|
Ophthalmosaurinae
Ophthalmosaurinae is an extinct subfamily of ophthalmosaurid thunnosaur ichthyosaurs from the Middle Jurassic to the late Early Cretaceous (Bajocian - Albian) of Europe, North America and South America. Currently, the oldest and the basalmost, known ophthalmosaurine is ''Mollesaurus'' from the early Bajocian of Argentina. Ophthalmosaurines were characterized by a large extracondylar area of the basioccipital in the form of a thick and concave peripheral band, posterodistally deflected ulnar facet of the humerus, large ulna with concave and edgy posterior surface and ischiopubis with obturator foramen. Phylogeny Ophthalmosaurinae was named in 1887 by Georg Baur. It is a stem-based taxon defined phylogenetically for the first time by Fischer ''et al.'' (2012) as "all taxa closer to ''Ophthalmosaurus icenicus'' than to '' Platypterygius hercynicus''". The cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in clad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acamptonectes
''Acamptonectes'' is a genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaurs, a type of dolphin-like marine reptiles, that lived during the Early Cretaceous around 130 million years ago. The first specimen, a partial adult skeleton, was discovered in Speeton, England, in 1958, but was not formally described until 2012 by Valentin Fischer and colleagues. They also recognised a partial juvenile (organism), subadult skeleton belonging to the genus from Cremlingen, Germany, and specimens from other localities in England. The genus contains the single species ''Acamptonectes densus''; the generic name means "rigid swimmer" and the specific name means "compact" or "tightly packed". A small ichthyosaur, ''Acamptonectes'' is estimated to have been long. The Generic name (biology), generic name refers to unusual adaptations in the body of ''Acamptonectes'' that made its trunk rigid, including tightly fitting bones in the occiput (back and lower part of the skull) and interlocking vertebral centra ("bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmosaurid
Ophthalmosauridae is an extinct family of thunnosaur ichthyosaurs from the Middle Jurassic to the early Late Cretaceous (Bajocian - Cenomanian) worldwide. Almost all ichthyosaurs from the Middle Jurassic onwards belong to the family, until the extinction of ichthyosaurs in the early Late Cretaceous. Ophthalmosaurids appeared worldwide during early Bajocian, subsequent to the disappearance of most other ichthyosaur lineages after the end of the Toarcian. Currently, the oldest known ophthalmosaurids is '' Mollesaurus'' from the early Bajocian of Argentina, as well as indeterminate remains of the same age from Luxembourg and Canada. Named by George H. Baur, in 1887, the family contains the basal taxa like ''Ophthalmosaurus''. Appleby (1956) named the taxon Ophthalmosauria which was followed by some authors, but these two names are often treated as synonyms; Ophthalmosauridae has the priority over Ophthalmosauria. However, some researchers argue that Ophthalmosauridae should be restri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
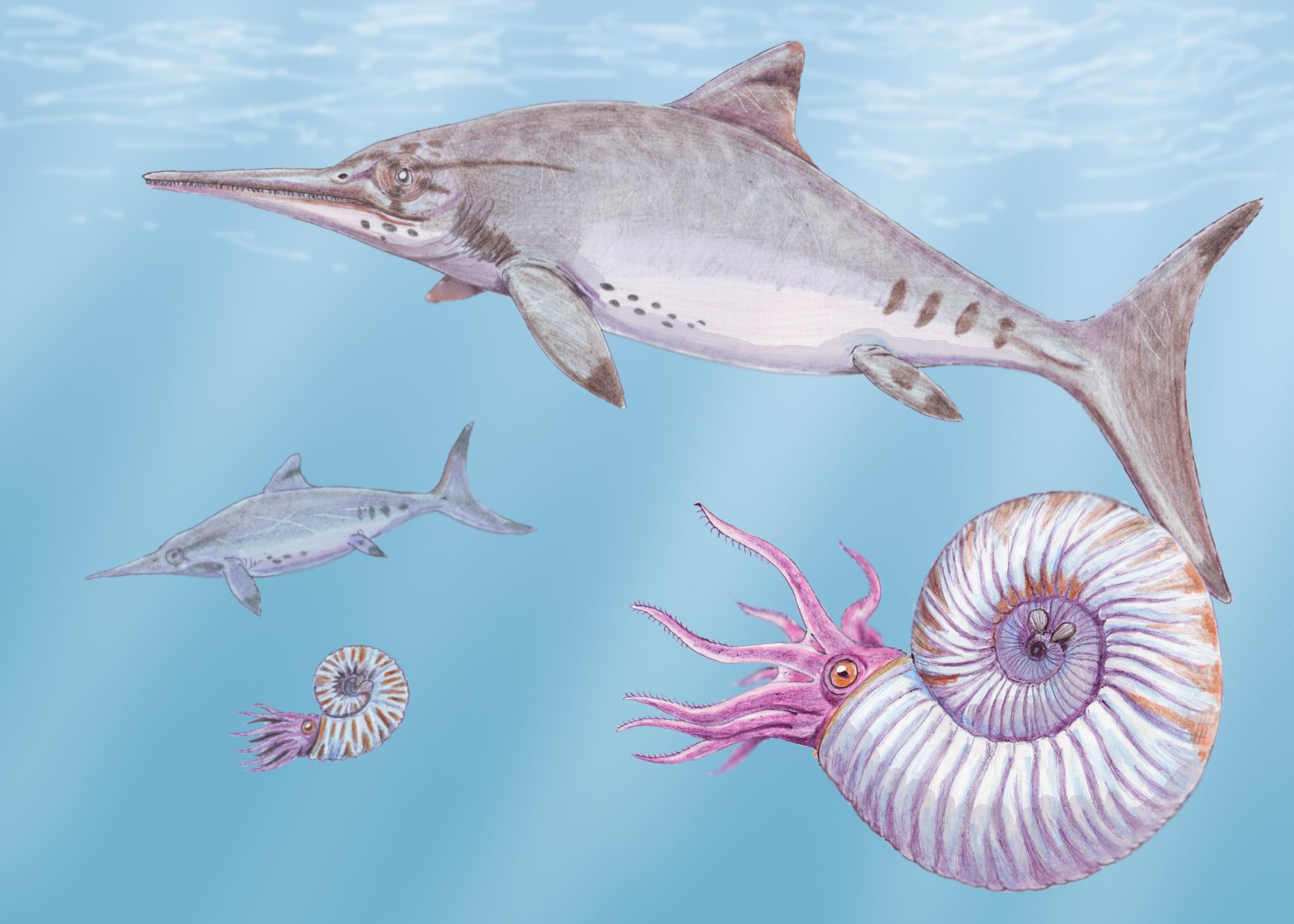
Ophthalmosaurus Icenicus
''Ophthalmosaurus'' (Greek ὀφθάλμος ''ophthalmos'' 'eye' and σαῦρος ''sauros'' 'lizard') is a genus of ichthyosaur known from the Middle-Late Jurassic. Possible remains from the earliest Cretaceous, around 145 million years ago, are also known. It was a relatively medium-sized ichthyosaur, measuring long and weighing . Named for its extremely large eyes, it had a jaw containing many small but robust teeth. Major fossil finds of this genus have been recorded in Europe with a second species possibly being found in North America. Description ''Ophthalmosaurus'' was a medium-sized ichthyosaur, growing to measure in length and weighing between . It had a robust, streamlined body that was nearly as wide as it was tall in frontal view. Like other derived ichthyosaurs ''Ophthalmosaurus'' had a powerful tail ending in a pronounced bi-lobed caudal fluke whose lower half was formed around the caudal spine whereas the upper lobe was made up entirely from soft tissue. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollesaurus
''Mollesaurus'' is an extinct genus of large ophthalmosaurine ichthyosaur known from northwestern Patagonia of Argentina. Etymology ''Mollesaurus'' was named by Marta S. Fernández in 1999 and the type species is ''Mollesaurus periallus''. The generic name is derived from the name of the Los Molles Formation, where the holotype was collected, and ''sauros'', Greek for "lizard". The specific name is derived from ''periallos'', Greek for "before all others", in reference to the fact that it is the oldest ophthalmosaurid and one of the oldest thunnosaurs. History of study ''Mollesaurus'' is known from the holotype MOZ 2282 V, articulated partial skeleton which preserved partial skull and most of the vertebral column. It was collected in the Chacaico Sur locality from the ''Emileia giebeli'' ammonoid zone of the Los Molles Formation, Cuyo Group, dating to the early Bajocian stage of the Middle Jurassic, about 171.6-170 million years ago. ''Mollesaurus'', along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassodraco
''Thalassodraco'' (meaning "sea dragon") is an extinct genus of ophthalmosauridae, ophthalmosaurid Ichthyosauria, ichthyosaur from the Late Jurassic (Tithonian) Kimmeridge Clay Formation of England. The type species, ''T. etchesi'', was named in 2020, with the epithet in honour of the discoverer of the holotype, Steve Etches. Discovery and naming The holotype, MJML K1885 and the isolated slab MJML K1886, and referred specimen, MJML K1174, were discovered by plumber turned Paleontology, palaeontologist Steve Etches in 2009 and he added it to his personal fossil collection. He put the fossil on display alongside the rest of his collection when his museum, The Etches Collection, opened to the public in 2016. According to Jacobs & Martill (2020), Etches' museum contains "''many ichthyosaurs, including several articulated specimens and numerous isolated skull bones, vertebrae, girdle elements and fore and hind limbs. The majority of these specimens remain unstudied and several appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptanodon
''Baptanodon'' is an ichthyosaur of the Late Jurassic period (160-156 million years ago), named for its supposed lack of teeth (although teeth of this genus have since been discovered). It had a graceful long dolphin-shaped body, and its jaws were well adapted for catching squid. Major fossil finds of this genus have been recorded in North America. The type species, ''Sauranodon natans'', was originally included under ''Sauranodon'' in 1879,O. C. Marsh. 1879. A new order of extinct reptiles (Sauranodonta), from the Jurassic Formation of the Rocky Mountains. ''The American Journal of Science and Arts, series 3'' but this name was preoccupied. Discovery and species ''Baptanodon'' is a replacement name for ''Sauranodon'' applied to ichthyosaur material in 1879 and was moved to its own genus ''Baptanodon'' in 1880 when ''Sauranodon'' was found to be preoccupied. ''Baptanodon'' was considered a junior synonym of ''Ophthalmosaurus'' by Maisch & Matzke (2000).Maisch MW, Matzke AT. 2000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gengasaurus
''Gengasaurus'' is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur from the Jurassic. The type and only species, ''Gengasaurus nicosiai'', was named in 2017, after the locality of Genga, Marche. It lived in Italy about 152 million years ago. History The near complete holotype was discovered in 1976 in the Late Jurassic (Tithonian In the geological timescale, the Tithonian is the latest age (geology), age of the Late Jurassic Epoch and the uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 149.2 ±0.7 annum, Ma and 143.1 ±0.6 (mi ...) Calcari ad aptici e Saccocoma Formation at Camponocecchio and it was described in 1980 and 2000 as the "Genga ichthyosaur" before it was named and described in 2016Ilaria Paparella, Erin E. Maxwell, Angelo Cipriani, Scilla Roncacè and Michael W. Caldwell (2016) - The first ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur from the Upper Jurassic of the Umbrian–Marchean Apennines (Marche, Central Italy). ''Geological Maga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nannopterygius
''Nannopterygius'' (meaning "small wing/flipper" in Greek) is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur that lived during the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous (Callovian to Berriasian stages). Fossils are known from England, Kazakhstan, Russia, and NorwayMcGowan, C. & Motani, R. (2003). ''Ichthyopterygia''. ''In'' Sues, H.-D. Handbook of Paleoherpetology, vol. 8. Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil, Munich, 175 pp., 19pls. and six species are currently assigned to the genus. Description ''Nannopterygius'' was small for an ichthyosaur, measuring up to long at maximum. About of this was tail, including a deeply forked and probably homocercal caudal fin. The head is long, with a typical long narrow rostrum. The eyes are large, hence its classification as an ophthalmosaurid, and have a bony sclerotic ring inside the eye socket. There are at least 60 disc-shaped vertebrae, although owing to the condition of the fossil it is not possible to tell exactly how many there were, show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platypterygius Hercynicus
''Platypterygius'' is a historically paraphyletic genus of platypterygiine ichthyosaur from the Cretaceous period. It was historically used as a wastebasket taxon, and most species within ''Platypterygius'' likely are undiagnostic at the genus or species level, or represent distinct genera, even being argued as invalid. While fossils referred to ''Platypterygius'' have been found throughout different continents, the holotype specimen was found in Germany. Description As ''Platypterygius'' contains multiple species not especially close to each other, little can be said in terms of shared characteristics. According to an analysis by Fischer (2012), all anatomical features used to unify ''Platypterygius'' species are either not actually present in each species, or much more widespread among unrelated ophthalmosaurs. Generally, species referred to this genus were large bodied macropredators based on their robust dentition. This is also supported by ''P. australis'' having been foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropterygius
''Arthropterygius'' is a widespread genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur which existed in Canada, Norway, Russia, and Argentina from the late Jurassic period and possibly to the earliest Cretaceous. Description ''Arthropterygius'' appears to have been a relatively large ichthyosaur, with all species measuring between long. The partially preserved specimen PMO 222.655 has been estimated at based on comparisons to the contemporary ophthalmosauridae, ophthalmosaurid ''Undorosaurus''. This specimen was probably mature or close to maturity at time of death, judging by the convex head of the humerus and the smooth texture of the humeral shaft. Skull and axial skeleton The skull of ''Arthropterygius'' has become well known due to the discovery of a well preserved skull from Svalbard. It is unusual among ichthyosaurs in having a very short, yet also robust rostrum for its skull length. As a result, the orbit appears very large (about 0.34× the skull length). The skull bears a very l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |