|
Odhavram
Odhavram (4 October 1889 – 13 January 1957) was an Indian religious teacher. He championed Gurukula education to improve the situation of the poor. Early life Odhavram was born in Jakhau, a small village located on the west coast of Gujarat, India, in the district of Kutch. He was born in an agrarian Bhanushali family in 1889 on the festival of Ram Navami, an auspicious day in the Hindu calendar. He was named Udhav. As a child, he showed interest in religious texts. He loved music and singing traditional Indian poems known as Bhajans. When he was 9 years old he studied under Guru Shanakaranand from Mandvi, Kutch. He learned Sanskrit and the Vedas and often took the Bhagavad Gita to school to narrate single lines to his friends. He liked to discuss the Gita with pandits and scholars of Hindu law, philosophy and music. After a life-threatening accident at an ashram, he returned to Jakhau to dedicate his life to Hinduism and the advancement of Kutch and Gujarat. Ishwar Ashram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandhay
Vandhay or Vandhai is a village in Bhuj Taluka of Kutch District of Gujarat. It is .25 km from Bhuj, district and taluka headquarters. It is a very small village with a population of around 350 people and about 70 houses. The nearest big villages are Deshalpar and Anandsar, Madhapar and Jiyapar. Nearby towns are Anjar (69.4 km), Nakhatrana (30.4 km), Mundra (61.2 km), Gandhidham (88.9 km) and Bhuj (27.3 km). However, this village has religious significance for many Hindu communities of Kutch as the Ashrams of one of the famous saint of Kutch Sant Shri Odhavramji is located here. Odhavramji started the first Gurukul of Kutch, named ''Ishwarramji Gurukul'', in year 1937 and Blind School in 1938 both of which are in the village. Also the Gadi of Ramanandi sect headed by Sadhu Val Dasji, a contemporary of Sant Garib Dasji of Kukma of same sect is here.Shree Kutch Gurjar Kshatriya Samaj : A Brief History & Glory of our Fore-Fathers. Calcutta. Auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhanushali
Bhanushali is a Suryavanshi Kshtriya Hindu community. The majority reside in Kutch district of the Indian state of Gujarat. Some are also found in the Saurashtra region and other parts of Gujarat. Some have also moved to Thane and Mumbai region of Maharashtra. They speak Kutchi language. Origins Bhanushali is a descendant of Lord Rama's son Lav. The name "Bhanushali", translates to "Radiant sun" or "Bearers of the Sun ". Bhanushali is derived from the mythological king Bhanusal. The community was also known as Vegusor/Vagar after the place of Vegukot or Vegugad in Rann of Kutch. Bhanushalis are mainly divided in to three sections, i.e Kutchi Bhanushalis and halari Bhanushali and Sindhi Bhanushalis. The Caste is vegetarian. Bhanushalis have 96 exogamous sub divisions, some of them are: Mange, Vadore, Gajra, Gori, Bhadra, Nanda, Harbala etc. History The Bhanushalis are of suryavanshi Kshatriya descent. And they were warriors before the rule of the british empire came to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakhau
Jakhau (''Ja-kha-oo'', pronounced as Ja-kho by locals) is a village in Gujarat, western India. Administratively, it is under Abdasa Taluka, Kutch District, of Gujarat. Jakhau is 17 km by road west-southwest of Naliya, the taluka headquarters. Jakhau Salt, the port of Jakhau, is situated a further 15 km westwards. History The village and port are named after the legendary Jakh Botera who were shipwrecked on the Kutch coast and came ashore at Jakhau. Variously described as tall and fair-complexioned with an advanced culture (hence why locals name them Yakshas-demigods), their traditional number is 72 with at least one woman. Their origins are obscure-but one school of thought is that they were of Zoroastrian Irani or Parsi origins and good at horsemanship, medicine and archery. One cruel king puanra is said to have been controlled/put to an end by them-thus they attained gods status in region. In the Middle Ages, Jakhau was a thriving port and warehousing village. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patidar
Patidar (Gujarati language, Gujarati: ), formerly known as Kunbi, Kanbi (Gujarati language, Gujarati: ), is an Indian land-owning and peasant Caste system in India, caste and community native to Gujarat. The community comprises at multiple subcastes, most prominently the Leva Patel, Levas and Kadava Patidar, Kadvas. They form one of the dominant castes in Gujarat. The title of Patidar originally conferred to the land owning aristocratic class of Gujarati Kanbis; however, it was later applied ''en masse'' to the entirety of the Kanbi population who lay claim to a land owning identity, partly as a result of land reforms during the British Raj. According to 2011 Socio Economic and Caste Census their population is approximately 1.5 crores and they form 21.7% of Gujarat's population. History The Kanbi/Patidars are divided into several subcastes. The Levas are from central Gujarat and the Kadavas are from North Gujarat, northern Gujarat. The Matis, who are a sub-subcaste of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Kutch District
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Reformers
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Avestan geography, Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek language, Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati People
The Gujarati people, or Gujaratis, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who reside in or can trace their ancestry or heritage to a region of the Indian subcontinent primarily centered in the present-day western Indian state of Gujarat. They primarily speak Gujarati language, Gujarati, an Indo-Aryan language. While Gujaratis mainly inhabit Gujarat, they have a Gujarati diaspora, diaspora worldwide. Geographical locations Despite significant migration primarily for economic reasons, most Gujaratis in India live in the state of Gujarat in Western India. Gujaratis also form a significant part of the populations in the neighboring metropolis of Mumbai Metropolitan Region, Mumbai and union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, formerly Portuguese Empire, colonial possessions of Portugal. There are very large Gujarati immigrant communities in other parts of India, most notably in Mumbai, Pune, Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore and other cities l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mistri
Mistri, or Mistry, is a term for a master-craftsman, foreman or supervisor of manual workers in India. Mistri is being replaced with terms "supervisor" and master craftsman with "Senior Technician" by the Indian Railway who replaced the designation of Mistris and Master Craftsman with terms "supervisor" and "senior technician" in year 2005 making the term Mistri redundant. The word ''Mistri'', or ''Mistry'', is adopted into the Gujarati language from the Portuguese word ''Mestre'' meaning ''Master'' or ''Teacher''. The Portuguese were present in Gujarat since 1500 in Diu. The Mistris of Kutch and Kadia Kshatriya communities worked on building Diu Fort and the Portuguese called them ''Mestre'' due to their skills at fort building. Mistri besides carpenter for ( Kumawat, Suthar community) also meant Contractor American anthropology, 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutch Gurjar Kshatriya
Kutch Gurjar Kshatriya (also known as Mistri or Mestri) are a minority Hindu community of Gujarat in India, who claim to be Kshatriya. They are an artisan community related with masonry, artistic carvings, sculpting and building and construction works. They are also known as the Mistris of Kutch adopting word Mistri, a term used in British India for master-craftsman, thekedar, foreman or supervisor or for those who were expert in building and construction.Mistri Encyclopaedia of Backward Castes By Neelam Yadav Page 316. History  The community is believ ...
The community is believ ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharamshalas
A dharamshala, also written as dharmashala, is a public resthouse or shelter in the Indian subcontinent. It also refers to Sikhism, Sikh places of worship before the introduction of Gurdwaras. Just as Caravanserai, sarai are for travellers and caravans, dharamshalas are built for religious travellers at pilgrimage sites. In Nepal there are dharamshalas especially built for pilgrims as well as dharamshalas for locals. Etymology ''Dharamshala'' (Devanagari: धर्मशाला; ITRANS: Dharmashaalaa; IAST: Dharmaśālā) is a word (derived from Sanskrit) that is a compound of ''dharma'' (धर्म) and ''shālā'' (शाला). A loose translation into English would be 'spiritual dwelling' or, more loosely, 'sanctuary'. Rendering a precise literal translation into English is problematic due to the vast and conceptually rich semantic field of the word ''Dharma#Etymology, dharma'', and the cultural aspect of India. In common Hindu usage, the word ''dharamshala'' refers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
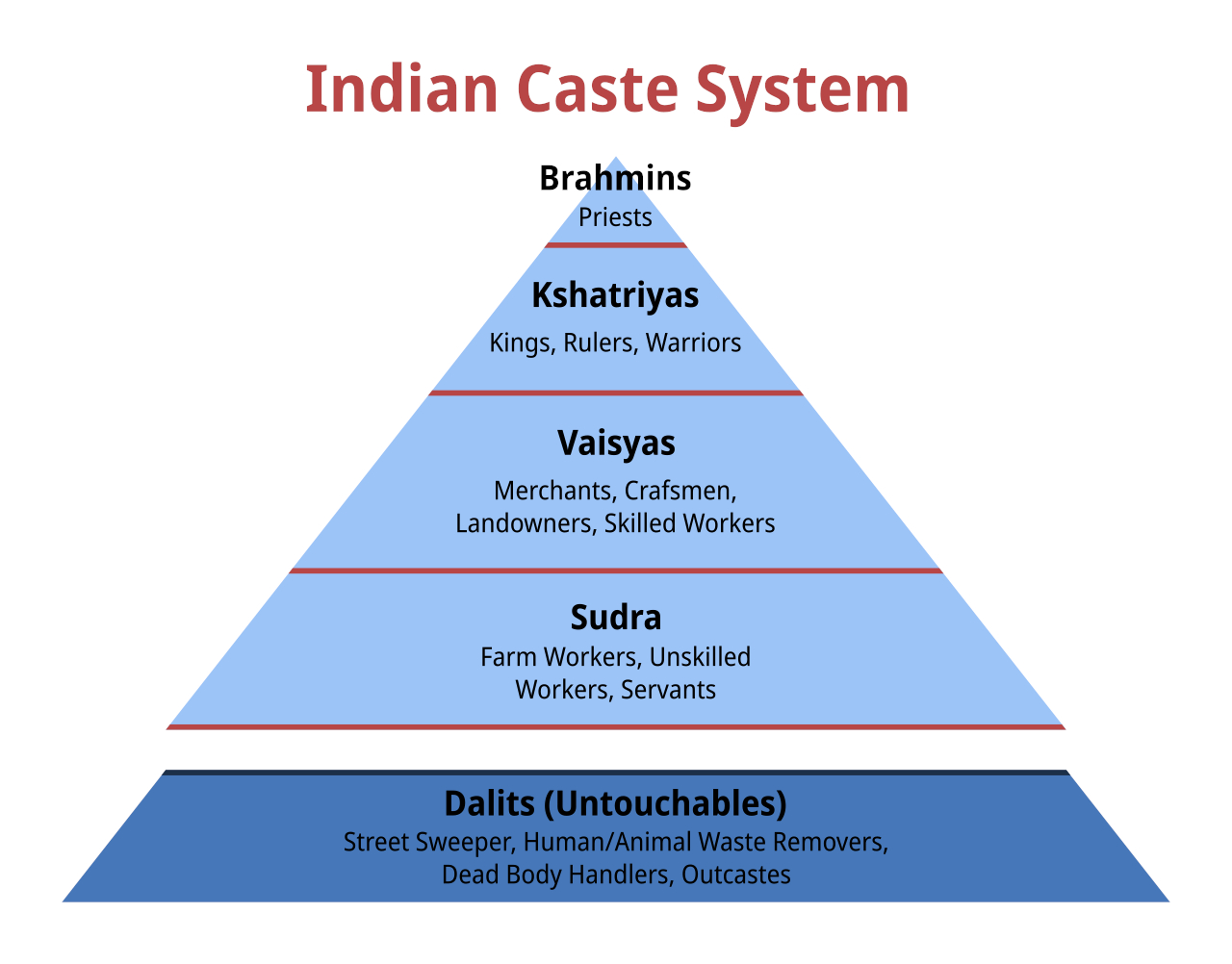
Harijan
Dalit ( from meaning "broken/scattered") is a term used for untouchables and outcasts, who represented the lowest stratum of the castes in the Indian subcontinent. They are also called Harijans. Dalits were excluded from the fourfold varna of the caste hierarchy and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Several scholars have drawn parallels between Dalits and the '' Burakumin'' of Japan, the '' Baekjeong'' of Korea and the peasant class of the medieval European feudal system. Dalits predominantly follow Hinduism with significant populations following Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Islam. The constitution of India includes Dalits as one of the Scheduled Castes; this gives Dalits the right to protection, positive discrimination (known as reservation in India), and official development resources. Terminology The term ''Dalit'' is for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swadeshi Movement
The Swadeshi movement was a self-sufficiency movement that was part of the Indian independence movement and contributed to the development of Indian nationalism. Before the BML Government's decision for the partition of Bengal was made public in December 1903, there was a lot of growing discontentment among the Indians. In response the Swadeshi movement was formally started from Town Hall at Calcutta on 7 August 1905 to curb foreign goods by relying on domestic production. Mahatma Gandhi described it as the soul of swaraj (self-rule). The movement took its vast size and shape after rich Indians donated money and land dedicated to Khadi and Gramodyog societies which started cloth production in every household. It also included other village industries so as to make village self-sufficient and self-reliant. The Indian National Congress used this movement as arsenal for its freedom struggle and ultimately on 15 August 1947, a hand-spun Khadi tricolor Ashoka Chakra Indian flag wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |