|
Onychophore
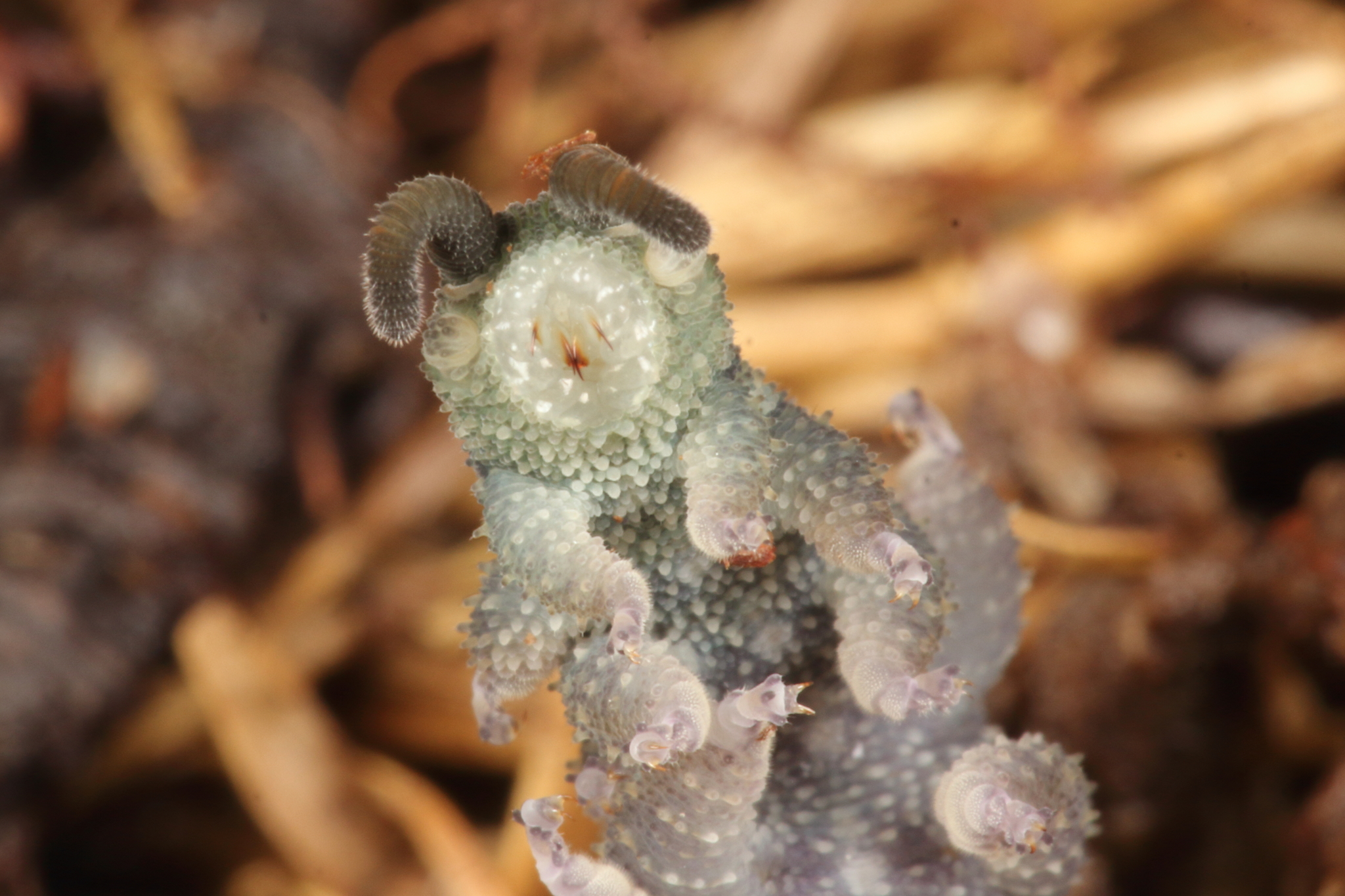
Onychophora (from , , "claws"; and , , "to carry"), commonly known as velvet worms (for their velvety texture and somewhat wormlike appearance) or more ambiguously as peripatus (after the first described genus, ''Peripatus''), is a phylum of elongate, soft-bodied, many-legged animals. In appearance they have variously been compared to worms with legs, caterpillars, and slugs. They prey upon other invertebrates, which they catch by ejecting an adhesive slime. Approximately 200 species of velvet worms have been described, although the true number is likely to be much greater. The two extant families of velvet worms are Peripatidae and Peripatopsidae. They show a peculiar distribution, with the peripatids being predominantly equatorial and tropical, while the peripatopsids are all found south of the equator. It is the only phylum within Animalia that is wholly endemic to terrestrial environments, at least among extant members. Velvet worms are generally considered close relatives o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plicatoperipatus Jamaicensis
''Plicatoperipatus'' is a monospecific genus of velvet worm containing the single species ''Plicatoperipatus jamaicensis''. It is endemic to Jamaica. Females of this species can have as many as 43 pairs of legs, the maximum number found in the phylum Onychophora. In a large sample collected in 1988, however, females ranged from 35 to 39 leg pairs, with 37 as the mean and the most common number, and males ranged from 31 to 37 leg pairs, with 35 as the mean and the most common number. This species ranges from 25 mm to 65 mm in length. In the 1988 sample, the mean length for males was 33 mm, and the mean length for mature females was 51 mm. This species is viviparous, with mothers supplying nourishment to their embryos through a placenta. Conservation This species is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN Red List The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripatopsidae
Peripatopsidae or the Southern Velvet Worms are one of two extant families of velvet worm. This family includes more than 140 described species distributed among 41 genera, but some authorities deem only 131 of these species to be valid. The French zoologist Eugène Louis Bouvier proposed this family in 1905 with '' Peripatopsis'' as the type genus. Description The Peripatopsidae exhibit relatively many characteristics that are perceived as original or "primitive" with respect to the Peripatidae. The species in this family have relatively few legs, ranging from 13 pairs (in '' Ooperipatellus nanus'') to a maximum of 29 pairs (in '' Paraperipatus papuensis''). Behind or between the last leg pair is the genital opening (gonopore). This family includes both oviparous genera (e.g., '' Ooperipatellus'' and '' Ooperipatus'') and viviparous genera, which adopt various modes of supplying nourishment to their embryos, ranging from lecithotrophic ovoviviparity (with yolky eggs retained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripatus
''Peripatus'' is a genus of velvet worms in the Peripatidae family. The name "peripatus" (unitalicised and uncapitalised) is also used to refer to the Onychophora as a whole, although this group comprises many other genera besides ''Peripatus''. The genus ''Peripatus'' is found in Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America. This genus is viviparous, with mothers supplying nourishment to their embryos through a placenta. Description Velvet worms in this genus may have as few as 24 or 25 pairs of legs (in ''P. antiguensis'' or '' P. dominicae'', respectively) or as many as 36 leg pairs (in '' P. evelinae''). Males in this genus bear crural tubercles on more than two pregenital leg pairs. The dorsal primary papillae in this genus feature an apical piece that is larger than the basal piece. Species The genus contains the following species: * '' Peripatus basilensis'' Brues, 1935 – Hispaniola (Haiti, Dominican Republic) * '' Peripatus bouvieri'' Fuhrmann, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oroperipatus
''Oroperipatus'' is a genus of Neotropical Onychophora, velvet worms in the family Peripatidae. Species in this genus are found in South America west of the Andes and in Mexico. This genus is viviparous, with mothers supplying nourishment to their embryos through a placenta. Description Velvet worms in this genus can have as few as 22 pairs of legs (in ''Oroperipatus omeyrus, O. omeyrus'') or as many as 40 leg pairs (in ''Oroperipatus bluntschli, O. bluntschli'', ''Oroperipatus weyrauchi, O. weyrauchi'', and ''Oroperipatus tiputini, O. tiputini''). Species in this genus have from four to seven distal foot papillae, with two or more on the anterior part of the foot and two or more on the posterior part of the foot. This genus also features a nephridial tubercle on the fourth and fifth leg pairs inserted into a complete third spinous pad. Species The genus contains the following species: * ''Oroperipatus balzani'' (Camerano, 1897) * ''Oroperipatus belli'' (Bouvier, 1904) * ''Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Carboniferous
Late or LATE may refer to: Everyday usage * Tardy, or late, not being on time * Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead Music * Late (The 77s album), ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000 * Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993 * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch (album), Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other uses * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * Late (The Handmaid's Tale), "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Laivateollisuus, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia * Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law * Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics * Late, a synonym for ''cooler'' in Stellar classification#"Early" and "late" nomencla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/ os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongeperipatus Solorzanoi
''Mongeperipatus solorzanoi'', also known as Solórzano's velvet worm, is a species of velvet worm in the family Peripatidae. This species is the largest known velvet worm, reaching 22 cm (8.7 in.) in length. This velvet worm is found in the Caribbean coastal forest of Costa Rica. Discovery This species was first described in 2010 by the biologists Bernal Morera-Brenes and Julián Monge-Nájera based on fourteen female specimens and two male specimens. These specimens include a female holotype found by the Costa Rican herpetologist Alejandro Solórzano in Guayacán de Siquirres in Costa Rica in 1996, four young paratypes born to the holotype soon after her capture, and other paratypes collected in 2000. The specific name ''solorzanoi'' is in honor of Solórzano, who discovered the species. The holotype is deposited in the Museo de Zoología de la Universidad de Costa Rica in San José, Costa Rica. Taxonomy Morera-Brenes and Monge-Nájera first described this species i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ooperipatellus Nanus
''Ooperipatellus nanus'' is a species of velvet worm in the family Peripatopsidae. This species is endemic to New Zealand and is found in the South Island. Taxonomy This species was first described by Hilke Ruhberg in 1985. Description ''Ooperipatellus nanus'' is a small species of velvet worm that grows to a length of approximately 10 mm. This species is tan or brown in color on its back but yellow on its underside. It is oviparous and has 13 pairs of legs, which is the minimum number found in the phylum Onychophora. Distribution ''Ooperipatellus nanus'' has only been found in Southland, in the Takitimu Mountains. Life cycle This species produce young by laying eggs from which the young subsequently hatch. Host species ''Ooperipatellus nanus'' are found mainly in rotting beech logs. Conservation status This species has been classified as having the "At Risk, Naturally Uncommon" with the qualifier of "One Location" conservation status under the New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface appendages. In many kinds of eukaryotic cells, the protrusions are known as membrane protrusions or cell appendages (examples include microvilli and cilia). Types in animals In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including antennae, mouthparts (including mandibles, maxillae and maxillipeds), gills, locomotor legs ( pereiopods for walking, and pleopods for swimming), sexual organs ( gonopods), and parts of the tail (uropods). Typically, each body segment carries one pair of appendages. An appendage which is modified to assist in feeding is known as a maxilliped or gnathopod. In annelids lateral protrusions from the body are called parapodia. In echinoderms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder () has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in a solid ball versus sphere surface)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term "cylinder" could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the '' right circular cylinder''. Types The definitions and results in this section are taken from the 1913 text ''Plane and Solid Geometry'' by George A. Wentworth and David Eugene Smith . A ' is a surface consisting of all the points on all the lines which are parallel to a given line and which pass through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segmentation (biology)
Segmentation in biology is the division of some animal and plant body plans into a linear series of repetitive segments that may or may not be interconnected to each other. This article focuses on the segmentation of animal body plans, specifically using the examples of the taxa Arthropoda, Chordata, and Annelida. These three groups form segments by using a "growth zone" to direct and define the segments. While all three have a generally segmented body plan and use a growth zone, they use different mechanisms for generating this patterning. Even within these groups, different organisms have different mechanisms for segmenting the body. Segmentation of the body plan is important for allowing free movement and development of certain body parts. It also allows for regeneration in specific individuals. Definition Segmentation is a difficult process to satisfactorily define. Many taxa (for example the molluscs) have some form of serial repetition in their units but are not conventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viviparity
In animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the mother, with the maternal circulation providing for the metabolic needs of the embryo's development, until the mother gives birth to a fully or partially developed juvenile that is at least metabolically independent. This is opposed to oviparity, where the embryos develop independently outside the mother in eggs until they are developed enough to break out as hatchlings; and ovoviviparity, where the embryos are developed in eggs that remain carried inside the mother's body until the hatchlings emerge from the mother as juveniles, similar to a live birth. Etymology The term "viviparity" and its adjective form "viviparous" both derive from the Latin ''vivus'', meaning "living"; and ''pario'', meaning "give birth to". Reproductive mode Five modes of reproduction have been differentiated in animals based on relations between zygote and parents. The five include two nonviviparous modes: ovulipari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |