|
Organomolybdenum
Organomolybdenum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds with Mo-C bonds. The heavier group 6 elements molybdenum and tungsten form organometallic compounds similar to those in organochromium chemistry but higher oxidation states tend to be more common. Mo(0) and more reduced states Molybdenum hexacarbonyl is the precursor to many substituted derivatives. It reacts with organolithium reagents to give anionic acyls which can be O-alkylated to give Fischer carbenes. 144px, Structure of (Mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl, (mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl. Mo(CO)6 reacts with arenes to give piano-stool complexes such as (Mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl, (mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl. Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl, which is related to (arene)Mo(CO)3, reacts with trityl salts to give the cycloheptatrienyl complex: :(C7H8)Mo(CO)3 + (C6H5)3C+ → C7H7)Mo(CO)3sup>+ + (C6H5)3CH file:CHTMo(CO)3.png, 144px, Structure of Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum Tricarbonyl
Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl is the organomolybdenum compound with the formula (C7H8)Mo(CO)3. It is a red-orange solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. The compound has no practical value but is a prototypical complex of cycloheptatriene. Synthesis, structure, and reactions The compound is prepared by thermal reaction of the triene with molybdenum hexacarbonyl: :C7H8 + Mo(CO)6 → (C7H8)Mo(CO)3 + 3 CO The compound is a piano stool complex, consisting of Mo(CO)3 bound to six carbon centers of the triene. The methylene group projects from the plane of the six coordinated carbon atoms. The compound reacts with trityl salts to give the cycloheptatrienyl complex:M. L. H. Green Malcolm Leslie Hodder Green (16 April 1936 – 24 July 2020) was Professor of Inorganic Chemistry at the University of Oxford. He made many contributions to organometallic chemistry. Education Born in Eastleigh, Hampshire, he was ed ..., D. K. P. Ng "Cycloheptatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm. Molybdenum does not occur naturally as a free metal on Earth; it is found only in various oxidation states in minerals. The free element, a silvery metal with a grey cast, has the sixth-highest melting point of any element. It readily forms hard, stable carbides in alloys, and for this reason most of the world production of the element (about 80%) is used in steel alloys, including high-strength alloys and superalloys. Most molybdenum compounds have low so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
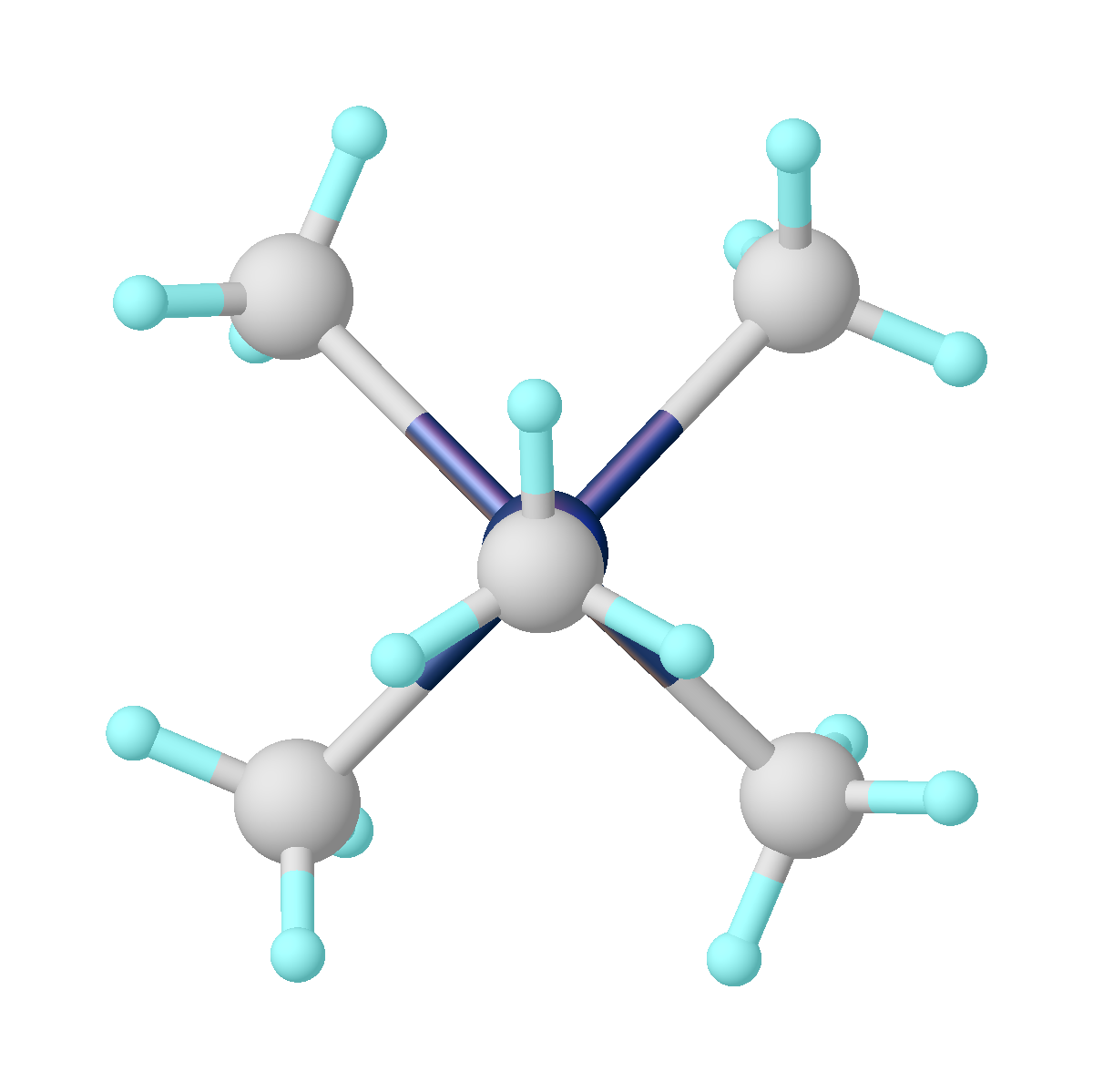
Molybdocene Dichloride
Molybdocene dichloride is the organomolybdenum compound with the formula (hapticity, η5-C5H5)2MoCl2 and IUPAC name dichlorobis(η5-cyclopentadienyl)molybdenum(IV), and is commonly abbreviated as Cp2MoCl2. It is a brownish-green air- and moisture-sensitive powder. In the research laboratory, it is used to prepare many derivatives. Preparation and structure The compound is prepared from molybdocene dihydride by treatment with chloroform: :(C5H5)2MoH2 + 2 CHCl3 → (C5H5)2MoCl2 + 2 CH2Cl2 The compound adopts a "clamshell" structure where the Cp rings are not parallel, the average Cp(centroid)-M-Cp angle being 130.6°. The two chloride ligands are cis, the Cl-Mo-Cl angle of 82° being narrower than in niobocene dichloride (85.6°), which in turn is less than in zirconacene dichloride (92.1°). This trend helped to establish the orientation of the HOMO in this class of complex. Uses Unlike the titanocene and zirconacene derivatives, the molybdocene compounds have yielded no commercia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdocene Dihydride
Molybdocene dihydride is the organomolybdenum compound with the formula ( η5-C5H5)2MoH2. Commonly abbreviated as Cp2MoH2, it is a yellow air-sensitive solid that dissolves in some organic solvents. The compound is prepared by combining molybdenum pentachloride, sodium cyclopentadienide, and sodium borohydride. The dihydride converts to molybdocene dichloride upon treatment with chloroform Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with formula C H Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to PTFE. It is also a precursor to various re .... The compound adopts a "clamshell" structure where the Cp rings are not parallel.K. Prout, T. S. Cameron, R. A. Forder, and in parts S. R. Critchley, B. Denton and G. V. Rees "The crystal and molecular structures of bent bis-π-cyclopentadienyl-metal complexes: (a) bis-π-cyclopentadienyldibromorhenium(V) tetrafluoroborate, (b) bis-π-cyclopent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(Mesitylene)molybdenum Tricarbonyl
(Mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl is an organomolybdenum compound derived from the aromatic compound mesitylene (1,3,5-trimethylbenzene) and molybdenum carbonyl. It exists as pale yellow crystals, which are soluble in organic solvents but decompose when in solution. It has been examined as a catalyst and reagent. Synthesis (Mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl arises from the reaction of molybdenum hexacarbonyl with hot mesitylene: :Mo(CO) + (CH)CH → Mo(CO) CH)CH+ 3 CO It can also be synthesized, with good yields by displacement of pyridine ligands of the trispyridine complex Mo(CO)(pyridine) in the presence of Lewis acids. This reaction proceeds at lower temperatures of the compound than the direct method :PyMo(CO) + (CH)CH + 3BF·O(CH) → CH)CHo(CO) + 3PyBF Structure and properties The mesitylene group is bonded to the molybdenum centre through delocalized π - electron ring. The aromaticity of the ligand is indicated by its ability to undergo Friedel-Crafts reactions, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Imido Complex
In coordination chemistry and organometallic chemistry, transition metal imido complexes is a coordination compound containing an imido ligand. Imido ligands can be terminal or bridging ligands. The parent imido ligand has the formula NH, but most imido ligands have alkyl or aryl groups in place of H. The imido ligand is generally viewed as a dianion, akin to oxide. Structural classes Complexes with terminal imido ligands In some terminal imido complexes, the M=N−C angle is 180° but often the angle is decidedly bent. Complexes of the type M=NH are assumed to be intermediates in nitrogen fixation by synthetic catalysts.Nugent, W. A.; Mayer, J. M., "Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds," J. Wiley: New York, 1988. 220px, Typical Schrock-style olefin metathesis catalyst features imides as spectator ligands.">spectator_ligand.html" ;"title="olefin metathesis catalyst features imides as spectator ligand">olefin metathesis catalyst features imides as spectator ligands. Complexes with bridg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansa Metallocene
An ''ansa''-metallocene is a type of organometallic compound containing two cyclopentadienyl ligands that are linked by a bridging group such that both cyclopentadienyl groups are bound to the same metal. The link prevents rotation of the cyclopentadienyl ligand and often modifies the structure and reactivity of the metal center. Some ansa-metallocenes are active in Ziegler-Natta catalysis, although none are used commercially. The term ''ansa''-metallocene (ansa being Greek for "handle") was coined by Lüttringhaus and Kullick to describe alkylidene-bridged ferrocenes, which were developed in the 1950s. Often ''ansa''-metallocenes are described in terms of the angle defined by the two Cp rings. In titanocene dichloride, this angle is 58.5° whereas in the ''ansa''-titanocene Me2Si(C5H4)2TiCl2 the angle is 51.2°. The prototypical linker groups are of the type (CH2)n where n = 1, 2, and 3. More easily installed are linker groups consisting of heteroatoms, e.g. (CH3)2Si. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Oxo Complex
A transition metal oxo complex is a coordination complex containing an oxo ligand. Formally O2-, an oxo ligand can be bound to one or more metal centers, i.e. it can exist as a terminal or (most commonly) as bridging ligands (Fig. 1). Oxo ligands stabilize high oxidation states of a metal.Nugent, W. A., Mayer, J. M. "Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds." John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1988. They are also found in several metalloproteins, for example in molybdenum cofactors and in many iron-containing enzymes. One of the earliest synthetic compounds to incorporate an oxo ligand is potassium ferrate (K2FeO4), which was likely prepared by Georg E. Stahl in 1702. Reactivity Olation and acid-base reactions A common reaction exhibited by metal-oxo compounds is olation, the condensation process that converts low molecular weight oxides to polymers with M-O-M linkages. Olation often begins with the deprotonation of a metal-hydroxo complex. It is the basis for mineralization and the precipita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olefin Metathesis
Olefin metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the relative simplicity of olefin metathesis, it often creates fewer undesired by-products and hazardous wastes than alternative organic reactions. For their elucidation of the reaction mechanism and their discovery of a variety of highly active catalysts, Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R. Schrock were collectively awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Catalysts The reaction requires metal catalysts. Most commercially important processes employ heterogeneous catalysts. The heterogeneous catalysts are often prepared by in-situ activation of a metal halides (MClx) using organoaluminium or organotin compounds, e.g. combining MClx–EtAlCl2. A typical catalyst support is alumina. Commercial catalysts are often based on molybdenum and ruthenium. Well-defined organometallic comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentadienylmolybdenum Tricarbonyl Dimer
Cyclopentadienylmolybdenum tricarbonyl dimer is the chemical compound with the formula Cp2Mo2(CO)6, where Cp is C5H5. A dark red solid, it has been the subject of much research although it has no practical uses. Structure and synthesis The molecule exists in two rotamers, gauche and anti. The six CO ligands are terminal and the Mo-Mo bond distance is 3.2325 Å. The compound is prepared by treatment of molybdenum hexacarbonyl with sodium cyclopentadienide followed by oxidation of the resulting NaMo(CO)3(C5H5). Other methods have been developed starting with Mo(CO)3(CH3CN)3 instead of Mo(CO)6. Reactions Thermolysis of this compound in hot solution of diglyme (bis(2-methoxyethyl)ether) results in decarbonylation, giving the tetracarbonyl, which has a formal triple bond between the Mo centers (''d''MoMo = 2.448 Å):Cotton, F. A.; Walton, R. A. "Multiple Bonds Between Metal Atoms" Oxford (Oxford): 1993, p 564ff. . :(C5H5)2Mo2(CO)6 → (C5H5)2Mo2(CO)4 + 2 CO The resulting cyclopenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |