|
Old Sodbury
Old Sodbury is a small village and former civil parish in the valley of the River Frome just below and to the west of the Cotswold escarpment and to the east of Chipping Sodbury and Yate, now in the parish of Sodbury, in the South Gloucestershire district, in the ceremonial county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated in the Hundred of Grumbald's Ash. The village extends from Chipping Sodbury in the West to the Cotswold Edge in the East and is on the Cotswold Way. The Badminton Road ( A432) winds eastwards towards Badminton, Gloucestershire through the village, up to the Cross Hands junction with the A46, which runs along the top of the Cotswold escarpment from Bath to Stroud. In 1931 the parish had a population of 837. On 1 April 1946 the parish was abolished to form Sodbury. The village lies on an old coaching route, and is much more ancient than its westerly neighbour, Chipping Sodbury: hence the name 'Old' Sodbury. Name and fort The name of the village is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Vision Of Britain Through Time
The Great Britain Historical GIS (or GBHGIS) is a spatially enabled database that documents and visualises the changing human geography of the British Isles, although is primarily focussed on the subdivisions of the United Kingdom mainly over the 200 years since the first census in 1801. The project is currently based at the University of Portsmouth, and is the provider of the website ''A Vision of Britain through Time''. NB: A "GIS" is a geographic information system, which combines map information with statistical data to produce a visual picture of the iterations or popularity of a particular set of statistics, overlaid on a map of the geographic area of interest. Original GB Historical GIS (1994–99) The first version of the GB Historical GIS was developed at Queen Mary, University of London between 1994 and 1999, although it was originally conceived simply as a mapping extension to the existing Labour Markets Database (LMDB). The system included digital boundaries for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Edward IV
Edward IV (28 April 1442 – 9 April 1483) was King of England from 4 March 1461 to 3 October 1470, then again from 11 April 1471 until his death in 1483. He was a central figure in the Wars of the Roses, a series of civil wars in England fought between the Yorkist and Lancastrian factions between 1455 and 1487. Edward inherited the Yorkist claim to the throne at the age of eighteen when his father, Richard, Duke of York, was killed at the Battle of Wakefield in December 1460. After defeating Lancastrian armies at Mortimer's Cross and Towton in early 1461, he deposed King Henry VI and took the throne. His marriage to Elizabeth Woodville in 1464 led to conflict with his chief advisor, Richard Neville, Earl of Warwick, known as the "Kingmaker". In 1470, a revolt led by Warwick and Edward's brother George, Duke of Clarence, briefly re-installed Henry VI. Edward fled to Flanders, where he gathered support and invaded England in March 1471; after victories at the battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brictric Son Of Algar
Brictric was a powerful English thane whose many English landholdings, mostly in the West Country, are recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086. Life According to the account by the ''Continuator of Wace'' and others, in his youth Brictric declined the romantic advances of Matilda of Flanders (c. 1031 – 1083), later wife of King William the Conqueror, and his great fiefdom was thereupon seized by her. Whatever the truth of the matter, years later when she was ruling England as regent, she used her authority to confiscate Brictric's lands and threw him into prison, where he died. Samuel Lysons in his '' Magna Britannia'' refers to a Godeva as being the "widow of Brictric, in dower" of two manors in Devon in a footnote to his table of the general division of property at the time of the Domesday survey. Brictric's other lands were granted after Matilda's death in 1083 by her eldest son King William Rufus (1087–1100) to Robert FitzHamon (died 1107), the conqueror of Glamorgan, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetbury
Tetbury is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish inside the Cotswold (district), Cotswold district in Gloucestershire, England. It lies on the site of an ancient hill fort, on which an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon monastery was founded, probably by Ine of Wessex, in 681. The population of the parish was 5,250 in the 2001 census, increasing to 5,472 at the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census. The population further increased to 6,453 in the 2021 Census. History During the Middle Ages, Tetbury became an important market for Cotswolds, Cotswold wool and yarn. Notable buildings in the town include the The Church House, Tetbury, Church House and the late 18th century Gothic revival architecture, Gothic revival parish church of Church of St Mary the Virgin, Tetbury, St Mary the Virgin and St Mary Magdalene and much of the rest of the town centre, dates from the 16th and 17th centuries. The Tetbury Market House, Market House, dating from 1655 with restorations done in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
See Of Worcester
The Diocese of Worcester forms part of the Church of England (Anglican) Province of Canterbury in England. The diocese was founded around 679 by St Theodore of Canterbury at Worcester to minister to the kingdom of the Hwicce, one of the many Anglo Saxon petty-kingdoms of that time. The original borders of the diocese are believed to be based on those of that ancient kingdom. Covering an area of it currently has parishes in: *the County of Worcestershire *the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley *northern Gloucestershire *urban villages along the edge of the south-east of the Metropolitan Borough of Wolverhampton *the Metropolitan Borough of Sandwell Currently the diocese has 190 parishes with 281 churches and 163 stipendiary clergy. The diocese is divided into two archdeaconries: *the Archdeaconry of Worcester *the Archdeaconry of Dudley On its creation the diocese included what is now southern and western Warwickshire (an area known as Felden). On 24 January 1837 the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milred
Milred (died 774) (also recorded as Mildred and Hildred) was an Anglo-Saxon prelate who served as Bishop of Worcester from until his death in 774. Life Milred was consecrated between 743 and 745. He attended the major council of Clofesho in 747, and is found as a regular witness to charters of the Mercian kings Æthelbald and Offa. Milred is known to have travelled to Germany, where he met Boniface and Lull, in the early 750s. A letter from Milred to Lull written soon after his return, on the subject of Boniface's martyrdom shows that the writer was familiar with the works of Virgil and Horace. A work by Milred, a compilation of epigrams and Epigraph (literature), epigraphs on Anglo-Saxon churchmen, some of whom are known only from this work, is now lost apart from a single 10th-century copy of one page, held by the library of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Antiquarian John Leland recorded some other parts of this work, which now survive only in his 16th-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Deorham
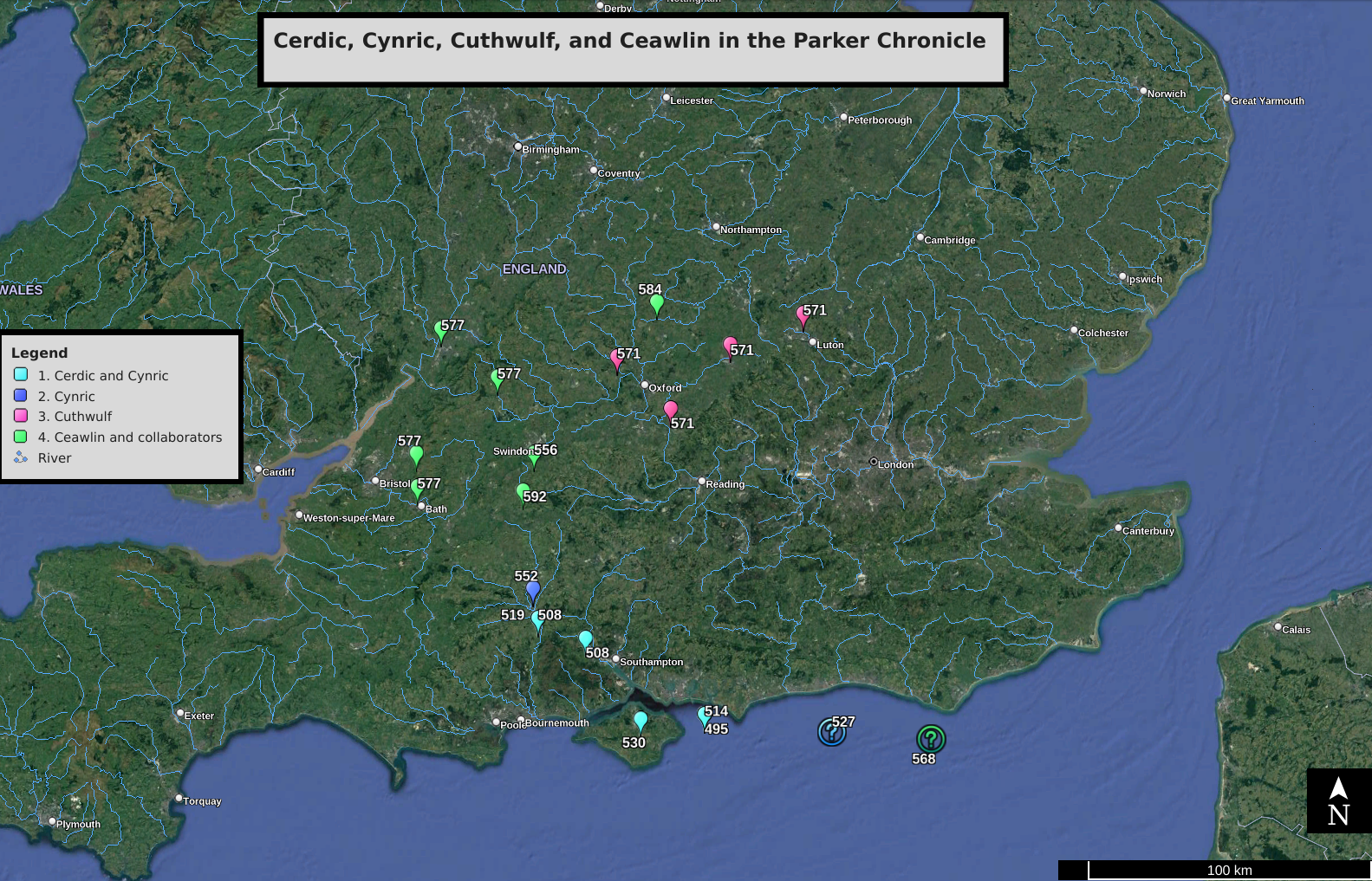
The Battle of Deorham (or Dyrham) is portrayed by the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' as an important military encounter between the West Saxons and the Britons in the West Country in 577. The ''Chronicle'' depicts the battle as a major victory for Wessex's forces, led by Ceawlin and one Cuthwine, resulting in the capture of the Romano-British towns of (Gloucester), (Cirencester), and (Bath). Evidence The only evidence for the battle is an entry in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', in the so-called 'common stock' of annals on which all manuscripts of the ''Chronicle'' build that was edited into its current form in the later ninth century.. As given in the earliest manuscript, the Parker Chronicle, the annal reads: Scholars agree that the place-name here survives in the name of Dyrham in what is now South Gloucestershire, on the Cotswolds escarpment a few miles north of Bath, and that it is here that the battle is portrayed as taking place. The identification of the other ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotswold
The Cotswolds ( ) is a region of central South West England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper River Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and the Vale of Evesham. The area is defined by the bedrock of Jurassic limestone that creates a type of grassland habitat that is quarried for the golden-coloured Cotswold stone. It lies across the boundaries of several English counties: mainly Gloucestershire and Oxfordshire, and parts of Wiltshire, Somerset, Worcestershire, and Warwickshire. The highest point is Cleeve Hill at , just east of Cheltenham. The predominantly rural landscape contains stone-built villages, towns, stately homes and gardens featuring the local stone. A large area within the Cotswolds has been designated as a National Landscape (formerly known as Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, or AONB) since 1966. The designation covers , with boundaries roughly across and long, stretching south-west from just south of St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillfort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roman Empire, Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of Earthworks (Archaeology), earthworks or stone Rampart (fortification), ramparts, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. If enemies were approaching, the inhabitants would spot them from a distance. Prehistoric Europe saw a growing population. It has been estimated that in about 5000 BC during the Neolithic between 2 million and 5 million lived in Europe; in the Late Iron Age it had an estimated population of around 15 to 30 million. Outside Greece and Italy, which were more densely populated, the vast majority of settlements in the Iron Age were small, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by the Latin name , meaning "Book of Winchester, Hampshire, Winchester", where it was originally kept in the royal treasury. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' states that in 1085 the king sent his agents to survey every shire in England, to list his holdings and dues owed to him. Written in Medieval Latin, it was Scribal abbreviation, highly abbreviated and included some vernacular native terms without Latin equivalents. The survey's main purpose was to record the annual value of every piece of landed property to its lord, and the resources in land, labour force, and livestock from which the value derived. The name "Domesday Book" came into use in the 12th century. Richard FitzNeal wrote in the ( 1179) that the book was so called because its de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |