|
Open System (systems Theory)
An open system is a system that has external interactions. Such interactions can take the form of information, energy, or material transfers into or out of the system boundary, depending on the discipline which defines the concept. An open system is contrasted with the concept of an isolated system which exchanges neither energy, matter, nor information with its environment. An open system is also known as a flow system. The concept of an open system was formalized within a framework that enabled one to interrelate the theory of the organism, thermodynamics, and evolutionary theory. This concept was expanded upon with the advent of information theory and subsequently systems theory. Today the concept has its applications in the natural and social sciences. In the natural sciences an open system is one whose border is permeable to both energy and mass. By contrast, a closed system is permeable to energy but not to matter. The definition of an open system assumes that there a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praxis Intervention
Praxis intervention is a form of participatory action research that emphasizes working on the praxis potential, or phronesis, of its participants. This contrasts with other forms of participatory action research, which emphasize the collective modification of the external world. ''Praxis potential'' means the members' potential to reflexively work on their respective mentalities; ''participant'' here refers not just to the clientele beneficiaries of the praxis intervention project, but also the organisers and experts participating in such a project. Praxis intervention is intended to lead its members through a "participant objectivation". The method prioritizes unsettling the settled mentalities, especially where the settled mindsets prevalent in the social world or individuals is suspected to have sustained or contributed to their suffering or marginality. Reflexive and routine praxis Karl Marx conceptualized praxis in two forms: reflexive and non-reflexive. The reflexive p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or religious organization, organizations, that generally relate humanity to supernatural, transcendence (religion), transcendental, and spirituality, spiritual elements—although there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. It is an essentially contested concept. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacredness, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). and a supernatural being or beings. The origin of religious belief is an open question, with possible explanations including awareness of individual death, a sense of community, and dreams. Religions have sacred histories, narratives, and mythologies, preserved in oral traditions, sac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology Of Religion
Sociology of religion is the study of the beliefs, practices and organizational forms of religion using the tools and methods of the discipline of sociology. This objective investigation may include the use both of Quantitative research, quantitative methods (surveys, polls, demographic and census analysis) and of Qualitative research, qualitative approaches (such as participant observation, interviewing, and analysis of archival, historical and documentary materials). Modern sociology as an academic discipline began with the analysis of religion in Émile Durkheim's 1897 suicide (Durkheim book), study of suicide rates among Catholic Church, Catholic and Protestantism, Protestant populations, a foundational work of social research which served to distinguish sociology from other disciplines, such as psychology. The works of Karl Marx (1818–1883) and Max Weber (1864–1920) emphasized the relationship between religion and the economic system, economic or social structure of soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niklas Luhmann
Niklas Luhmann (; ; December 8, 1927 – November 11, 1998) was a German sociologist, philosopher of social science, and systems theorist. Niklas Luhmann is one of the most influential German sociologists of the 20th century. His thinking was based on the philosophical tradition and at the same time the reception of a wide variety of concepts from modern science. From this foundation he developed a functionalist-oriented systems theory, which claims to be able to describe all social phenomena in a theoretically consistent language. Social systems are understood as communication contexts that have autonomy from the actors involved in them. On this basis, three types of social systems can be distinguished: interaction, organization and society. On his general theory he developed a social theory, which describes modern society as a global society that is characterized by an internal differentiation into various autonomously working ''functional areas'' such as politics, la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talcott Parsons
Talcott Parsons (December 13, 1902 – May 8, 1979) was an American sociologist of the classical tradition, best known for his social action theory and structural functionalism. Parsons is considered one of the most influential figures in sociology in the 20th century. After earning a PhD in economics, he served on the faculty at Harvard University from 1927 to 1973. In 1930, he was among the first professors in its new sociology department. Later, he was instrumental in the establishment of the Department of Social Relations at Harvard. Based on empirical data, Parsons' social action theory was the first broad, systematic, and generalizable theory of social systems developed in the United States and Europe. Some of Parsons' largest contributions to sociology in the English-speaking world were his translations of Max Weber's work and his analyses of works by Weber, Émile Durkheim, and Vilfredo Pareto. Their work heavily influenced Parsons' view and was the foundation for hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Functionalism
Structural functionalism, or simply functionalism, is "a framework for building theory that sees society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability". This approach looks at society through a macro-level orientation, which is a broad focus on the social structures that shape society as a whole, and believes that society has evolved like organisms. This approach looks at both social structure and social functions. Functionalism addresses society as a whole in terms of the function of its constituent elements; namely norms, customs, traditions, and institutions. A common analogy called the organic or biological analogy, popularized by Herbert Spencer, presents these parts of society as human body "organs" that work toward the proper functioning of the "body" as a whole. In the most basic terms, it simply emphasizes "the effort to impute, as rigorously as possible, to each feature, custom, or practice, its effect on the functioning of a suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
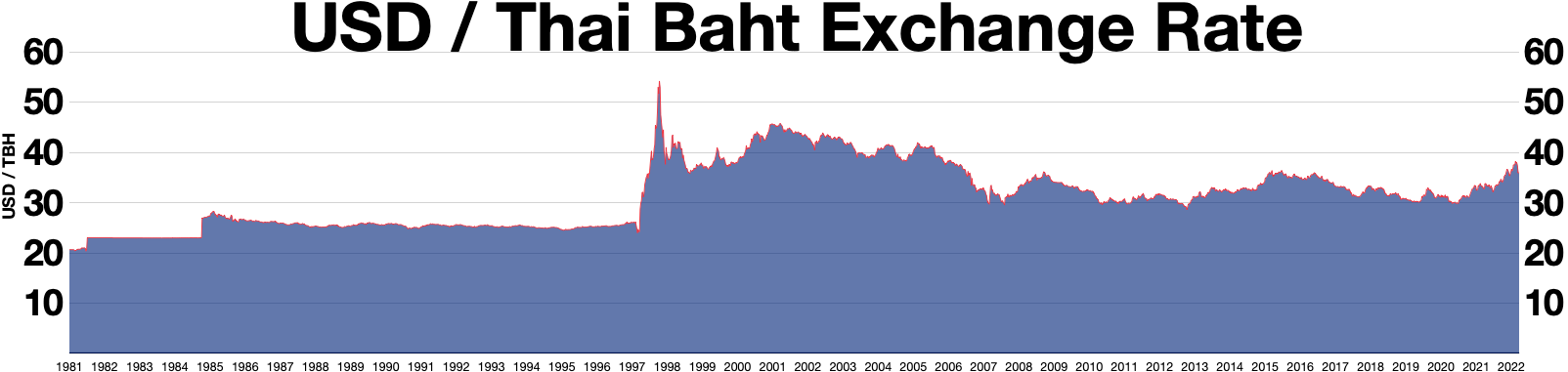
1997 Asian Financial Crisis
The 1997 Asian financial crisis gripped much of East Asia, East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided. Originating in Thailand, where it was known as the ''Tom yum, Tom Yum Kung crisis'' () on 2 July, it followed the financial collapse of the Thai baht after the Thai government was forced to floating currency, float the baht due to lack of list of circulating currencies, foreign currency to support its currency fixed exchange rate, peg to the U.S. dollar. Capital flight ensued almost immediately, beginning an international chain reaction. At the time, Thailand had acquired a burden of foreign debt. As the crisis spread, other Southeast Asian countries and later Japan and South Korea saw slumping currencies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accumulation By Dispossession
Accumulation by dispossession is a concept presented by the Marxist geographer David Harvey. It defines neoliberal capitalist policies that result in a centralization of wealth and power in the hands of a few by dispossessing the public and private entities of their wealth or land. Such policies are visible in many western nations from the 1970s and to the present day. Harvey argues these policies are guided mainly by four practices: privatization, financialization, management and manipulation of crises, and state redistributions. Practices Privatization Privatization and commodification of public assets have been among the most criticized and disputed aspects of neoliberalism. Summed up, they could be characterized by the process of transferring property from public ownership to private ownership. According to Marxist theory, this serves the interests of the capitalist class, or bourgeoisie, as it moves power from the nation's governments to private parties. At the same tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privatization
Privatization (rendered privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when a heavily regulated private company or industry becomes less regulated. Government functions and services may also be privatised (which may also be known as "franchising" or "out-sourcing"); in this case, private entities are tasked with the implementation of government programs or performance of government services that had previously been the purview of state-run agencies. Some examples include revenue collection, law enforcement, water supply, and prison management. Another definition is that privatization is the sale of a state-owned enterprise or municipally owned corporation to private investors; in this case shares may be traded in the public market for the first time, or for the first time since an enterprise's previous natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Direct Investment
A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an ownership stake in a company, made by a foreign investor, company, or government from another country. More specifically, it describes a controlling ownership an asset in one country by an entity based in another country. The magnitude and extent of control, therefore, distinguishes it from a foreign portfolio investment or foreign indirect investment. Foreign direct investment includes expanding operations or purchasing a company in the target country. Definitions Broadly, foreign direct investment includes mergers and acquisitions, building new facilities, reinvesting profits earned from overseas operations, and intra company loans. In a narrow sense, foreign direct investment refers just to building new facility, and a lasting management interest (10 percent or more of voting stock) in an enterprise operating in an economy other than that of the investor. FDI is the sum of equity capital, long-term capital, and short-term capital as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by a number of basic constituent elements: private property, profit motive, capital accumulation, competitive markets, commodification, wage labor, and an emphasis on innovation and economic growth. Capitalist economies tend to experience a business cycle of economic growth followed by recessions. Economists, historians, political economists, and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include '' laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalism, state capitalism, and welfare capitalism. Different forms of capitalism feature varying degrees of free markets, public ownership, obstacles to free competition, and state-sanctioned social poli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |