|
OpenEHR
openEHR is an open standard specification in health informatics that describes the management and storage, retrieval and exchange of health data in electronic health records (EHRs). In openEHR, all health data for a person is stored in a "one lifetime", vendor-independent, person-centred EHR. The openEHR specifications include an EHR Extract specification but are otherwise not primarily concerned with the exchange of data between EHR-systems as this is the focus of other standards such as EN 13606 and HL7. The openEHR specifications are maintained by the openEHR Foundation, a not for profit foundation supporting the open research, development, and implementation of openEHR EHRs. The specifications are based on a combination of 15 years of European and Australian research and development into EHRs and new paradigms, including what has become known as the archetype methodology for specification of content. The openEHR specifications include information and service models for the EHR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EN 13606
The Health informatics - Electronic Health Record Communication (EN 13606) was the European Standard for an information architecture to communicate Electronic Health Records (EHR) of a patient. The standard was later adopted as ISO 13606 and later replaced with ISO 13606-2 and recently ISO 13606-5:2010. This standard was intended to support the interoperability of systems and components that need to communicate (access, transfer, add or modify) EHR data via electronic messages or as distributed objects: * preserving the original clinical meaning intended by the author; * reflecting the confidentiality of that data as intended by the author and patient. References External links EN13606 community and information sitePublished Archetypes by Minas Gerais, Brazil (Portuguese)Poseacle Converter and Repository See also * Archetype (information science) * Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) * Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) * Continuity of Care Record * Elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archetype (information Science)
In the field of informatics, an archetype is a formal re-usable model of a domain concept. Traditionally, the term ''archetype'' is used in psychology to mean an idealized model of a person, personality or behaviour (see '' Archetype''). The usage of the term in informatics is derived from this traditional meaning, but applied to domain modelling instead. An archetype is defined by the OpenEHR Foundation (for health informatics) as follows: :''An archetype is a computable expression of a domain content model in the form of structured constraint statements, based on some reference model. openEHR archetypes are based on the openEHR reference model. Archetypes are all expressed in the same formalism. In general, they are defined for wide re-use, however, they can be specialized to include local particularities. They can accommodate any number of natural languages and terminologies.'' Formal specifications The modern archetype formalism is specified and maintained by the openEHR Founda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Informatics Service Architecture
The European Committee for Standardization ( CEN) Standard Architecture for Healthcare Information Systems (ENV 12967), Health Informatics Service Architecture or HISA is a standard that provides guidance on the development of modular open information technology (IT) systems in the healthcare sector. Broadly, architecture standards outline frameworks which can be used in the development of consistent, coherent applications, databases and workstations. This is done through the definition of hardware and software construction requirements and outlining of protocols for communications. The HISA standard provides a formal standard for a service-oriented architecture (SOA), specific for the requirements of health services, based on the principles of Open Distributed Processing. The HISA standard evolved from previous work on healthcare information systems architecture commenced by Reseau d’Information et de Communication Hospitalier Europeen (RICHE) in 1989, and subsequently built upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archetype (information Science)
In the field of informatics, an archetype is a formal re-usable model of a domain concept. Traditionally, the term ''archetype'' is used in psychology to mean an idealized model of a person, personality or behaviour (see '' Archetype''). The usage of the term in informatics is derived from this traditional meaning, but applied to domain modelling instead. An archetype is defined by the OpenEHR Foundation (for health informatics) as follows: :''An archetype is a computable expression of a domain content model in the form of structured constraint statements, based on some reference model. openEHR archetypes are based on the openEHR reference model. Archetypes are all expressed in the same formalism. In general, they are defined for wide re-use, however, they can be specialized to include local particularities. They can accommodate any number of natural languages and terminologies.'' Formal specifications The modern archetype formalism is specified and maintained by the openEHR Founda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Standard
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a prerequisite to use open license, non-discrimination and extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in the development. There is no single definition, and interpretations vary with usage. The terms ''open'' and ''standard'' have a wide range of meanings associated with their usage. There are a number of definitions of open standards which emphasize different aspects of openness, including the openness of the resulting specification, the openness of the drafting process, and the ownership of rights in the standard. The term "standard" is sometimes restricted to technologies approved by formalized committees that are open to participation by all interested parties and operate on a consensus basis. The definitions of the term ''open standard'' used by academics, the European Union, and some of its member governments or parliaments such as Denmark, France, and Spain preclude open standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 13606
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization. ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance * Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007 * Iso Omena ("Big Apple"), a shopping center in Finland * Incentive stock option, a type of employee stock option * Independent Sales Organization, a company that partners with an acquiring bank to provide merchant services * Insurance Services Office, an American insurance underwriter * Intermarket sweep order, a type of limit order on financial markets * Iso (automobile), an Italian car manufacturer Arts and entertainment * Isomorphic Algorithms (ISOs), a fictional race in the digital world of '' Tron: Legacy'' * Iso (comics), a Marvel comics character Music * ''Iso'' (album), an album by Ismaël Lô * Iceland Symphony Orchestra * Indianapolis Symphony Orchestra, Indiana, US * International Symphony Orchestra, of Sarnia, Ontario and Port Hur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ProRec
The ProRec initiative of 1996 was a network of national non-profit organisations (the "ProRec centres"). The initiative was a consequence of the conclusions of the Concerted Action MEDIREC (1994-1995) regarding the reasons why Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems were not used more widely in any of the European Union. As part of the Lisbon Declaration suggestions were made to remedy this situation. The ProRec initiative is supported by the DG Information Society of the European Union. The DG Information Society supported the ProRec initiative with the ProRec Support Action (1996-1998), and the WIDENET Accompanying Measure (2000-2003). The goal of the initiative is to build awareness of the limitations, shortcomings and obstacles on the way towards widespread development, implementation and use of quality Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and pointing them out. Especially significant for implementing Electronic Health Record systems is the ability to communicate and interoperate. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
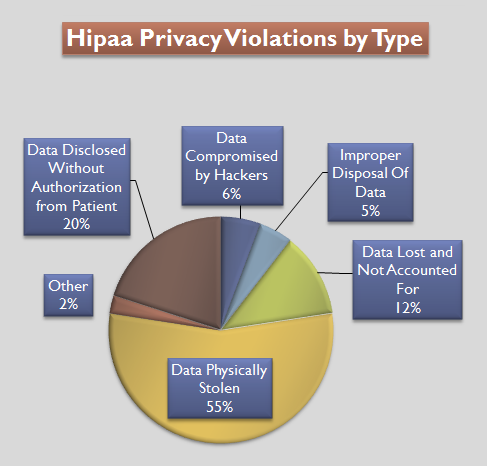
HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA or the Kennedy– Kassebaum Act) is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 21, 1996. It modernized the flow of healthcare information, stipulates how personally identifiable information maintained by the healthcare and healthcare insurance industries should be protected from fraud and theft, and addressed some limitations on healthcare insurance coverage. It generally prohibits healthcare providers and healthcare businesses, called ''covered entities'', from disclosing protected information to anyone other than a patient and the patient's authorized representatives without their consent. With limited exceptions, it does not restrict patients from receiving information about themselves. It does not prohibit patients from voluntarily sharing their health information however they choose, nor does it require confidential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Level 7
Health Level Seven or HL7 refers to a set of international standards for transfer of clinical and administrative data between software applications used by various healthcare providers. These standards focus on the application layer, which is "layer 7" in the OSI model. The HL7 standards are produced by Health Level Seven International, an international standards organization, and are adopted by other standards issuing bodies such as American National Standards Institute and International Organization for Standardization. Hospitals and other healthcare provider organizations typically have many different computer systems used for everything from billing records to patient tracking. All of these systems should communicate with each other (or "interface") when they receive new information, or when they wish to retrieve information, but not all do so. HL7 International specifies a number of flexible standards, guidelines, and methodologies by which various healthcare systems can c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Committee For Standardization
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN, french: Comité Européen de Normalisation) is a public standards organization whose mission is to foster the economy of the European Single Market and the wider European continent in global trading, the welfare of European citizens and the environment by providing an efficient infrastructure to interested parties for the development, maintenance and distribution of coherent sets of standards and specifications. The CEN was founded in 1961. Its thirty-four national members work together to develop European Standards (ENs) in various sectors to build a European internal market for goods and services and to position Europe in the global economy. CEN is officially recognized as a European standards body by the European Union, European Free Trade Association and the United Kingdom; the other official European standards bodies are the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization ( CENELEC) and the European Telecommunicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Organization For Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes. ISO was founded on 23 February 1947, and (as of November 2022) it has published over 24,500 international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. It has 809 Technical committees and sub committees to take care of standards development. The organization develops and publishes standardization in all technical and nontechnical fields other than electrical and electronic engineering, which is handled by the IEC.Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. 3 June 2021.International Organization for Standardization" ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Retrieved 2022-04-26. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and works in 167 countries . The three official languages of the ISO are English, F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Institute For Health Records
The European Institute for Health Records or EuroRec Institute is a non-profit organization founded in 2002 as part of the ProRec initiative. On 13 May 2003, the institute was established as a non-profit organization under French law. Current President of EuroRec is Prof. Dipak Kalra. The institute is involved in the promotion of high quality Electronic Health Record systems in the European Union. One of the main missions of the institute is to support, as the European authorised certification body, EHRs certification development, testing and assessment by defining functional and other criteria. The objectives of the institute are: # To federate the established ProRec centres that comply with a set of explicit criteria. # To develop specifically those activities that cannot be handled at the level of ProRec centres and/or within their scope, according to the principle of subsidiarity and in view of both synergy and economy of scale. European projects ARGOS The main goal of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |