|
Operation Backfire (WWII)
Operation Backfire was a military scientific operation of Allies of World War II, the Western Allies during and after the World War II, Second World War that was performed mainly by British personnel. The operation was designed to completely evaluate the entire V-2 rocket assembly, interrogate German personnel specialized in all phases of it, and then to test and launch missiles across the North Sea. Background With the end of the war, the Allies scrambled to acquire German technology. Several military operations had been previously mounted by the British to complete this task, including the Fedden Mission and Operation Surgeon. With the consent of U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower, Operation Backfire was orchestrated by Major Robert Staver of the Rocket Section of the Research and Development branch of the Ordnance Office, which had been tasked in directing the effort to find and interrogate the German rocket specialists who had built the V-2. Since 30 April 1945, Major Staver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
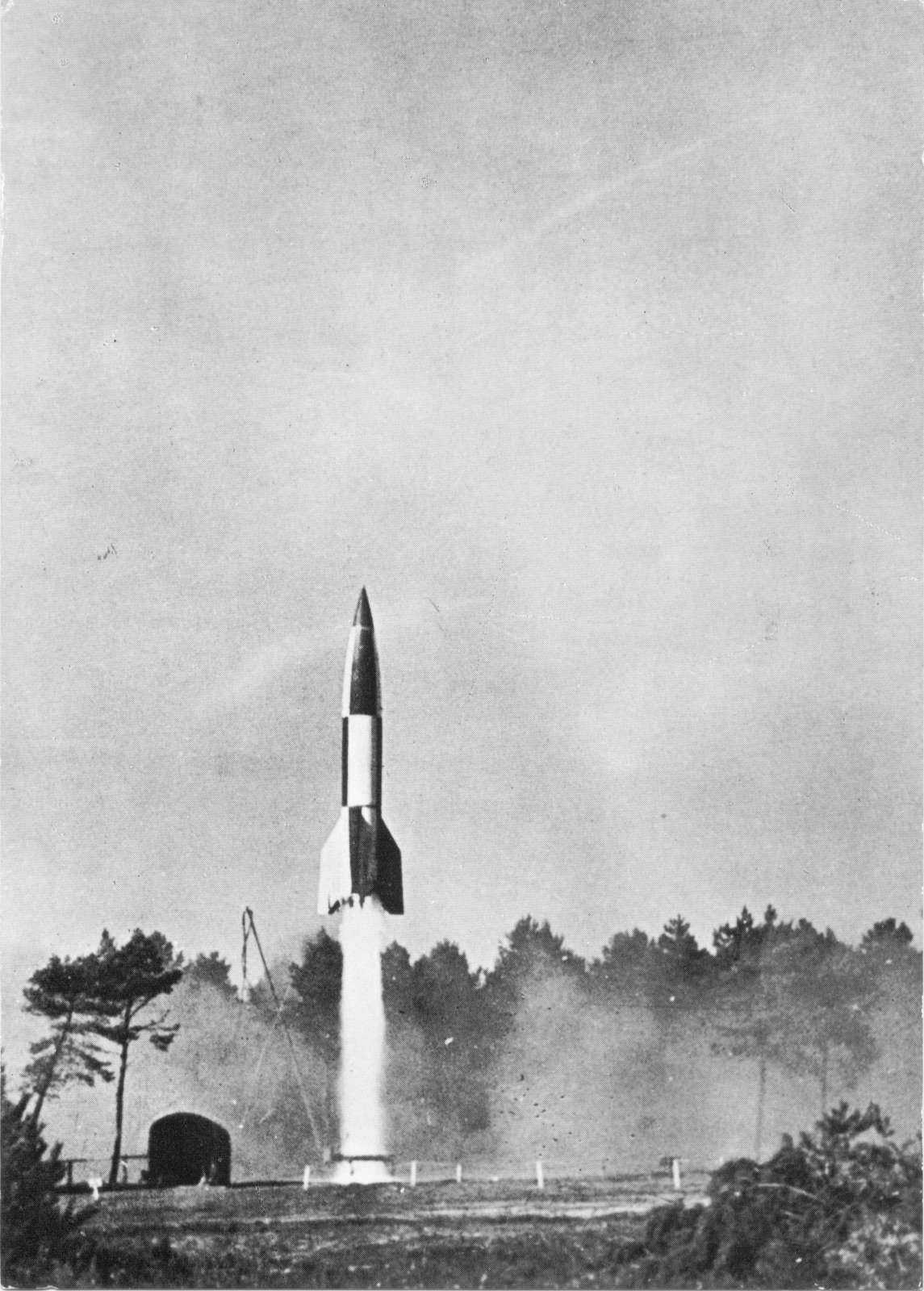
V-2 Lift-off
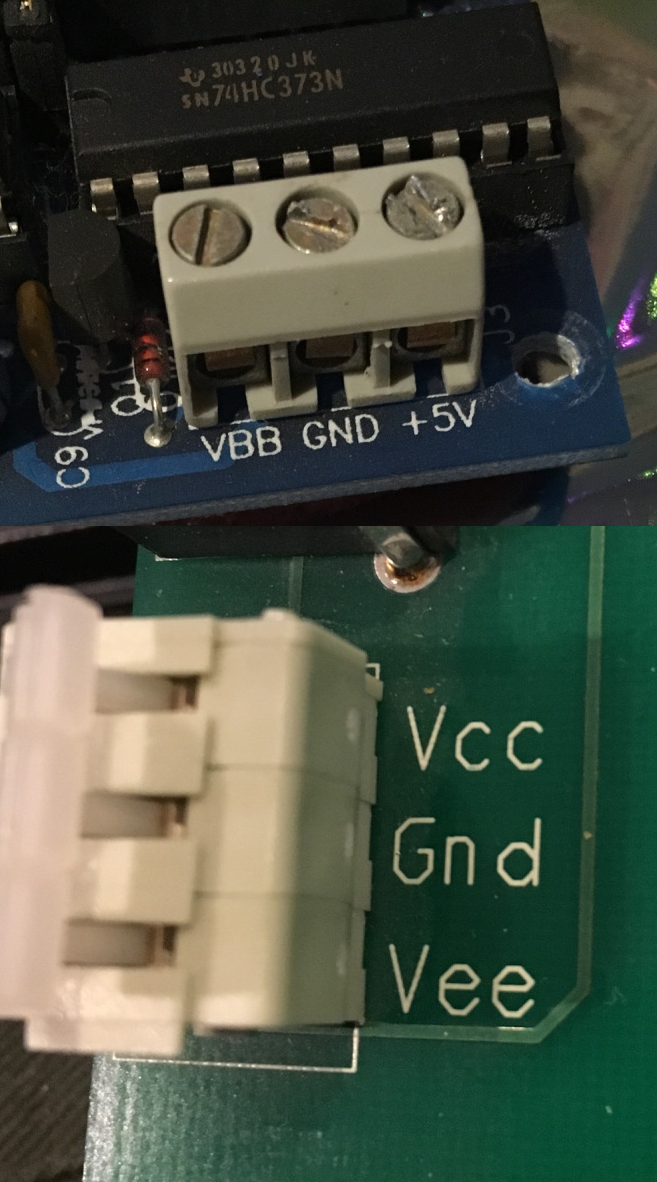
IC power-supply pins are voltage and current supply terminals found on integrated circuits (ICs) in electrical engineering, electronic engineering, and integrated circuit design. ICs have at least two pins that connect to the power supply rail, power rails of the circuit in which they are installed. These are known as the power-supply pins. However, the labeling of the pins varies by IC family and manufacturer. The double-subscript notation usually corresponds to a first letter in a given IC family (transistors) notation of the terminals (e.g. VDD supply for a drain terminal in FETs etc.). The simplest labels are V+ and V−, but internal design and historical traditions have led to a variety of other labels being used. V+ and V− may also refer to the non-inverting (+) and inverting (−) voltage inputs of ICs like op amps. For power supplies, sometimes one of the supply rails is referred to as Ground (electricity), ground (abbreviated "GND") positive and negative voltages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordhausen, Thuringia
Nordhausen () is a city in Thuringia, Germany. It is the capital of the Nordhausen (district), Nordhausen district and the urban centre of northern Thuringia and the southern Harz region; its population is 42,000. Nordhausen is located approximately north of Erfurt, west of Halle (Saale), Halle, south of Braunschweig and east of Göttingen. Nordhausen was first mentioned in records in the year 927 and became one of the most important cities in central Germany during the later Middle Ages. The city is situated on the Zorge (river), Zorge river, a tributary of the Helme (river), Helme within the fertile region of Goldene Aue ''(golden floodplain)'' at the southern edge of the Harz mountains. In the early 13th century, it became a free imperial city, so that it was an independent and republican self-ruled member of the Holy Roman Empire. Due to its long-distance trade, Nordhausen was prosperous and influential, with a population of 8,000 around 1500. It was the third-largest cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II Intelligence Operations
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research And Development In Nazi Germany
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, economic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II Guided Missiles Of Germany
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remnants Of Launchpads In Germany
In Germany, military test rockets were launched in Peenemünde (including Greifswalder Oie) and Cuxhaven, and larger non-military rockets were launched in Hespenbusch, Cuxhaven and Zingst. In World War II, A4-rockets were also launched as weapons from several western areas of Germany. Several launchpads were also constructed for the Bachem Ba 349 (also known as Natter), developed in 1944/45. Peenemünde From Test stand VII, the most important launchpad for test rockets in Peenemünde, the mud wall, the channel for static tests, the concrete slab used for launches and some remains of the assembly hall still exist. The area is not open to tourists. Greifswalder Oie From the former launchpad, a piece of rail and the former observation shelter still exist. The area is open to tourists. Cuxhaven In the area of Cuxhaven, a launchpad was constructed only for Operation Backfire. Launches for other operations in this area were made from mobile pads. A trench and some shelter rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Paperclip
The Operation Paperclip was a secret United States intelligence program in which more than 1,600 German scientists, engineers, and technicians were taken from former Nazi Germany to the US for government employment after the end of World War II in Europe, between 1945 and 1959; several were confirmed to be former members of the Nazi Party, including the SS or the Sturmabteilung, SA. The effort began in earnest in 1945, as the Allies advanced into Germany and discovered a wealth of scientific talent and advanced research that had contributed to Germany's wartime technological advancements. The US Joint Chiefs of Staff officially established Operation Overcast (operations "Overcast" and "Paperclip" were related, and the terms are often used interchangeably) on July 20, 1945, with the dual aims of leveraging German expertise for the ongoing war effort against Japan and to bolster US postwar military research. The operation, conducted by the Joint Intelligence Objectives Agency (JI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Rudolph
Arthur Louis Hugo Rudolph (November 9, 1906 – January 1, 1996) was a German rocket engineer who was a leader of the effort to develop the V-2 rocket for Nazi Germany. After World War II, the United States government's Office of Strategic Services (OSS) brought him to the U.S. as part of the clandestine Operation Paperclip, where he became one of the main developers of the U.S. space program. He worked within the U.S. Army and NASA, where he managed the development of several systems, including the Pershing missile and the Saturn V Moon rocket. In 1984, the U.S. government investigated him for war crimes, and he agreed to renounce his United States citizenship and leave the U.S. in return for not being prosecuted. Early life Rudolph was born in Stepfershausen, Meiningen, Germany, in 1906. His family were farmers, with a long tradition in the area. His father Gustav died in 1915 while serving in World War I. Arthur and his younger brother Walter were raised by their mother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-2 Rocket On Meillerwagen
IC power-supply pins are voltage and current supply terminals found on integrated circuits (ICs) in electrical engineering, electronic engineering, and integrated circuit design. ICs have at least two pins that connect to the power rails of the circuit in which they are installed. These are known as the power-supply pins. However, the labeling of the pins varies by IC family and manufacturer. The double-subscript notation usually corresponds to a first letter in a given IC family (transistors) notation of the terminals (e.g. VDD supply for a drain terminal in FETs etc.). The simplest labels are V+ and V−, but internal design and historical traditions have led to a variety of other labels being used. V+ and V− may also refer to the non-inverting (+) and inverting (−) voltage inputs of ICs like op amps. For power supplies, sometimes one of the supply rails is referred to as ground (abbreviated "GND") positive and negative voltages are relative to the ground. In digita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-Force
T-Force was the operational arm of a joint US Army–British Army mission to secure German scientific and industrial technology before it could be destroyed by retreating German forces or looters during the final stages of the Second World War and its aftermath. Key personnel were also to be seized and targets of opportunity exploited when encountered. The effort was a business and technology-oriented parallel of sorts to the Monuments Men pursuit of art and financial treasure. The program was designed to loot German intellectual assets and impede its ability to compete in the postwar political and economic spheres while giving a boost to the nations conducting it.''The Guardian''"How T-Force abducted Germany's best brains for Britain"/ref> Though unacknowledged at the time, the T-Force mission also included preventing advanced Nazi technology from falling into the hands of the Soviet Union—destroying whatever could not be seized and spirited away before Red Army troops arriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining Orientation (geometry), orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, due to the angular momentum#Conservation of angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged Vibrating structure gyroscope#MEMS gyroscopes, MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring laser gyroscope, ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |