|
Opalfish
The opalfish, ''Hemerocoetes monopterygius'', is a ray-finned fish Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of sk ... of the genus '' Hemerocoetes'', found only around New Zealand, at depths of between . Their length is between . Gallery File:Hemerocoetes monopterygius (Opalfish).gif, Drawing by Dr Tony Ayling File:Hemerocoetes_monopterygius_2022-09_(3).jpg, An opalfish surrounded by shells References * * * Tony Ayling & Geoffrey Cox, ''Collins Guide to the Sea Fishes of New Zealand'', (William Collins Publishers Ltd, Auckland, New Zealand 1982) * Wade Doak, ''A Photographic Guide to Sea Fishes of New Zealand'', (New Holland Publishers (NZ) Ltd, Auckland, New Zealand 2003) Hemerocoetidae Endemic marine fish of New Zealand Fish described in 1801 Taxobox binomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
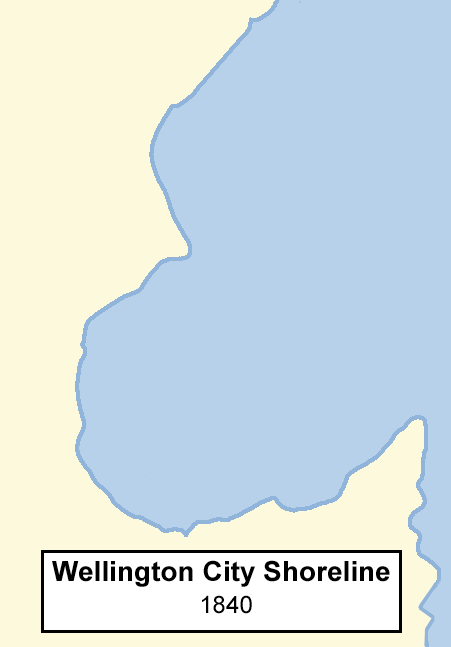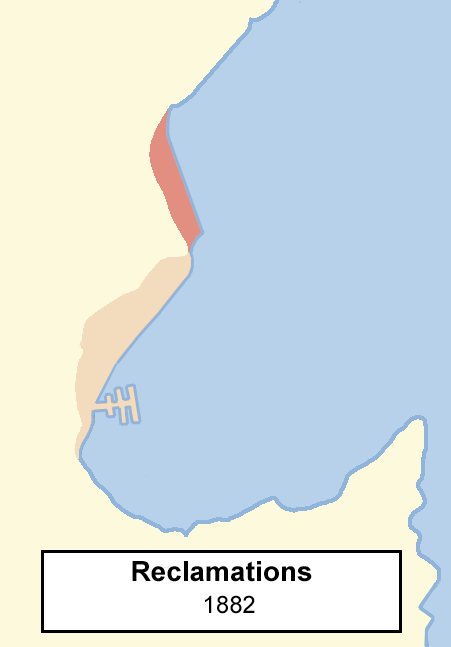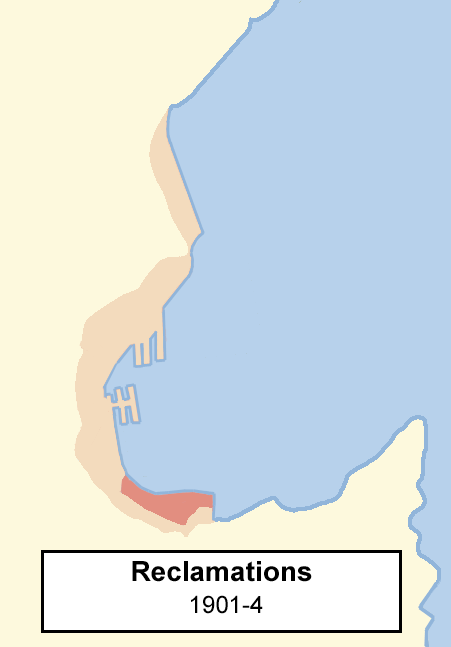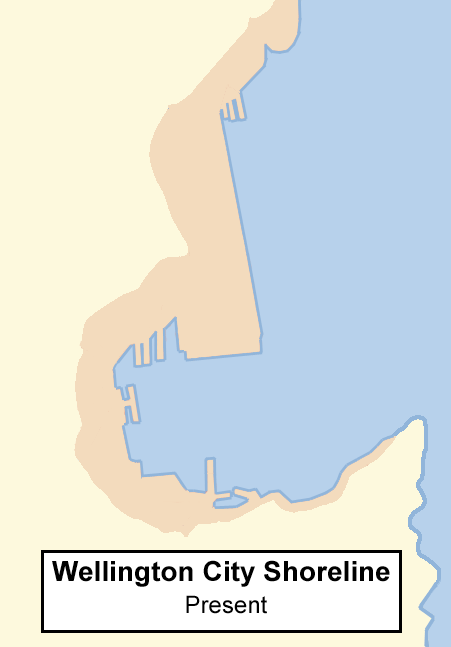
Wellington Harbour
Wellington Harbour ( ), officially called Wellington Harbour / Port Nicholson, is a large natural harbour on the southern tip of New Zealand's North Island. The harbour entrance is from Cook Strait. Central Wellington is located on parts of the western and southern sides of the harbour, and the suburban area of Lower Hutt is to the north and east. The harbour area bounded by a line between Pencarrow Head to Petone foreshore, was officially named Port Nicholson until it assumed its current dual name in 1984. Toponymy The earliest known Māori name for the area, ''Te Upoko-o-te-Ika-a-Māui'', is derived from Māori legend and translates literally as "the head of Māui's fish". ''Te Whanganui-a-Tara'', another Māori name for the area, translates literally as "the great harbour of Tara". It is believed to refer to Tara, a son of the Polynesian explorer Whātonga, who was sent down from the Māhia Peninsula by his father to explore southern lands for their people to se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Gottlob Theaenus Schneider
Johann Gottlob Theaenus Schneider (18 January 1750 – 12 January 1822) was a German Empire, German classicist and natural history, naturalist. Biography Schneider was born at Collm in Saxony. In 1774, on the recommendation of Christian Gottlob Heine, he became secretary to the famous Strasbourg scholar Richard François Brunck, and in 1811, became professor of ancient languages and eloquence at Breslau (chief librarian, 1816) where he died in 1822. Works Of his numerous works the most important was his ''Kritisches griechisch-deutsches Handwörterbuch'' (1797–1798), the first independent work of the kind since Henri Estienne, Stephanus's ''Thesaurus'', and the basis of Franz Passow, F. Passow's and all succeeding Greek lexicons (including, therefore, the contemporary standard ''A Greek-English Lexicon''). A special improvement was the introduction of words and expressions connected with natural history and science. In 1801, he corrected and expanded re-published Marcus Elieser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray-finned Fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spines called '' lepidotrichia'', as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). The vast majority of actinopterygians are teleosts. By species count, they dominate the subphylum Vertebrata, and constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 extant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemerocoetes
''Hemerocoetes'' is a genus of ray-finned fish Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of sk ...es belonging to the family Hemerocoetidae. References Hemerocoetidae Extant Rupelian first appearances Marine fish genera Taxa named by Achille Valenciennes Rupelian genus first appearances {{Acropomatiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wade Doak
Wade Thomas Doak (23 February 1940 – 12 September 2019) was a New Zealand marine conservationist, scuba diver, photographer and filmmaker. Born in Christchurch, Doak was educated at Christchurch Boys' High School from 1954 to 1958. He began diving in his teens, and met Kelly Tarlton at the Canterbury Underwater Club. In the 1960s, Doak moved to Northland, where he first dove around the Poor Knights Islands with Tarlton. Doak became an acknowledged expert on the marine ecology of the area, and was instrumental in the Poor Knights Islands being made a marine reserve A marine reserve is a type of marine protected area (MPA). An MPA is a section of the ocean where a government has placed limits on human activity. A marine reserve is a marine protected area in which removing or destroying natural or cultural ... in 1981 and receiving full protection in 1998. In the 2012 Queen's Birthday and Diamond Jubilee Honours, Doak was awarded the Queen's Service Medal, for services ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemerocoetidae
Hemerocoetidae is a family of percomorph ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Acropomatiformes. Genera The following genera are included within the Hemerocoetinae: * '' Acanthaphritis'' Günther, 1880 * '' Dactylopsaron'' Parin, 1990 * '' Enigmapercis'' Whitley, 1936 * ''Hemerocoetes'' Valenciennes, 1837 * '' Matsubaraea'' Taki, 1953 * '' Osopsaron'' Jordan Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ... & Starks, 1904 * '' Pteropsaron'' Jordan & Snyder, 1902 * '' Squamicreedia'' Rendahl, 1921 References {{Acropomatiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Marine Fish Of New Zealand
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1801
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |