|
Ommanney Glacier
Robertson Bay () is a large, roughly triangular bay that indents the north coast of Victoria Land between Cape Barrow and Cape Adare. Discovered in 1841 by Captain James Clark Ross, Royal Navy, who named it for Dr. John Robertson, surgeon on HMS ''Terror''. Features Robertson Bay extends between Cape Barrow in the west and Cape Adare in the east. Protection Cove in the south is the head of the bay. Cape Barrow is on Flat Island, east of Siren Bay and north of Cape Wood. Shipley Glacier divides and enters Robertson Bay to the west and to the south of the island, where it flows into Pressure Bay. Frank Newnes Glacier also flows into Pressure Bay, which is divided by Birthday Point from Berg Bay. Haffner Glacier empties into Berg Bay. The Sphinx Rock and Islands Point separate Berg Bay from Relay Bay. Reusch Glacier, Crume Glacier, Ommanney Glacier and Nielsen Glacier drain into Relay Bay, the last entering beside Calf Point to the west of Penelope Point and the Scott Keltie G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Deep Freeze
Operation Deep Freeze is the code name for a series of United States missions to Antarctica, beginning with "Operation Deep Freeze I" in 1955–56, followed by "Operation Deep Freeze II", "Operation Deep Freeze III", and so on. (There was an initial operation before Richard E. Byrd, Admiral Richard Byrd proposed 'Deep Freeze'). Given the continuing and constant US presence in Antarctica since that date, "Operation Deep Freeze" has come to be used as a general term for US operations in that continent, and in particular for the regular missions to resupply US Antarctic bases, coordinated by the Military of the United States, United States military. Task Force 199 was involved. For a few decades the missions were led by the United States Navy, though the Air National Guard and National Science Foundation are also important parts of the missions. In Antarctica, when the polar dawn starts late in the year things begin warming up and the mission usually runs from late in the year to ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
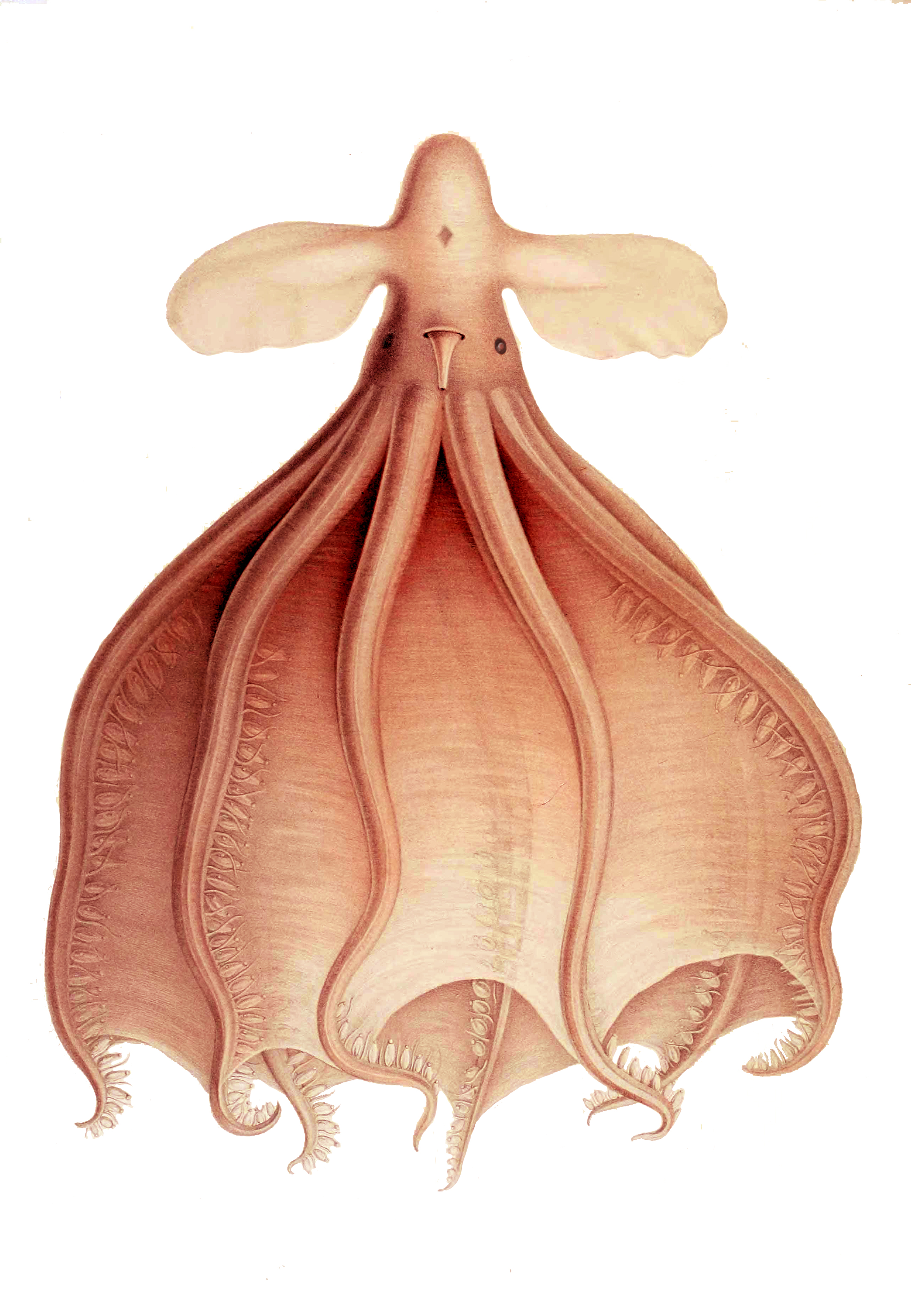
First On The Antarctic Continent (Page 181) BHL46525683
First most commonly refers to: * First, the ordinal form of the number 1 First or 1st may also refer to: Acronyms * Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array * Far Infrared and Sub-millimetre Telescope, of the Herschel Space Observatory * For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, an international youth organization * Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams The Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) is a global forum of incident response and security teams. They aim to improve cooperation between security teams on handling major cybersecurity incidents. FIRST is an association of incid ..., a global forum Arts and entertainment Albums * 1st (album), ''1st'' (album), by Streets, 1983 * 1ST (SixTones album), ''1ST'' (SixTones album), 2021 * First (David Gates album), ''First'' (David Gates album), 1973 * ''First'', by Denise Ho, 2001 * First (O'Bryan album), ''First'' (O'B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Pennell
Commander Harry Lewin Lee Pennell (1882 – 31 May 1916) was a Royal Navy officer who served on the Terra Nova Expedition. He was responsible for the first sighting of Oates Coast on 22 February 1911, and named it after Captain Lawrence Oates. He only spent short periods in Antarctica, returning with the ''Terra Nova'' to wait out the winters of 1911 and 1912 in Lyttelton, New Zealand. Due to the absence of Robert Falcon Scott on land, Pennell assumed the role of command on the Terra Nova, which would bring fresh supplies back to Antarctica with each voyage. Despite not being a part of the main landing party for the Pole, Pennell was a popular member of the expedition. Herbert Ponting, the photographer of the expedition, recalled in his book ''The Great White South'' that Pennell was "the most energetic man I have ever known....when Pennell was not occupied with navigating problems, he was either on watch, or conning from the crow's-nest, or else out on the yard-arms helping the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor L
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to: * Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname Arts and entertainment Film * ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film * ''Victor'' (1993 film), a French short film * ''Victor'' (2008 film), a TV film about Canadian swimmer Victor Davis * ''Victor'' (2009 film), a French comedy * ''Victor'', a 2017 film about Victor Torres by Brandon Dickerson * ''Viktor'' (2014 film), a Franco/Russian film * ''Viktor'' (2024 film), a documentary of a deaf person's perspective during Russian invasion of Ukraine Music * ''Victor'' (Alex Lifeson album), a 1996 album by Alex Lifeson * ''Victor'' (Vic Mensa album), 2023 album by Vic Mensa * "Victor", a song from the 1979 album '' Eat to the Beat'' by Blondie Businesses * Victor Talking Machine Company, early 20th century American recording company, forerunner of RCA Records * Victor Company of Japan, usually known as JVC, a Japanese electronics corporati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Wood, 1st Viscount Halifax
Charles Wood, 1st Viscount Halifax (20 December 1800 – 8 August 1885), known as Sir Charles Wood, 3rd Baronet, between 1846 and 1866, was a British Whigs (British political party), Whig politician and Member of the Parliament. He was Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1846 to 1852, First Lord of the Admiralty from 1855 to 1858, and Secretary of State for India from 1859 to 1866. Background Halifax was the son of Sir Francis Wood, 2nd Baronet of Barnsley, and his wife Anne, daughter of Samuel Buck. He was educated at Eton College, Eton and Oriel College, Oxford, where he studied classics and mathematics. Political career A Liberal Party (UK), Liberal and Member of Parliament from 1826 to 1866, Wood abandoned the seat of Great Grimsby (UK Parliament constituency), Great Grimsby and was returned in 1831 for the pocket borough of Wareham (UK Parliament constituency), Wareham, probably as a paying guest, which arrangement enabled him to remain in London in preparation for the readi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Barrow, 1st Baronet
Sir John Barrow, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1764 – 23 November 1848) was an English geographer, linguist, writer and civil servant best known for serving as the Second Secretary to the Admiralty from 1804 until 1845. Early life Barrow was born the only child of Roger Barrow, a tanner in the village of Dragley Beck, in the parish of Ulverston, Lancashire.Prior to 1 April 1974 Ulverston was in Lancashire He was a pupil at Town Bank Grammar School, Ulverston, but left at the age of 13 to found a Sunday school for poor local children. Barrow was employed as superintending clerk of an iron foundry at Liverpool. At only 16, he went on a whaling expedition to Greenland. By his twenties, he was teaching mathematics, in which he had always excelled, at a private school in Greenwich. China Barrow taught mathematics to the son of Sir George Leonard Staunton; through Staunton's interest, he was attached on the first British embassy to China from 1792 to 1794 as comptroller of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Barrow, 1st Bt By John Jackson
''Sir'' is a formal honorific address in English for men, derived from Sire in the High Middle Ages. Both are derived from the old French "" (Lord), brought to England by the French-speaking Normans, and which now exist in French only as part of "", with the equivalent "My Lord" in English. Traditionally, as governed by law and custom, Sir is used for men who are knights and belong to certain orders of chivalry, as well as later applied to baronets and other offices. As the female equivalent for knighthood is damehood, the ''suo jure'' female equivalent term is typically Dame. The wife of a knight or baronet tends to be addressed as Lady, although a few exceptions and interchanges of these uses exist. Additionally, since the late modern period, Sir has been used as a respectful way to address a man of superior social status or military rank. Equivalent terms of address for women are Madam (shortened to Ma'am), in addition to social honorifics such as Mrs, Ms, or Miss. Etym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Murray (oceanographer)
Sir John Murray (3 March 1841 – 16 March 1914) was a pioneering Canadian-born British oceanographer, marine biologist and limnologist. He is considered to be the father of modern oceanography. Early life and education Murray was born on 3 March 1841, at Cobourg, Canada West (now Ontario). He was the second son of Robert Murray, an accountant, and Elizabeth Macfarlane. His parents had emigrated from Scotland to Ontario in about 1834. He went to school in London, Ontario and later to Cobourg College. In 1858, at the age of 17 he moved to Stirling to live with his grandfather, John Macfarlane, and continue his education at Stirling High School. In 1864, he enrolled at University of Edinburgh to study medicine however he did not complete his studies and did not graduate. In 1868, he joined the whaling ship, ''Jan Mayen'', as ship's surgeon and visited Spitsbergen and Jan Mayen Island. During the seven-month trip, he collected marine specimens and recorded ocean currents, ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Scott Keltie
Sir John Scott Keltie (29 March 1840 – 12 January 1927) was a Scottish geographer, best known for his work with the Royal Geographical Society. History Keltie was born in Dundee and attended school in Perth. He matriculated at the University of St Andrews and the University of Edinburgh. He also completed a course of study at the Theological Hall of the United Presbyterian Church in Edinburgh, but did not go into a religious career. Keltie later moved to London in 1871 to join Macmillan Publishers, where in 1873 he became sub-editor of the journal ''Nature'' and began separately to write articles on geography for ''The Times''. In 1880, he was taken on as editor of ''The Statesman's Yearbook'' for Macmillan. In 1883, Keltie joined the Royal Geographical Society and quickly became heavily involved in its activities. He was later appointed its Inspector of Geographical Education in 1884, and undertook a thorough review of the state of geography education in the UK, producin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |