|
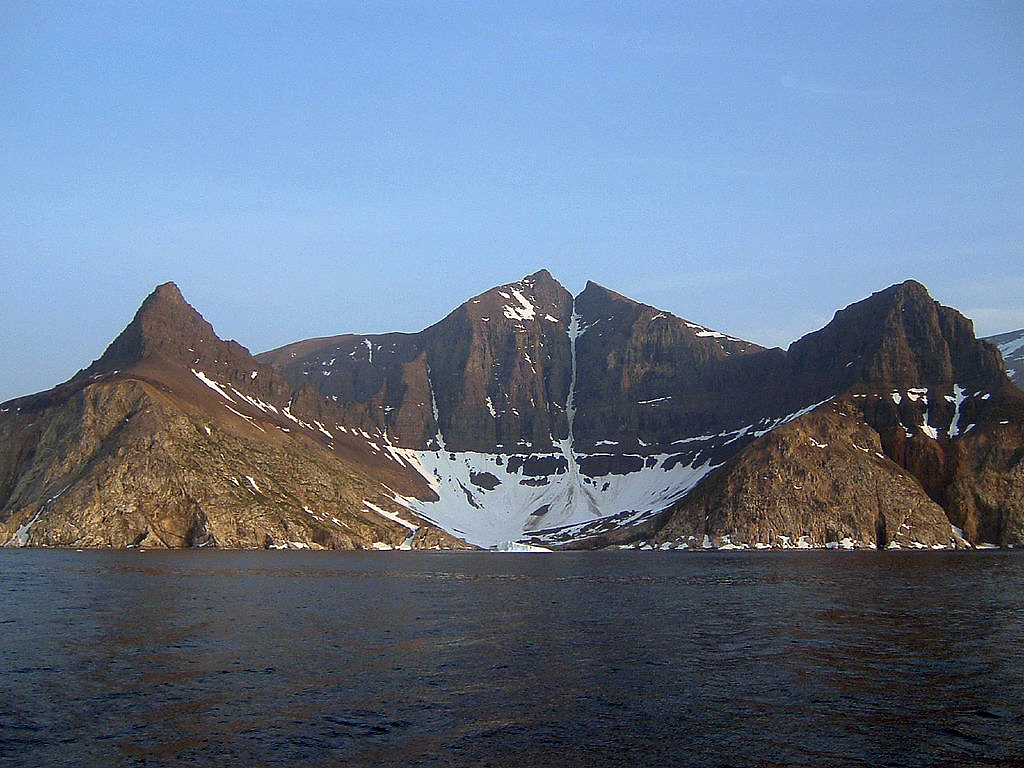
Opal Peak
Opal Peak is a mountain summit located northeast of the northern end of Maligne Lake in Jasper National Park, in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta, Canada. It is situated in the Opal Hills, west of Opal Lake and northwest of Leah Peak. __NOTOC__ Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, Opal Peak is located in a subarctic climate zone with cold, snowy winters, and mild summers. Temperatures can drop below -20 °C, with wind chill factors below -30 °C. Precipitation runoff from Opal Peak drains west into the Maligne River, which is a tributary of the Athabasca River. See also *List of mountains of Canada Most mountain peaks of Canada lie in the west, specifically in British Columbia, Alberta, and the Yukon. Mountains can be found all over British Columbia while those in Alberta are mainly situated on the eastern side of the Canadian Rockies. The ... * Geology of the Rocky Mountains References Gallery File:Opal Peak.jpg, Southwest aspect Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Elizabeth Ranges
The Queen Elizabeth Ranges is a group of mountain ranges in the Canadian Rockies on the southeastern side of Jasper National Park, Canada. The northern end of the ranges begins east of Medicine Lake and extends in a southeasterly direction past the southern shore of Maligne Lake. The group was named in 1953 to celebrate the coronation of Elizabeth II The coronation of the British monarch, coronation of Elizabeth II took place on 2 June 1953 at Westminster Abbey in London. She acceded to the throne at the age of 25 upon the death of her father, George VI, on 6 February 1952, being Proclamati ... as Canada's sovereign. These ranges include the following mountains and peaks: References Mountains of Jasper National Park Mountain ranges of Alberta Queen Elizabeth Ranges {{AlbertaRockies-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-thousanders Of Alberta
Two-thousanders are mountains that have a height of at least 2,000 metres above sea level, but less than 3,000 metres. The term is used in Alpine circles, especially in Europe (e.g. German: ''Zweitausender''). The two photographs show two typical two-thousanders in the Alps that illustrate different types of mountain. The Säuling (top) is a prominent, individual peak, whereas the Schneeberg (bottom) is an elongated limestone massif. In ranges like the Allgäu Alps, the Gesäuse or the Styrian-Lower Austrian Limestone Alps the mountain tour descriptions for mountaineers or hikers commonly include the two-thousanders, especially in areas where only a few summits exceed this level. Examples from these regions of the Eastern Alps are: * the striking Nebelhorn (2,224 m) near Oberstdorf or the Säuling (2,047 m) near Neuschwanstein, * the Admonter Reichenstein (2,251 m), Eisenerzer Reichenstein (2,165 m), Großer Pyhrgas (2,244 m) or Hochtor (2,369 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Rocky Mountains
The geology of the Rocky Mountains is that of a discontinuous series of mountain ranges with distinct geological origins. Collectively these make up the Rocky Mountains, a mountain system that stretches from Northern British Columbia through central New Mexico and which is part of the great mountain system known as the North American Cordillera. The rocky cores of the mountain ranges are, in most places, formed of pieces of continental crust that are over one billion years old. In the south, an older mountain range was formed 300 million years ago, then eroded away. The rocks of that older range were reformed into the Rocky Mountains. The Rocky Mountains took shape during an intense period of plate tectonic activity that resulted in much of the rugged landscape of the western North America. The Laramide orogeny, about 80–55 million years ago, was the last of the three episodes and was responsible for raising the Rocky Mountains. Subsequent erosion by glaciers has created t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mountains Of Canada
Most mountain peaks of Canada lie in the west, specifically in British Columbia, Alberta, and the Yukon. Mountains can be found all over British Columbia while those in Alberta are mainly situated on the eastern side of the Canadian Rockies. The Saint Elias Mountains in the Yukon hold some of country's highest mountains, including the highest, Mount Logan at . Alberta ;Highest peaks Mts. Columbia & King Edward.jpg, Mount Columbia & King Edward in background The Twins - South and North (l-r).jpg, The Twins massif - South Twin and North Twin (l-r) Mount Assiniboine massif.jpg, Mount Assiniboine seen from above Lake Magog Columbia Icefields - panoramio (1).jpg, Snow Dome seen from Icefields Parkway British Columbia Mount Assiniboine.jpg, Mount Assiniboine Mount Robson South.jpg, Mount Robson, highest in Canadian Rockies Garibaldi black tusk.jpg, The Black Tusk Snow Dome+Dome Glacier.jpg, Snow Dome and Dome Glacier Mount Mackenzie from Mount Revelstoke NP.jpg, Moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athabasca River
The Athabasca River (French: ''Rivière Athabasca'') is a river in Alberta, Canada, which originates at the Columbia Icefield in Jasper National Park and flows more than before emptying into Lake Athabasca. Much of the land along its banks is protected in national and provincial parks, and the river is designated a Canadian Heritage River for its historical and cultural importance. The scenic Athabasca Falls is located about upstream from Jasper. Etymology The name ''Athabasca'' comes from the Woods Cree word , which means " herethere are plants one after another", likely a reference to the spotty vegetation along the river. Course The Athabasca River originates in Jasper National Park, in an unnamed lake at the toe of the Columbia Glacier within the Columbia Icefield, between Mount Columbia, Snow Dome, and the Winston Churchill Range, at an elevation of approximately . It travels before draining into the Peace-Athabasca Delta near Lake Athabasca south of Fort Chip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maligne River
The Maligne River ( ) is a medium-sized river in the Canadian Rockies. It runs through parts of Jasper National Park in Alberta, Canada. The Maligne is a major tributary of the Athabasca River. The river takes from the French word for malignant or wicked. It is theorised that a Belgian priest (Pieter Jan De Smet ) voyageur created this name in reference to the current of the river near its confluence with the Athabasca River. Geography The Maligne River begins south of Maligne Lake. Forming from the meltwater of Replica Peak, the river heads north, passing under Mount Mary Vaux, Lysfran Peak, Mount Unwin, and Mount Charleton before emptying into Maligne Lake. The Maligne River drains the north end of Maligne Lake and heads northwest to Medicine Lake. It then flows west, entering the Athabasca River.Mussio Ventures. ''Central Alberta Backroad Mapbook.'' Burnaby: Backroad Mapbooks (2002) Below Maligne Lake, it is a losing stream A losing stream, disappearing stream, infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water occurring on the ground surface when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when the soil is saturated by water to its full capacity, and the rain arrives more quickly than the soil can absorb it. Surface runoff often occurs because impervious areas (such as roofs and pavement) do not allow water to soak into the ground. Furthermore, runoff can occur either through natural or man-made processes. Surface runoff is a major component of the water cycle. It is the primary agent of soil erosion by water. The land area producing runoff that drains to a common point is called a drainage basin. Runoff that occurs on the ground surface before reaching a channel can be a nonpoint source of pollution, as it can carry man-made contaminants or natural forms of pollution (such as rotting leaves). Man-made contaminants in runoff i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least one month) must have a 24-hour average temperature of at least to fall into this category of climate, and the coldest month should a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leah Peak
Leah Peak is a mountain summit located on the east shore of Maligne Lake in Jasper National Park, in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta, Canada. The nearest higher peak is Samson Peak, to the north. __NOTOC__ History Leah Peak was named by Mary Schäffer in her expedition through the area in 1908 to find Maligne Lake. She also named nearby Samson Peak. Leah Beaver was the wife of Samson Beaver. Samson was a Stoney Indian who befriended Mary and provided her with a hand drawn map to assist her with finding the way to the elusive lake. Samson visited the lake with his father at the age of 14, and 16 years later he drew the map from memory when he met Mary at Elliott Barnes' cabin on the Kootenay Plains in the Saskatchewan Valley.Leah Peak PeakFinder The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Rockies
The Canadian Rockies (french: Rocheuses canadiennes) or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera, which is the northern segment of the North American Cordillera, the expansive system of interconnected mountain ranges between the Interior Plains and the Pacific Coast that runs northwest–southeast from central Alaska to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in Mexico. Canada officially defines the Rocky Mountains system as the mountain chains east of the Rocky Mountain Trench extending from the Liard River valley in northern British Columbia to the Albuquerque Basin in New Mexico, not including the Mackenzie, Richardson and British Mountains/ Brooks Range in Yukon and Alaska (which are all included as the "Arctic Rockies" in the United States' definition of the Rocky Mountains system). The Canadian Rockies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opal Hills
Opal Hills is a sub-range of the Queen Elizabeth Ranges in Jasper National Park, Alberta, Canada. There is an 8.2 km (5.1 mi) hiking trail. Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, the Opal Hills are located in a subarctic climate The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, ge ... with cold, snowy winters, and mild summers. Temperatures can drop below -20 °C with wind chill factors below -30 °C. References External linksParks Canada site Hills of Alberta {{AlbertaRockies-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |