|
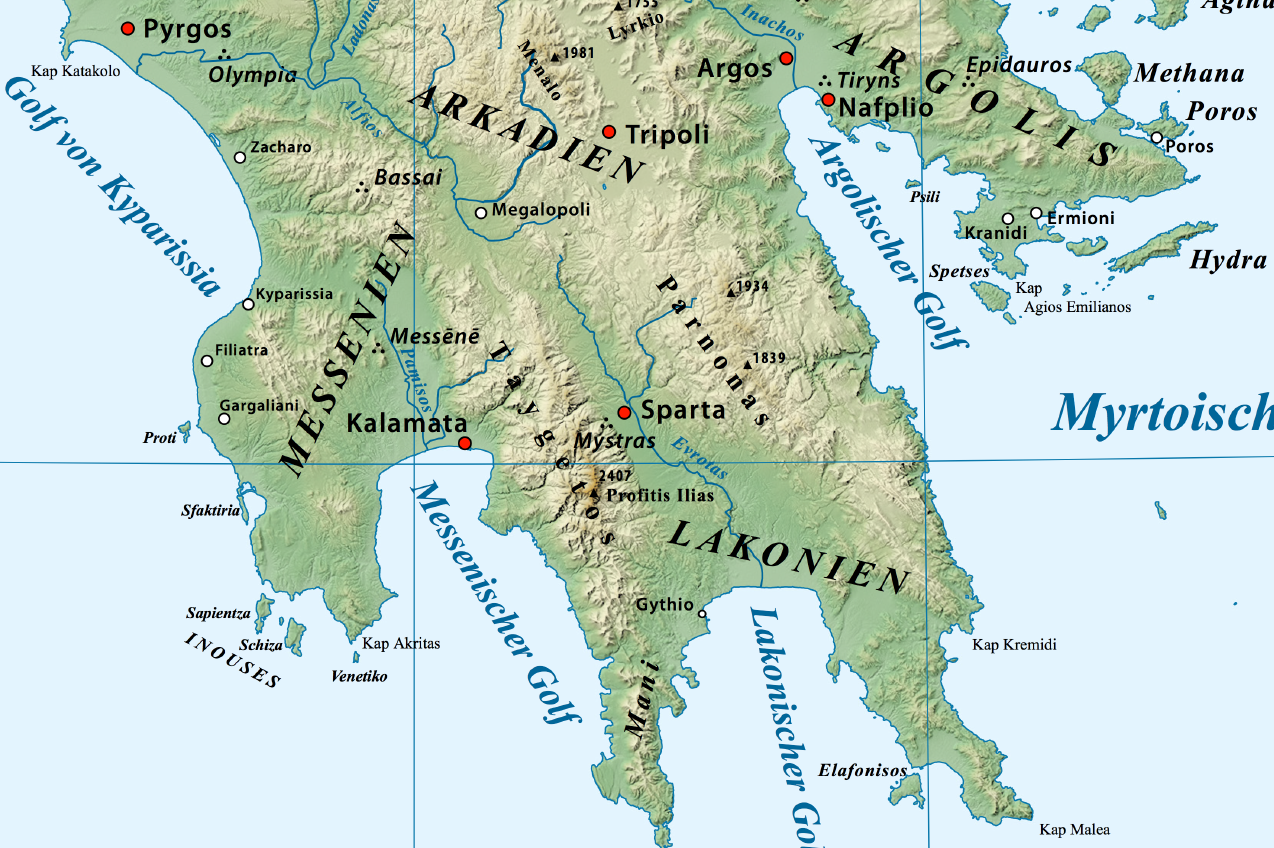
Oenus (river)
The Oenus (Ancient Greek: , - ''Oinountas'', also called ''Kelefina'') is a river in the Peloponnese peninsula, southern Greece. It rises in the watershed of Mt. Parnon, and, after flowing in a general southwesterly direction, falls into the Eurotas, at the distance of little more than a mile from Sparta. ( Polyb. ii. 65, 66; Liv. xxxiv. 28.) The principal tributary of the Oenus was the Gorgylus (Greek: Γόργυλος, Polyb. ii. 66), probably the river of Vrestená. (Leake, ''Peloponnesiaca'', p. 347.) The municipal unit Oinountas, part of the municipality Sparta Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ..., was named after the river Oenus. References * Landforms of Laconia Rivers of Greece Rivers of Peloponnese (region) 1Oenus {{Greece-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, spanning List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands and nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions. It has a population of over 10 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilisation and the birthplace of Athenian democracy, democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major History of science in cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurotas (river)
The Evrotas (Modern Greek: ) or Eurotas () is the main river of Laconia and one of the major rivers of the Peloponnese, in Greece. The river's springs are located just northwest of the border between Laconia and Arcadia, at Skortsinos. The river is also fed by underwater springs at Pellana and by tributaries coursing down from Mt. Taygetos and Mt. Parnon, which flank the Evrotas Valley to the west and east, respectively. The river is long, flowing in a north-south direction and emptying into the Laconian Gulf. Its drainage basin is . Etymology The classical Evrotas was changed to Iri in the Middle Ages and only changed back to Evrotas in recent times. Evrotas, however, is not the most ancient name of the river. It does not appear in the works of Homer, which purport to recount the stories and geography of Mycenaean Greece. In that legendary time, the Dorians are not known to have been present in the Evrotas Valley. At some time prior to being called Evrotas, the river was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea (, ; or , ; , ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania (and western Apulia, Italy) to the north, and the west coast of Greece, including the Peloponnese. All major islands in the sea, which are located in the east of the sea, belong to Greece. They are collectively named the Ionian Islands, the main ones being Corfu, Kefalonia, Zakynthos, Lefkada, and Ithaca. There are ferry routes between Patras and Igoumenitsa, Greece, and Brindisi and Ancona, Italy, that cross the east and north of the Ionian Sea, and from Piraeus westward. Calypso Deep, the deepest point in the Mediterranean at , is in the Ionian Sea, at . The sea is one of the most seismically active areas in the world. Etymology The name ''Ionian'' comes from the Greek word . Its etymology is unknown. Ancient G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century, the peninsula was known as the Morea, a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form. The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the mainland by several bridges across the canal, including two submers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parnon
Parnon or Parnonas () or Malevos (Μαλεβός) is a mountain range, or massif, on the east of the Laconian plain and the Evrotas Valley. It is visible from Athens above the top of the Argive mountains. The western part is in the Laconia prefecture and the northeastern part is in the Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia prefecture. The Parnon range separates Laconia from Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia. Its summit offers panoramic views of southeastern Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia and South Kynouria and much of Laconia that includes the northern and the central portions and reaches as far as the Taygetos mountains. It also views a part of the central Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia and the southern Argolis prefectures. It views the Myrtoan Gulf, Myrtoan and the Laconian Gulfs. Geography Physical The Parnon Massif is divided into three parts.Unless otherwise cited this section relies heavily on The northernmost, which is the highest, runs from just north of Ano Doliana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 BC, recording in detail events in Italy, Iberia, Greece, Macedonia, Syria, Egypt and Africa, and documented the Punic Wars and Macedonian Wars among many others. Polybius' ''Histories'' is important not only for being the only Hellenistic historical work to survive in any substantial form, but also for its analysis of constitutional change and the mixed constitution. Polybius' discussion of the separation of powers in government, of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", all influenced Montesquieu's '' The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's '' Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in 753 BC through the reign of Augustus in Livy's own lifetime. He was on good terms with members of the Julio-Claudian dynasty and was a friend of Augustus. Livy encouraged Augustus’s young grandnephew, the future emperor Claudius, to take up the writing of history. Life Livy was born in Patavium in northern Italy, now modern Padua, probably in 59 BC. At the time of his birth, his home city of Patavium was the second wealthiest on the Italian peninsula, and the largest in the province of Cisalpine Gaul (northern Italy). Cisalpine Gaul was merged into Italy proper during his lifetime and its inhabitants were given Roman citizenship by Julius Caesar. In his works, Livy often expressed his deep affection and pride for Patavium, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oinountas
Oinountas () is a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Sparta, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 301.812 km2. The name originates from the Oinountas, a small river that traverses the municipality. Subdivisions The municipal unit Oinountas is subdivided into the following communities (constituent villages in brackets): * Koniditsa (Koniditsa, Kopelia, Kouremenos) * Sellasia * Theologos (Agios Ioannis, Theologos, Kalyvia Theologou) * Vamvakou (Vamvakou, Megali Vrysi) * Varvitsa * Vasaras (Vasaras, Veria) * Voutianoi * Vresthena Geography The municipal unit Oinountas covers the area between the northeastern part of the Evrotas Valley up to the ridge of Parnon Mountain. The river Oinountas flows through the southeastern part of the municipal unit. History The municipality Oinountas was first established in 1835, the seat of administration being Vamvakou. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta (modern)
Sparta (, ) is a city and municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. It lies at the site of ancient Sparta within the Evrotas Valley. The municipality was merged with six nearby municipalities in 2011, for a total population (as of 2021) of 32,786, of whom 17,773 lived in the city. History Beginning in the 13th century, the political and cultural center of Laconia shifted to Mystras, some 4 km to the west. The settlement at ancient Sparta, named Lacedaemonia, continued to exist, although greatly depopulated, until modern times as a town of a few thousand people who lived among the ruins, in the shadow of Mystras. The Palaiologos family (the last Byzantine Greek imperial dynasty) also lived in Mystras. The Despotate of the Morea was captured by the Ottomans under Mehmed II in 1460. In 1834, after the Greek War of Independence, King Otto of Greece decreed the town should be expanded into a city. Modern-day Sparta, the capital of the prefecture of Lakonia, lies on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |