|
Ogurs
The Onoghurs, Onoğurs, or Oğurs (Ὀνόγουροι, Οὔρωγοι, Οὔγωροι; Onογurs, Ογurs; "ten tribes", "tribes") were a group of Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centuries, and spoke an Oghuric language. Etymology The name ''Onoğur'' is widely thought to derive from ''On-Oğur'' "ten Oğurs (tribes)". Modern scholars consider Turkic terms for tribe ''oğuz'' and ''oğur'' to be derived from Turkic ''*og/uq'', meaning "kinship or being akin to". The terms initially were not the same, as ''oq/ogsiz'' meant "arrow", while ''oğul'' meant "offspring, child, son", ''oğuš/uğuš'' was "tribe, clan", and the verb ''oğša-/oqša'' meant "to be like, resemble". The modern name of "Hungary" (see name of Hungary) is usually believed to be derived from On-Oğur (> (H)Ungari). Language The Onoghuric or Oghuric languages are a branch of the Turkic languages. Some scholars suggest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghuric Languages
The Oghuric, Onoguric or Oguric languages (also known as Bulgar, Bulgharic, Bolgar, Pre-Proto-Bulgaric or Lir-Turkic and r-Turkic) are a branch of the Turkic language family. The only extant member of the group is the Chuvash language. The first to branch off from the Turkic family, the Oghuric languages show significant divergence from other Turkic languages, which all share a later common ancestor. Languages from this family were spoken in some nomadic tribal confederations, such as those of the Onogurs or Ogurs, Bulgars and Khazars. History The Oghuric languages are a distinct group of the Turkic languages, standing in contrast to Common Turkic. Today they are represented only by Chuvash. The only other language which is conclusively proven to be Oghuric is the long-extinct Bulgar, while Khazar may be a possible relative within the group. The Hunnic language, spoken by the European Huns in the late fourth and fifth centuries AD, is occasionally described as a form of Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
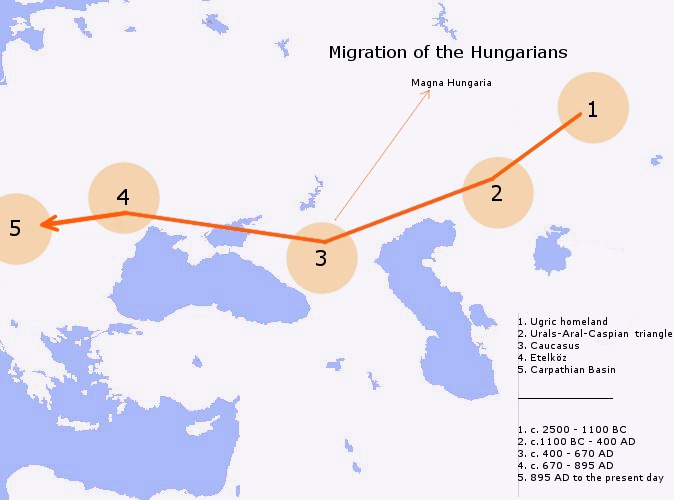
Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary lies within the drainage basin of the Danube, Danube River and is dominated by great lowland plains. It has a population of 9.6 million, consisting mostly of ethnic Hungarians, Hungarians (Magyars) and a significant Romani people in Hungary, Romani minority. Hungarian language, Hungarian is the Languages of Hungary, official language, and among Languages of Europe, the few in Europe outside the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Budapest is the country's capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, largest city, and the dominant cultural and economic centre. Prior to the foundation of the Hungarian state, various peoples settled in the territory of present-day Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuvash Language
Chuvash ( , ; , , ) is a Turkic languages, Turkic language spoken in European Russia, primarily in the Chuvashia, Chuvash Republic and adjacent areas. It is the only surviving member of the Oghur languages, Oghur branch of Turkic languages, one of the two principal branches of the Turkic family. The writing system for the Chuvash language is based on the Cyrillic script, employing all of the letters used in the Russian alphabet and adding four letters of its own: Ӑ, Ӗ, Ҫ and Ӳ. Distribution Chuvash is the native language of the Chuvash people and an official language of Chuvashia Republic, Chuvashia. There are contradictory numbers regarding the number of people able to speak Chuvash nowadays; some sources claim it is spoken by 1,640,000 persons in Russia and another 34,000 in other countries and that 86% of ethnic Chuvash and 8% of the people of other ethnicities living in Chuvashia claimed knowledge of Chuvash language during the 2002 Russian Census, 2002 census. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is the native language of the Russians. It was the ''de facto'' and ''de jure'' De facto#National languages, official language of the former Soviet Union.1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 Russian has remained an official language of the Russia, Russian Federation, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Russian language in Israel, Israel. Russian has over 253 million total speakers worldwide. It is the List of languages by number of speakers in Europe, most spoken native language in Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Benjamin Golden
Peter Benjamin Golden (born 1941) is an American professor emeritus of History, Turkish and Middle Eastern Studies at Rutgers University. He has written many books and articles on Turkic peoples, Turkic and Central Asian studies, such as ''An introduction to the history of the Turkic peoples''. Golden grew up in New York and attended High School of Music & Art, Music & Art High School. He graduated from City University of New York, CUNY Queens College, City University of New York, Queens College in 1963, before obtaining his Master of Arts, M.A. and Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. in History from Columbia University in 1968 and 1970, respectively. Golden also studied at the School of Language and History – Geography, Dil ve Tarih – Coğrafya Fakültesi (School of Language and History – Geography) in Ankara from 1967 to 1968. He taught at Rutgers University from 1969 until his retirement in 2012. He was Director of the Middle Eastern Studies Program at Rutgers from 2008 to 2011. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onoğurs
The Onoghurs, Onoğurs, or Oğurs (Ὀνόγουροι, Οὔρωγοι, Οὔγωροι; Onογurs, Ογurs; "ten tribes", "tribes") were a group of Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centuries, and spoke an Oghuric language. Etymology The name ''Onoğur'' is widely thought to derive from ''On-Oğur'' "ten Oğurs (tribes)". Modern scholars consider Turkic terms for tribe ''oğuz'' and ''oğur'' to be derived from Turkic ''*og/uq'', meaning "kinship or being akin to". The terms initially were not the same, as ''oq/ogsiz'' meant "arrow", while ''oğul'' meant "offspring, child, son", ''oğuš/uğuš'' was "tribe, clan", and the verb ''oğša-/oqša'' meant "to be like, resemble". The modern name of "Hungary" (see name of Hungary) is usually believed to be derived from On-Oğur (> (H)Ungari). Language The Onoghuric or Oghuric languages are a branch of the Turkic languages. Some scholars sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Language
Belarusian (, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language. It is one of the two Languages of Belarus, official languages in Belarus, the other being Russian language, Russian. It is also spoken in parts of Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, Ukraine, and the United States by the Belarusian diaspora. Before Belarus Dissolution of the Soviet Union, gained independence in 1991, the language was known in English language, English as ''Byelorussian'' or ''Belorussian'', or alternatively as ''White Russian''. Following independence, it became known as ''Belarusian'', or alternatively as ''Belarusan''. As one of the East Slavic languages, Belarusian shares many grammatical and lexical features with other members of the group. To some extent, Russian, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and Belarusian retain a degree of mutual intelligibility. Belarusian descends from a language generally referred to as Ruthenian language, Ruthenian (13th to 18th centuries), which had, in turn, descend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Peoples
Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to the Turkic subfamily...". "The Turkic peoples represent a diverse collection of ethnic groups defined by the Turkic languages." According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia, potentially in the Altai-Sayan region, Mongolia or Tuva.: "The ultimate Proto-Turkic homeland may have been located in a more compact area, most likely in Eastern Mongolia": "The best candidate for the Turkic Urheimat would then be northern and western Mongolia and Tuva, where all these haplogroups could have intermingled, rather than eastern and southern Mongolia..." Initially, Proto-Turkic speakers were potentially both hunter-gatherers and farmers; they later became nomadic Pastoralism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovene Language
Slovene ( or ) or Slovenian ( ; ) is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic language of the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. Most of its 2.5 million speakers are the inhabitants of Slovenia, the majority of them ethnic Slovenes. As Slovenia is part of the European Union, Slovene is also one of its 24 Languages of the European Union, official and working languages. Its grammar is highly fusional languages, fusional, and it has a Dual (grammatical number), dual grammatical number, an archaic feature shared with some other Indo-European languages. Two accentual norms (one characterized by Pitch-accent language, pitch accent) are used. Its flexible word order is often adjusted for emphasis or stylistic reasons, although basically it is an subject–verb–object word order, SVO language. It has a T–V distinction: the use of the V-form demonstrates a respectful attitude towards superiors and the elderly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denis Sinor
Denis Sinor (born Dénes Zsinór, April 17, 1916 in Kolozsvár (Austria-Hungary, now Cluj-Napoca, Romania) – January 12, 2011 in Bloomington, Indiana) was a Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Central Asian Studies at the Department of Central Eurasian Studies at Indiana University and a tenured lecturer at Cambridge University between 1948 and 1962, and was one of the world's leading scholars for the history of Central Asia. Under his directorship, the Central Asian Studies at Indiana University became one of the world's foremost centers for Central Asian history, languages and linguistics. He grew up in Hungary and Switzerland and went to university in Budapest. During the Second World War, he was a member of the French resistance, served in the French army, and became a French citizen. Sinor wrote eight books and edited an additional thirteen. He authored more than 160 articles in several languages such as English, German, French, Hungarian, Russian and many other, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |