|
Oenotria
The Oenotrians or Enotrians were an ancient Italic people who inhabited a territory in Southern Italy from Paestum to southern Calabria. By the sixth century BC, the Oenotrians had been absorbed into other Italic tribes. Etymology A likely derivation of the ethnonym ''Oenotrian'' is the Greek (), as the Oenotrians inhabited a territory rich in vineyards, with ''Oenotria'' or ''Enotria'' () being extended to refer to the entirety of Southern Italy. Hesychius mentions the word (), a kind of a vine stake. History It is thought that the Oenotrians represent the southern branch of a very old ethno-linguistic group, different from the proto-Latin one, which occupied the Tyrrhenian Sea area from Liguria to Sicily ( Ligurian/ Sicanian layer). They are generally depicted as belonging to the Pelasgians. According to Antoninus Liberalis and Hellanicus, their arrival triggered the migration of the Elymians to Sicily around 1260 BC. Ancient authors from the 1st century BC state that O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian Sea to the west. It has 1,832,147 residents as of 2025 across a total area of . Catanzaro is the region's capital. Calabria is the birthplace of the name of Italy, given to it by the Ancient Greeks who settled in this land starting from the 8th century BC. They established the first cities, mainly on the coast, as Greek colonisation, Greek colonies. During this period Calabria was the heart of Magna Graecia, home of key figures in history such as Pythagoras, Herodotus and Milo of Croton, Milo. In Roman times, it was part of the ''Regio III Lucania et Bruttii'', a region of Roman Italy, Augustan Italy. After the Gothic War (535–554), Gothic War, it became and remained for five centuries a Byzantine empire, Byzantine dominion, fully recove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italus
Italus or Italos (from ) was a legendary king of the Oenotrians, ancient people of Italic origin who inhabited the region now called Calabria, in southern Italy. In his ''Fabularum Liber'' (or ''Fabulae''), Gaius Julius Hyginus recorded the myth that Italus was a son of Penelope and Telegonus (a son of Odysseus). According to Aristotle ( ''Politics'') and Thucydides (''History of the Peloponnesian War''), Italus was the eponym of Italy (''Italia''). Aristotle, writing in the 4th century BCE, relates that, according to tradition, Italus converted the Oenotrians from a pastoral society to an agricultural one and gave them various ordinances, being the first to institute their system of common meals. Writing centuries later, the Greek historian Dionysius of Halicarnassus Dionysius of Halicarnassus (, ; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucani (ancient People)
The Lucanians () were an Italic tribe living in Lucania, in what is now southern Italy, who spoke the Oscan language, a member of the Italic languages. Today, the inhabitants of the Basilicata region are still called Lucani, and so is their dialect. Language and writing The Lucani spoke the Oscan language. There are a few inscriptions and coins in the area that survive from the 4th or 3rd century BC; they use the Greek alphabet. History Around the middle of the 5th century BC, the Lucani moved south into Oenotria, driving the indigenous tribes, known to the Greeks as Oenotrians, Chones, and Lauternoi, into the mountainous interior. The Lucanians were engaged in hostilities with the Greek colony of Taras/Tarentum and with Alexander, king of Epirus who was called in by the Tarentine people to their assistance in 334 BC. In 331, treacherous Lucanian exiles killed Alexander of Epirus. In 298 they made alliance with Rome, and Roman influence was extended by the colonies of Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
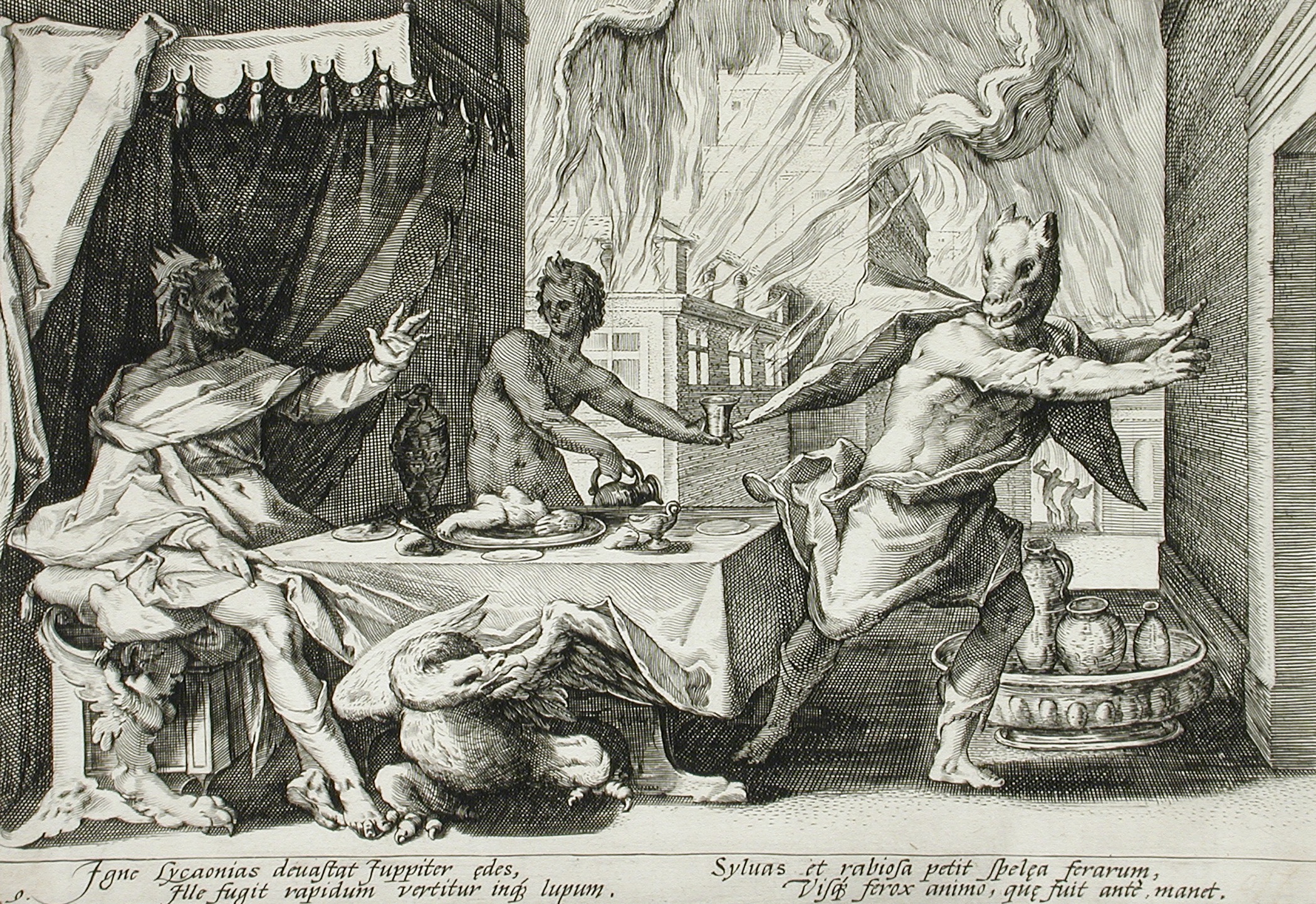
Lycaon (king Of Arcadia)
In Greek mythology, Lycaon (/laɪˈkeɪɒn/; , ) was a king of Arcadia who, in the most popular version of the myth, killed and cooked his son Nyctimus and served him to Zeus, to see whether the god was sufficiently all-knowing to recognize human flesh. Disgusted, Zeus transformed Lycaon into a wolf, while Nyctimus was restored to life. Despite being notorious for his horrific deeds, Lycaon was also remembered as a culture hero: he was believed to have founded the city Lycosura, to have established a cult of Zeus Lycaeus and to have started the tradition of the Lycaean Games, which Pausanias thinks were older than the Panathenaic Games. According to Gaius Julius Hyginus (d. AD 17), Lycaon dedicated the first temple to Hermes of Cyllene.Hyginus, ''Fabulae'225/ref> Family Lycaon was the son of Pelasgus and either the Oceanid Meliboea or Deianira, daughter of an elder Lycaon. His wife was called Cyllene, an Oread nymph who gave her name to Mount Cyllenê though sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italic People
The concept of Italic peoples is widely used in linguistics and historiography of ancient Italy. In a strict sense, commonly used in linguistics, it refers to the Osco-Umbrians and Latino-Faliscans, speakers of the Italic languages, a subgroup of the Indo-European language family. In a broader sense, commonly used in historiography, all the ancient peoples of Italy are referred to as Italic peoples, including the non-Indo-European ones, as Rhaetians, Ligures and Etruscans. As the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins achieved a dominant position among these tribes, by virtue of the expansion of the Ancient Rome, Roman civilization, the other Italic tribes adopted Latin language and culture as part of the process of Romanization (cultural), Romanization. Classification The Italics were an ethnolinguistic group who are identified by their use of the Italic languages, which form one of the branches of Indo-European languages. Outside of the specialised linguistic literature, the term is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicani
The Sicani or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, according to Diodorus Siculus, the boundary with the last in the ancient Himera river ( Salso) after a series of battles between these tribes. History The Sicani are the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name. In the 5th century BCE, the Greek historian Thucydides, claims that the Sicani originated on the Iberian Peninsula, from around a river they called "Sicanus" and had migrated to Sicily following an invasion by the Ligurians. (The name Sicanus has been linked to the river known in modern Spanish as the Júcar.) Thucydides' source is unknown, although he often draws on the Sicilian historian Antiochus of Syracuse. Conversely, Timaeus of Tauromenium (writing c. 300 BCE) considers the Sicani to be indigenous to Sicily. A third theory, put forward by some modern schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Peoples Of Italy
This list of ancient peoples living in Italy (geographical region), Italy summarises the many different Italian populations that existed in antiquity. Among them, the Roman people, Romans succeeded in Romanization (cultural), Romanizing the entire Italian peninsula following the Roman expansion in Italy, which provides the time-window in which most of the names of the remaining ancient Italian peoples first appear in existing written documentation. Many names are exonyms assigned by the ancient writers of works in ancient Greek and Latin, while others are scholarly inventions. Nearly all of these peoples and tribes spoke Indo-European language, Indo-European languages: Italic peoples, Italics, Celts, Ancient Greeks, and tribes likely occupying various intermediate positions between these language groups. On the other hand, some Italian peoples (such as the Rhaetians, Camuni, Etruscans) likely spoke Pre-Indo-European languages, non- or pre-Indo-European languages. In addition, peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metapontum
Metapontum or Metapontium () was an ancient city of Magna Graecia, situated on the gulf of Taranto, Tarentum, between the river Bradanus and the Casuentus (modern Basento). It was distant about 20 km from Heraclea (Lucania), Heraclea and 40 from Tarentum. The ruins of Metapontum are located in the frazione of Metaponto, in the comune of Bernalda, in the Province of Matera, Basilicata region, southern Italy. History Foundation Though Metapontum was an ancient ancient Greece, Greek Achaean colony, various traditions assigned to it a much earlier origin. Strabo and Gaius Julius Solinus, Solinus ascribe its foundation to a body of Pylos, Pylians, a part of those who had followed Nestor (mythology), Nestor to Troy. Justin (historian), Justin, conversely, tells us it was founded by Epeius of Phocis, Epeius; in proof of which the inhabitants showed, in a temple of Minerva, the tools which the hero had used to build the Trojan Horse. Another tradition, reported by Ephorus, says ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions. The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or culture of the Historical region, historical and cultural region that was once politically under the administration of the former Kingdoms of Kingdom of Naples, Naples and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily (officially denominated as one entity and , i.e. "Kingdom of Sicily on the other side of Strait of Messina, the Strait" and "across the Strait") and which later shared a common organization into Italy's largest List of historical states of Italy, pre-unitarian state, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The island of Sardinia, which was not part of the aforementioned polity and had been under the rule of the Alps, Alpine House of Savoy, which would eventually annex the Bourbons' southern Italian kingdom altogether, is nonetheless often subsumed into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elymians
The Elymians () were an ancient tribe, tribal people who inhabited the western part of Sicily during the Bronze Age and Classical antiquity. Origins According to Thucydides, the Elymians were refugees coming from the destroyed Troy. Instead for Hellanicus of Lesbos they arrived in Sicily coming from Italy, driven out by the Oenotrians. Furthermore for the Greek historian, the Elymians would also have contributed to the formation of the Sicels. The Elymian language is considered to have been a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. While an ancient tradition that the Elymians came from Troy – and were originally an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian people – is corroborated by archeological data, the more generally supported opinion is that Elymian was an Italic language, with similarities to Classical Latin, Latin. Hence an Italic peoples, Italic origin for the Elymians is considered to be more likely. Greek historian Philistus refers to the presenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Peoples Of Italy
This list of ancient peoples living in Italy summarises the many different Italian populations that existed in antiquity. Among them, the Romans succeeded in Romanizing the entire Italian peninsula following the Roman expansion in Italy, which provides the time-window in which most of the names of the remaining ancient Italian peoples first appear in existing written documentation. Many names are exonyms assigned by the ancient writers of works in ancient Greek and Latin, while others are scholarly inventions. Nearly all of these peoples and tribes spoke Indo-European languages: Italics, Celts, Ancient Greeks, and tribes likely occupying various intermediate positions between these language groups. On the other hand, some Italian peoples (such as the Rhaetians, Camuni, Etruscans) likely spoke non- or pre-Indo-European languages. In addition, peoples speaking languages of the Afro-Asiatic family, specifically the largely Semitic Phoenicians and Carthaginians, settled and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italic Tribes
The concept of Italic peoples is widely used in linguistics and historiography of ancient Italy. In a strict sense, commonly used in linguistics, it refers to the Osco-Umbrians and Latino-Faliscans, speakers of the Italic languages, a subgroup of the Indo-European language family. In a broader sense, commonly used in historiography, all the ancient peoples of Italy are referred to as Italic peoples, including the non-Indo-European ones, as Rhaetians, Ligures and Etruscans. As the Latins achieved a dominant position among these tribes, by virtue of the expansion of the Roman civilization, the other Italic tribes adopted Latin language and culture as part of the process of Romanization. Classification The Italics were an ethnolinguistic group who are identified by their use of the Italic languages, which form one of the branches of Indo-European languages. Outside of the specialised linguistic literature, the term is also used to describe the ancient peoples of Italy as define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |