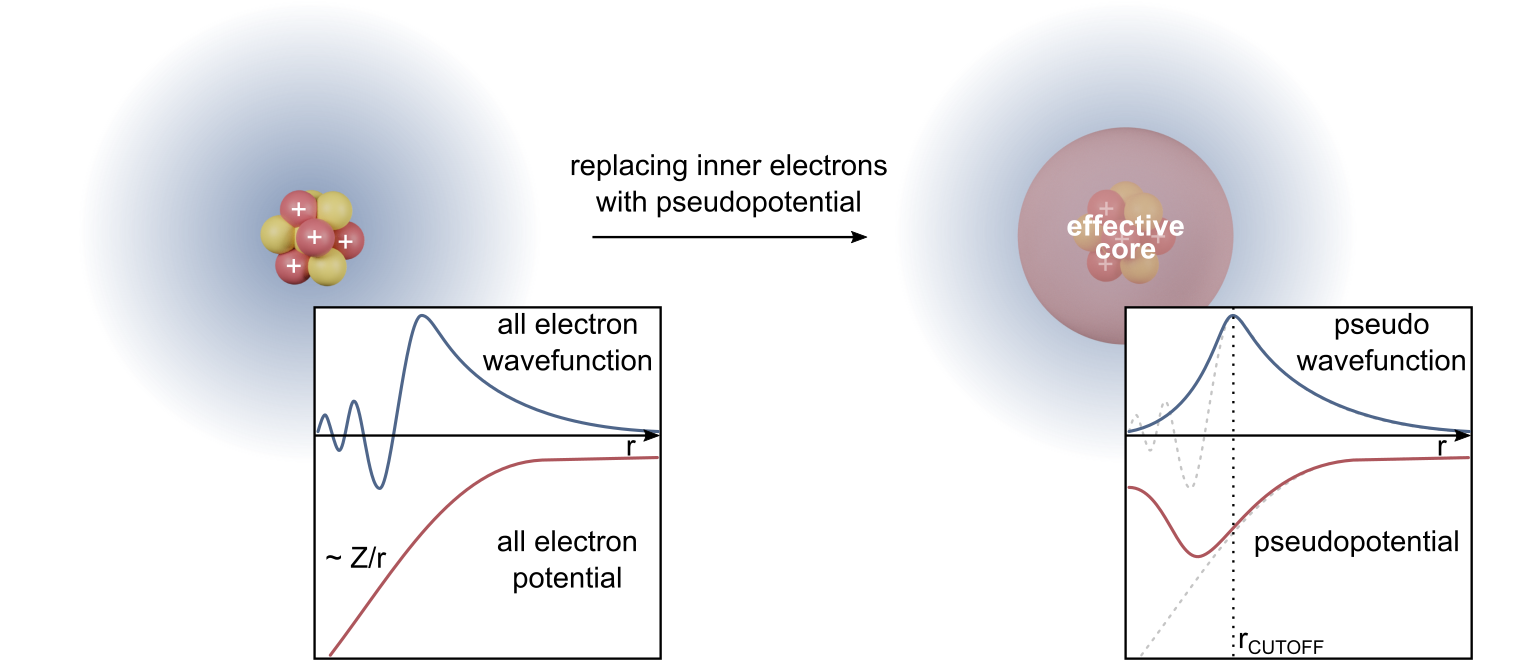
|
Optimized Effective Potential Method
The optimized effective potential method (OEP) in Kohn-Sham (KS) density functional theory (DFT) is a method to determine the potentials as functional derivatives of the corresponding KS orbital-dependent energy density functionals. This can be in principle done for any arbitrary orbital-dependent functional, but is most common for exchange energy as the so-called exact exchange method (EXX), which will be considered here. Origin The OEP method was developed more than 10 years prior to the work of Pierre Hohenberg, Walter Kohn and Lu Jeu Sham in 1953 by R. T. Sharp and G. K. Horton in order to investigate, what happens to Hartree-Fock (HF) theory when, instead of the regular nonlocal exchange potential, a local exchange potential is demanded. Much later after 1990 it was found out that this ''ansatz'' is useful in density functional theory. Background via chain rule In density functional theory the exchange correlation (xc) potential is defined as the functional derivativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local-density Approximation
Local-density approximations (LDA) are a class of approximations to the exchange–correlation (XC) energy functional in density functional theory (DFT) that depend solely upon the value of the electronic density at each point in space (and not, for example, derivatives of the density or the Kohn–Sham orbitals). Many approaches can yield local approximations to the XC energy. However, overwhelmingly successful local approximations are those that have been derived from the homogeneous electron gas (HEG) model. In this regard, LDA is generally synonymous with functionals based on the HEG approximation, which are then applied to realistic systems (molecules and solids). In general, for a spin-unpolarized system, a local-density approximation for the exchange-correlation energy is written as :E_^rho= \int \rho(\mathbf)\epsilon_(\rho(\mathbf))\ \mathrm\mathbf\ , where ''ρ'' is the electronic density and ''єxc'' is the exchange-correlation energy per particle of a homogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulations to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry incorporated into computer programs to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. The importance of this subject stems from the fact that, with the exception of some relatively recent findings related to the hydrogen molecular ion (dihydrogen cation), achieving an accurate quantum mechanical depiction of chemical systems analytically, or in a closed form, is not feasible. The complexity inherent in the many-body problem exacerbates the challenge of providing detailed descriptions of quantum mechanical systems. While computational results normally complement information obtained by chemical experiments, it can occasionally predict unobserved chemical phenomena. Overview Computational chemistry differs from theoretical chemistry, which involves a mathematical description of chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Functional Theory
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals - that is, functions that accept a function as input and output a single real number. In the case of DFT, these are functionals of the spatially dependent electron density. DFT is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry. DFT has been very popular for calculations in solid-state physics since the 1970s. However, DFT was not considered accurate enough for calculations in quantum chemistry until the 1990s, when the approximations used in the theory were greatly refined to better m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condition Number
In numerical analysis, the condition number of a function measures how much the output value of the function can change for a small change in the input argument. This is used to measure how sensitive a function is to changes or errors in the input, and how much error in the output results from an error in the input. Very frequently, one is solving the inverse problem: given f(x) = y, one is solving for ''x,'' and thus the condition number of the (local) inverse must be used. The condition number is derived from the theory of propagation of uncertainty, and is formally defined as the value of the asymptotic worst-case relative change in output for a relative change in input. The "function" is the solution of a problem and the "arguments" are the data in the problem. The condition number is frequently applied to questions in linear algebra, in which case the derivative is straightforward but the error could be in many different directions, and is thus computed from the geometry of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Of Convergence
In mathematical analysis, particularly numerical analysis, the rate of convergence and order of convergence of a sequence that converges to a limit are any of several characterizations of how quickly that sequence approaches its limit. These are broadly divided into rates and orders of convergence that describe how quickly a sequence further approaches its limit once it is already close to it, called asymptotic rates and orders of convergence, and those that describe how quickly sequences approach their limits from starting points that are not necessarily close to their limits, called non-asymptotic rates and orders of convergence. Asymptotic behavior is particularly useful for deciding when to stop a sequence of numerical computations, for instance once a target precision has been reached with an iterative root-finding algorithm, but pre-asymptotic behavior is often crucial for determining whether to begin a sequence of computations at all, since it may be impossible or imprac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as :a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b, linear maps such as :(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n, and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathematics), matrices. Linear algebra is central to almost all areas of mathematics. For instance, linear algebra is fundamental in modern presentations of geometry, including for defining basic objects such as line (geometry), lines, plane (geometry), planes and rotation (mathematics), rotations. Also, functional analysis, a branch of mathematical analysis, may be viewed as the application of linear algebra to Space of functions, function spaces. Linear algebra is also used in most sciences and fields of engineering because it allows mathematical model, modeling many natural phenomena, and computing efficiently with such models. For nonlinear systems, which cannot be modeled with linear algebra, it is often used for dealing with first-order a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basis Set (chemistry)
In theoretical chemistry, theoretical and computational chemistry, a basis set is a set of Function (mathematics), functions (called basis functions) that is used to represent the Wave function, electronic wave function in the Hartree–Fock method or Density functional theory, density-functional theory in order to turn the partial differential equations of the model into algebraic equations suitable for efficient implementation on a computer. The use of basis sets is equivalent to the use of an approximate resolution of the identity: the Atomic orbital, orbitals , \psi_i\rangle are expanded within the basis set as a linear combination of the basis functions , \psi_i\rangle \approx \sum_\mu c_ , \mu\rangle, where the expansion coefficients c_ are given by c_ = \sum_\nu \langle \mu, \nu \rangle^ \langle \nu , \psi_i \rangle. The basis set can either be composed of atomic orbitals (yielding the linear combination of atomic orbitals approach), which is the usual choice within the qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral
In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a Summation, sum, which is used to calculate area, areas, volume, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental operations of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. the other being Derivative, differentiation. Integration was initially used to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under a curve, or determining displacement from velocity. Usage of integration expanded to a wide variety of scientific fields thereafter. A definite integral computes the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the Graph of a function, graph of a given Function (mathematics), function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal Coordinate axis, axis of the plane are positive while areas below are n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green's Function
In mathematics, a Green's function (or Green function) is the impulse response of an inhomogeneous linear differential operator defined on a domain with specified initial conditions or boundary conditions. This means that if L is a linear differential operator, then * the Green's function G is the solution of the equation where \delta is Dirac's delta function; * the solution of the initial-value problem L y = f is the convolution Through the superposition principle, given a linear ordinary differential equation (ODE), one can first solve for each , and realizing that, since the source is a sum of delta functions, the solution is a sum of Green's functions as well, by linearity of . Green's functions are named after the British mathematician George Green, who first developed the concept in the 1820s. In the modern study of linear partial differential equations, Green's functions are studied largely from the point of view of fundamental solutions instead. Under many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory (quantum Mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, perturbation theory is a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one. The idea is to start with a simple system for which a mathematical solution is known, and add an additional "perturbing" Hamiltonian representing a weak disturbance to the system. If the disturbance is not too large, the various physical quantities associated with the perturbed system (e.g. its energy levels and eigenstates) can be expressed as "corrections" to those of the simple system. These corrections, being small compared to the size of the quantities themselves, can be calculated using approximate methods such as asymptotic series. The complicated system can therefore be studied based on knowledge of the simpler one. In effect, it is describing a complicated unsolved system using a simple, solvable system. Approximate Hamiltonians Perturbation theory is an important tool for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermitian Adjoint
In mathematics, specifically in operator theory, each linear operator A on an inner product space defines a Hermitian adjoint (or adjoint) operator A^* on that space according to the rule :\langle Ax,y \rangle = \langle x,A^*y \rangle, where \langle \cdot,\cdot \rangle is the inner product on the vector space. The adjoint may also be called the Hermitian conjugate or simply the Hermitian after Charles Hermite. It is often denoted by in fields like physics, especially when used in conjunction with bra–ket notation in quantum mechanics. In dimension (vector space), finite dimensions where operators can be represented by Matrix (mathematics), matrices, the Hermitian adjoint is given by the conjugate transpose (also known as the Hermitian transpose). The above definition of an adjoint operator extends verbatim to bounded operator, bounded linear operators on Hilbert spaces H. The definition has been further extended to include unbounded ''Densely defined operator, densely def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |