|
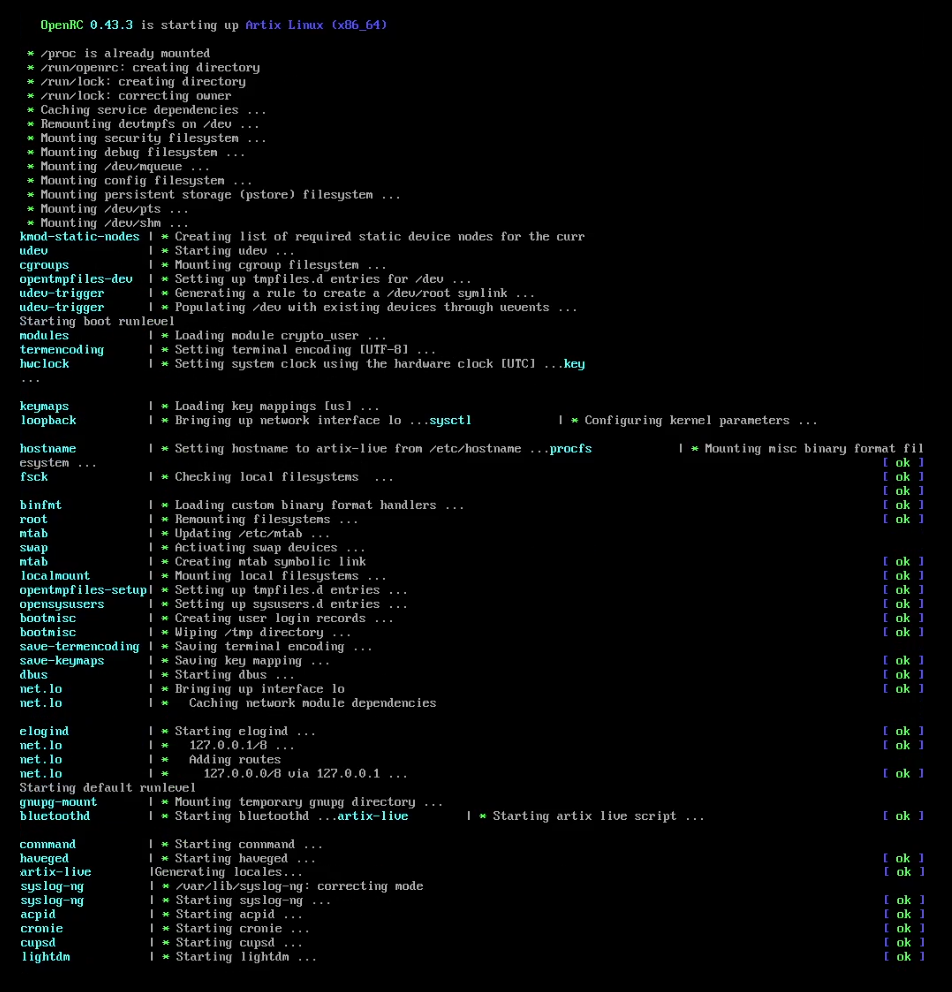
OpenRC
OpenRC is a dependency-based init system for Unix-like computer operating systems. It was created by Roy Marples, a NetBSD developer who was also active in the Gentoo Linux, Gentoo project. It became more broadly adopted as an init system outside of Gentoo following the decision by some Linux distributions not to adopt systemd. Adoption OpenRC is the default init system or Process supervision, process supervisor for: * Alpine Linux * Funtoo * Gentoo Linux * Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre * Maemo#Maemo Leste, Maemo Leste * Nitrux OpenRC is an available init system or Process supervision, process supervisor for: * Artix Linux (some consider it the default) * Devuan * Parabola GNU/Linux-libre * Arch Linux (Available through the Arch User Repository) * PostmarketOS Design OpenRC is made up of several modular components, the main ones being an init (optional), the core dependency management system and a daemon supervisor (optional). It is written in C and POSIX-compliant shell, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artix Linux
Artix Linux (or simply Artix ) is a rolling-release Linux distribution based on Arch Linux. Artix does not use systemd, instead opting to provide init and service management freedom. Artix offers OpenRC, runit, s6, and dinit in place of systemd. Artix Linux has its own repositories, and it is not recommended by developers to use Arch packages due to differences such as naming conventions and contrasting init systems. Arch OpenRC and Manjaro OpenRC were started in 2012. In 2017, these projects were merged and Artix Linux was created. Release history Artix initially offered two installation environments, a base command-line ISO image and the graphical Calamares installer based on LXQt desktop, with an i3 version following later. Those early versions featured the OpenRC init system. The latest installation media are also available in a variety of desktop environments like LXDE, LXQt, XFCE, MATE, Cinnamon and KDE Plasma. Additionally, two unofficial community editions f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Linux
Alpine Linux is a Linux distribution designed to be small, simple, and secure. It uses musl, BusyBox, and OpenRC instead of the more commonly used glibc, GNU Core Utilities, and systemd.Security-Oriented Alpine Linux 3.7 Has UEFI Support, GRUB Support in Installer ''Softpedia News''10 Most Secure Linux Distros For Complete Privacy & Anonymity , 2017 Edition ''FossBytes'' This makes Alpine one of few Linux distributions not to be base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemd
systemd is a software suite that provides an array of system components for Linux operating systems. The main aim is to unify service configuration and behavior across Linux distributions. Its primary component is a "system and service manager" — an init system used to Bootstrapping, bootstrap user space and manage process (computing), user processes. It also provides replacements for various Daemon (computing), daemons and utilities, including device management, login management, network connection management, and event logging. The name ''systemd'' adheres to the Unix convention of naming daemons by appending the letter ''d''. It also plays on the term "System D", which refers to a person's ability to adapt quickly and improvise to solve problems. Since 2015, the majority of Linux distributions have adopted systemd, having replaced other init systems such as SysV init. It has been praised by developers and users of distributions that adopted it for providing a stable, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Init
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init (short for ''initialization'') is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1. In Unix systems such as System III and System V, the design of init has diverged from the functionality provided by the init in Research Unix and its BSD derivatives. Up until the early 2010s, most Linux distributions employed a traditional init that was somewhat compatible with System V, while some distributions such as Slackware use BSD-style startup scripts, and other distributions such as Gentoo have their own customized versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sysvinit
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init (short for ''initialization'') is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1. In Unix systems such as System III and System V, the design of init has diverged from the functionality provided by the init in Research Unix and its Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD derivatives. Up until the early 2010s, most Linux distributions employed a traditional init that was somewhat compatible with System V, while some distributions such as Slackware Linux, Slackware use BSD-style startup scripts, and other distributions such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Init
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init (short for ''initialization'') is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1. In Unix systems such as System III and System V, the design of init has diverged from the functionality provided by the init in Research Unix and its BSD derivatives. Up until the early 2010s, most Linux distributions employed a traditional init that was somewhat compatible with System V, while some distributions such as Slackware use BSD-style startup scripts, and other distributions such as Gentoo have their own customized versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devuan
Devuan is an open source, Debian-based Linux distribution that aims to maintain compatibility with other init systems and avoid lock-in by systemd. Devuan offers sysvinit, runit or OpenRC as alternatives to systemd. History With the release of Debian 8, some developers and users felt alienated due to the project's adoption of systemd and subsequent removal of support for other existing init systems. This decision prompted some Debian community members to start a fork of Debian without systemd. Instead of continuing the Debian practice of using Toy Story character names as release codenames, Devuan aliases its releases using planet names. The first stable release shared the Debian 8 codename '' Jessie''. However, the Devuan release was named for minor planet 10464. The first stable release of Devuan was published on May 25, 2017. Devuan 2.0.0 ''ASCII'' was released on June 9, 2018, and 2.1 ''ASCII'' was released on November 21, 2019. ASCII provides a choice of five di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentoo Linux
Gentoo Linux (pronounced ) is a Linux distribution built using the Portage package management system. Unlike a binary software distribution, the source code is compiled locally according to the user's preferences and is often optimized for the specific type of computer. Precompiled binaries are available for some packages. Gentoo runs on a wide variety of processor architectures. Gentoo package management is designed to be modular, portable, easy to maintain, and flexible. Gentoo describes itself as a meta-distribution because of its adaptability, in that the majority of its users have configurations and sets of installed programs which are unique to the system and the applications they use. Gentoo Linux is named after the gentoo penguin, the fastest swimming species of penguin. The name was chosen to reflect the potential speed improvements of machine-specific optimizing, which is a major feature of Gentoo. History Gentoo Linux was initially created by Daniel Robbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Distribution
A Linux distribution, often abbreviated as distro, is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro—if distributed on its own—is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers (for example, Linux Mint) to servers (for example, Red Hat Enterprise Linux) and from embedded devices (for example, OpenWrt) to supercomputers (for example, Rocks Cluster Distribution). A distro typically includes many components in addition to the Linux kernel. Commonly, it includes a package manager, an init system (such as systemd, OpenRC, or runit), GNU tools and libraries, documentation, IP network configuration utilities, the getty TTY setup program, and many more. To provide a desktop experience (most commonly the Mesa userspace graphics drivers) a display server (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PostmarketOS
postmarketOS (abbreviated as pmOS) is an operating system primarily for smartphones, based on the Alpine Linux distribution. postmarketOS was launched on 26 May 2017 with the source code available on GitHub before migrating to GitLab in 2018. It is capable of running different X and Wayland based user interfaces, such as Plasma Mobile, MATE, GNOME, and XFCE; later updates added support for Unity8 and Phosh. It is also capable of running Docker, if the device specific kernel has cgroups and relevant configs enabled. The project aims to provide a ten-year lifecycle for smartphones. History Oliver Smith started developing postmarketOS in 2016. Architecture Unlike many other projects porting conventional Linux distributions to Android phones, postmarketOS does not use the Android build system or userspace. Each phone has only one unique package, and flashable installation images are generated using the pmbootstrap tool. The project intends to support the mainline Lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and library (computing), libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license. List of Linux distributions, Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre
Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre is a Linux distribution for the i686 and x86-64 architectures, including the GNU operating system components and the Linux-libre kernel instead of the generic Linux kernel. Free Software Foundation considers it a completely free operating system, true to their Free System Distribution Guidelines. Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre uses pacman as the package manager and some patchsets from the Debian development though stopping using patchsets from Debian beyond the version Debian 12. History Hyperbola was born at the 17th annual '' Fórum Internacional Software Livre'' (Porto Alegre, Brazil). On 5 August 2017, support for systemd was dropped in favor of OpenRC as its default init system to support the Init Freedom Campaign begun by Devuan. On 6 December 2018, Hyperbola was the first Brazilian distribution recognized as a completely free project by GNU, making it part of the FSF list of free distributions. On 23 September 2019, Hyperbola announced its first r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |