Dynamic susceptibility contrast, a technique in perfusion MRI * Subarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
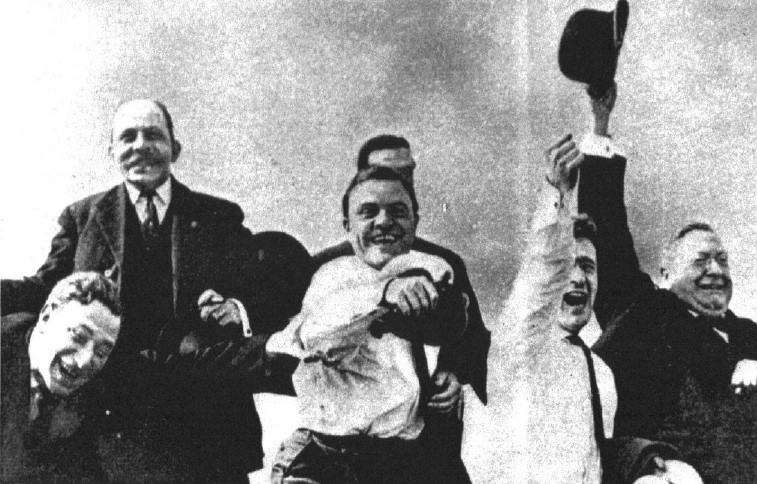
Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, (18 May 1872 – 2 February 1970) was a British philosopher, logician, mathematician, and public intellectual. He had influence on mathematics, logic, set theory, and various areas of analytic philosophy.Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy"Bertrand Russell", 1 May 2003. He was one of the early 20th century's prominent logicians and a founder of analytic philosophy, along with his predecessor Gottlob Frege, his friend and colleague G. E. Moore, and his student and protégé Ludwig Wittgenstein. Russell with Moore led the British "revolt against British idealism, idealism". Together with his former teacher Alfred North Whitehead, A. N. Whitehead, Russell wrote ''Principia Mathematica'', a milestone in the development of classical logic and a major attempt to reduce the whole of mathematics to logic (see logicism). Russell's article "On Denoting" has been considered a "paradigm of philosophy". Russell was a Pacifism, pacifist who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
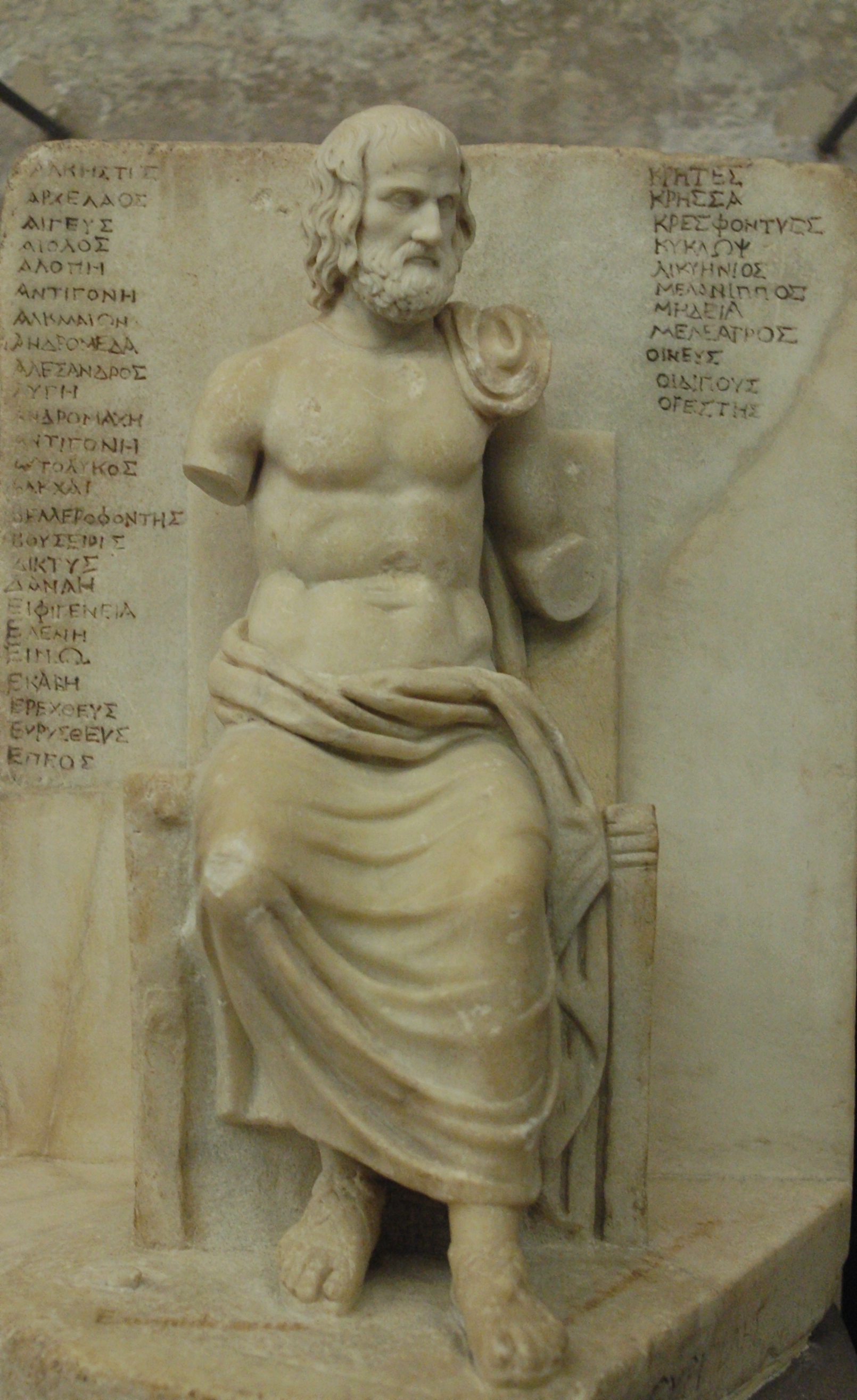
Euripides
Euripides () was a Greek tragedy, tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him, but the ''Suda'' says it was ninety-two at most. Of these, eighteen or nineteen have survived more or less complete (''Rhesus (play), Rhesus'' is suspect). There are many fragments (some substantial) of most of his other plays. More of his plays have survived intact than those of Aeschylus and Sophocles together, partly because his popularity grew as theirs declinedMoses Hadas, ''Ten Plays by Euripides'', Bantam Classic (2006), Introduction, p. ixhe became, in the Hellenistic Age, a cornerstone of ancient literary education, along with Homer, Demosthenes, and Menander.L.P.E.Parker, ''Euripides: Alcestis'', Oxford University Press (2007), Introduction p. lx Euripides is identified with theatrical innovations that have profoundly influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthusiasm
In modern usage, enthusiasm refers to intense enjoyment, interest, or approval expressed by a person. The term is related to playfulness, inventiveness, optimism, zest, verve, and high energy. The word was originally used to refer to a person possessed by God, or someone who exhibited intense piety. Historical usage The word ''enthusiasm'' originates from the Greek from (, “in”) and (, “god”), meaning "inspired or possessed by god". Applied by the Greeks to manifestations of divine possession, by Apollo (as in the case of the Pythia), or by Dionysus (as in the case of the Bacchantes and Maenads), the term enthusiasm was also used in a transferred or figurative sense. Socrates taught that the inspiration of poets is a form of enthusiasm. The term was confined to a belief in religious inspiration, or to intense religious fervor or emotion. From this, a Syrian sect of the fourth century was known as the Enthusiasts. They believed that "by perpetual prayer, asceti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |