|
Oligomycin
Oligomycins are macrolides created by ''Streptomyces'' that are strong antibacterial agents but are often poisonous to other organisms, including humans. Function Oligomycins have use as antibiotics. However, in humans, they have limited or no clinical use due to their toxic effects on mitochondria and ATP synthase. Oligomycin A is an inhibitor of ATP synthase. In oxidative phosphorylation research, it is used to prevent stage 3 (phosphorylating) respiration. Oligomycin A inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (FO subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production). The inhibition of ATP synthesis by oligomycin A will significantly reduce electron flow through the electron transport chain; however, electron flow is not stopped completely due to a process known as ''proton leak'' or '' mitochondrial uncoupling''. This process is due to facilitated diffusion of protons into the mitochondrial matrix through an uncoupling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligomycins
Oligomycins are macrolides created by ''Streptomyces'' that are strong antibacterial agents but are often poisonous to other organisms, including humans. Function Oligomycins have use as antibiotics. However, in humans, they have limited or no clinical use due to their toxic effects on mitochondria and ATP synthase. Oligomycin A is an inhibitor of ATP synthase. In oxidative phosphorylation research, it is used to prevent stage 3 (phosphorylating) respiration. Oligomycin A inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (FO subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production). The inhibition of ATP synthesis by oligomycin A will significantly reduce electron flow through the electron transport chain; however, electron flow is not stopped completely due to a process known as ''proton leak'' or ''mitochondrial uncoupling''. This process is due to facilitated diffusion of protons into the mitochondrial matrix through an uncoupling pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. The energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose is released by the cell in the citric acid cycle, producing carbon dioxide and the energetic reducing agent, electron donors NADH and FADH. Oxidative phosphorylation uses these molecules and O2 to ATP synthase, produce ATP, which is used throughout the cell whenever energy is needed. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from the electron donors to a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolide
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but has since been used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential longevity therapeutic. Macrolides are a diverse group with many members of very different properties: * Macrolides with 14-, 15-, or 16-membered rings and two attached sugar molecules are antibiotics that bind to bacterial ribosomes, the key representative being erythromycin. The term "macrolide antibiotics" tend to refer to just this class. * Some macrolides with very large (20+ membered) rings are immunosuppresants, the prototypical one being rapamycin. * Some 23-membered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins. Being passive, facilitated transport does not directly require chemical energy from ATP hydrolysis in the transport step itself; rather, molecules and ions move down their concentration gradient according to the principles of diffusion. Facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion in several ways: # The transport relies on molecular binding between the cargo and the membrane-embedded channel or carrier protein. # The rate of facilitated diffusion is saturable with respect to the concentration difference between the two phases; unlike free diffusion which is linear in the concentration difference. # The temperature dependence of facilitated transport is substantially different due to the presence of an act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diketones
In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl () Functional group, groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their Reactivity (chemistry), reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical (dialdehydes, diketones, diesters, ''etc.'') or unsymmetrical (keto-esters, keto-acids, ''etc.''). 1,2-Dicarbonyls 1,2-Dialdehyde The only 1,2-dialdehyde is glyoxal, . Like many alkyldialdehydes, glyoxal is encountered almost exclusively as its hydrate and oligomers thereof. These derivatives often behave equivalently to the aldehydes since hydra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiro Compounds
In organic chemistry, spiro compounds are compounds that have at least two molecular rings sharing one common atom. Simple spiro compounds are bicyclic (having just two rings). The presence of only one common atom connecting the two rings distinguishes spiro compounds from other bicyclics.For all four categories, see The specific chapters can be found aan respectively, same access date. For the description featuring adjacent atoms for all but the isolated category, see Clayden, op. cit. Spiro compounds may be fully carbocyclic (all carbon) or heterocyclic (having one or more non-carbon atom). One common type of spiro compound encountered in educational settings is a heterocyclic one— the acetal formed by reaction of a diol with a cyclic ketone. The common atom that connects the two (or sometimes three) rings is called the ''spiro atom''. In carbocyclic spiro compounds like spiro .5ndecane, the spiro-atom is a quaternary carbon, and as the ''-ane'' ending implies, these ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolide Antibiotics
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but has since been used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential longevity therapeutic. Macrolides are a diverse group with many members of very different properties: * Macrolides with 14-, 15-, or 16-membered rings and two attached sugar molecules are antibiotics that bind to bacterial ribosomes, the key representative being erythromycin. The term "macrolide antibiotics" tend to refer to just this class. * Some macrolides with very large (20+ membered) rings are immunosuppresants, the prototypical one being rapamycin. * Some 23-membered macrol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
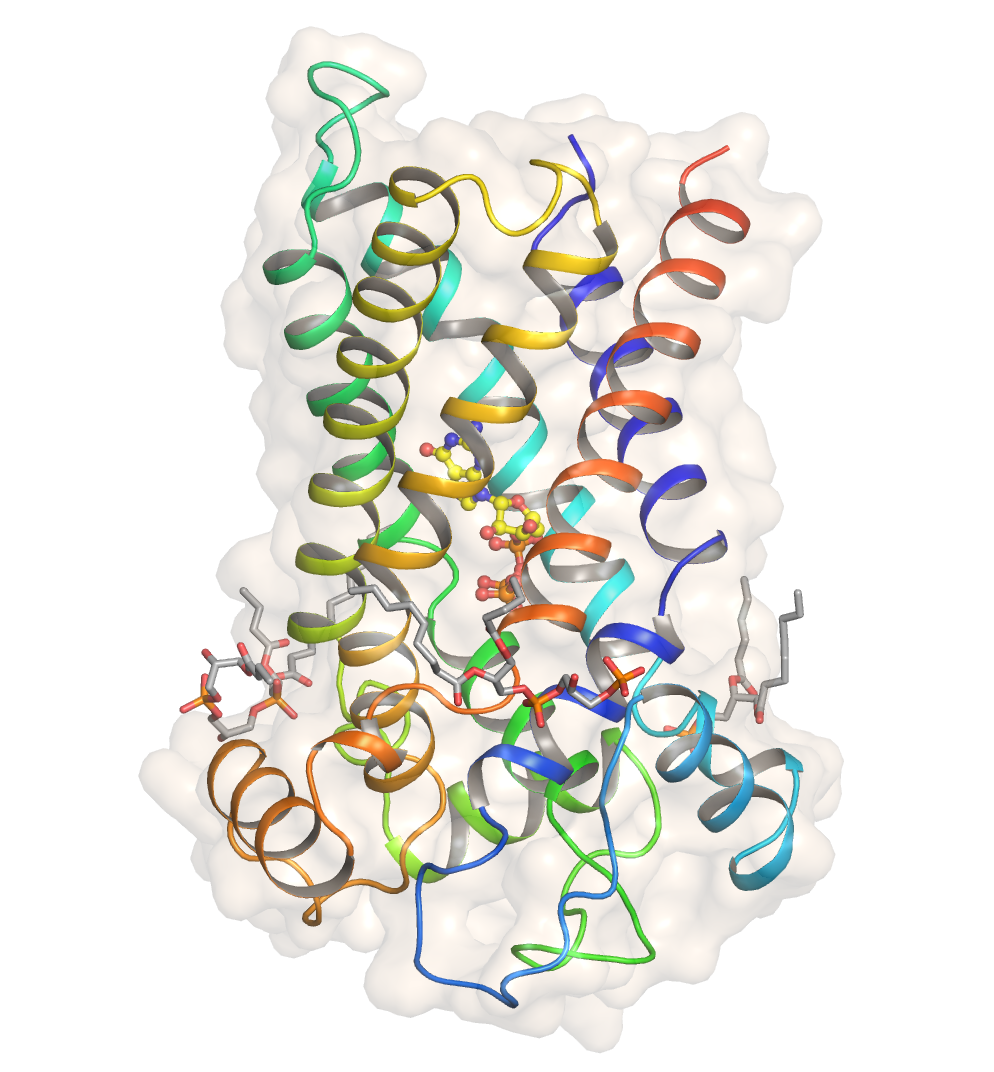
UCP1
Thermogenin (called uncoupling protein by its discoverers and now known as uncoupling protein 1, or UCP1) is a mitochondrial carrier protein found in brown adipose tissue (BAT). It is used to generate heat by non-shivering thermogenesis, and makes a quantitatively important contribution to countering heat loss in babies which would otherwise occur due to their high surface area-volume ratio. Recent findings indicate that the UCP1 protein plays a crucial role in thermogenesis by catalyzing the dissipative production of heat through protons derived from NADH and FADH2. These electron carriers are produced in the TCA cycle from the oxidation of acetyl-CoA, which comes from the breakdown of free fatty acids. Intriguingly, the acetyl-CoA products undergo a recycling process that facilitates their re-utilization, thereby sustaining the cycle known as the HEAT cycle . Structure The atomic structure of human uncoupling protein 1 UCP1 has been solved by cryogenic-electron microscopy. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncoupling Protein
An uncoupling protein (UCP) is a mitochondrial inner membrane protein that is a regulated proton channel or transporter. An uncoupling protein is thus capable of dissipating the proton gradient generated by NADH-powered pumping of protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the mitochondrial intermembrane space. The energy lost in dissipating the proton gradient via UCPs is not used to do biochemical work. Instead, heat is generated. This is what links UCP to thermogenesis. However, not every type of UCPs are related to thermogenesis. Although UCP2 and UCP3 are closely related to UCP1, UCP2 and UCP3 do not affect thermoregulatory abilities of vertebrates. UCPs are positioned in the same membrane as the ATP synthase, which is also a proton channel. The two proteins thus work in parallel with one generating heat and the other generating ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate, the last step in oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondria respiration is coupled to ATP synthesis (ADP phosphorylati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial Matrix
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. It can also be referred as the mitochondrial fluid. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the relatively aqueous cytoplasm. The mitochondrial matrix contains the mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, soluble enzymes, small organic molecules, nucleotide cofactors, and inorganic ions. /sup> The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate, and the beta oxidation of fatty acids. The composition of the matrix based on its structures and contents produce an environment that allows the anabolic and catabolic pathways to proceed favorably. The electron transport chain and enzymes in the matrix play a large role in the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid cycle produces NADH and FADH2 through oxidation that will be reduced in oxidative pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial Uncoupling
An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria by dissociating the reactions of ATP synthesis from the electron transport chain. The result is that the cell or mitochondrion expends energy to generate a proton-motive force, but the proton-motive force is dissipated before the ATP synthase can recapture this energy and use it to make ATP. Because the intracellular supply of protons is replenished, uncouplers actually stimulate cellular metabolism and oxygen consumption (despite their inhibitory effects on oxidative phosphorylation) and increase the energy cost of generating ATP. Uncouplers are capable of transporting protons through mitochondrial and lipid membranes. Description Classical uncouplers have five properties: # the complete release of respiratory control # the substitution of all coupled processes (ATP synthesis ATP synthase is an enzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |