|
Odd-chain Fatty Acid
Odd-chain fatty acids are those fatty acids that contain an odd number of carbon atoms. In addition to being classified according to their saturation or unsaturation, fatty acids are also classified according to their odd or even numbers of constituent carbon atoms. With respect to natural abundance, most fatty acids are even chain, e.g. palmitic (C16) and stearic (C18). In terms of physical properties, odd and even fatty acids are similar, generally being colorless, soluble in alcohols, and often somewhat oily. The odd-chain fatty acids are biosynthesized and metabolized slightly differently from the even-chained relatives. In addition to the usual C12-C22 long chain fatty acids, some very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) are also known. Some of these VLCFAs are also of the odd-chain variety. Metabolism Biosynthesis The most common OCFA are the saturated C15 and C17 derivatives, respectively pentadecylic acid and margaric acid. Even-chained fatty acids are synthesiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmalonyl-CoA
Methylmalonyl-CoA is the thioester consisting of coenzyme A linked to methylmalonic acid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of succinyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (aka the Citric Acid Cycle, or Krebs Cycle). Biosynthesis and metabolism Methylmalonyl-CoA results from the metabolism of fatty acid with an odd number of carbons, of amino acids valine, isoleucine, methionine, threonine or of cholesterol side-chains, forming Propionyl-CoA. The latter is also formed from propionic acid, which bacteria produce in the intestine. Propionyl-CoA and bicarbonate are converted to Methylmalonyl-CoA by the enzyme propionyl-CoA Carboxylase. It then is converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT). This reaction is a reversible isomerization. In this way, the compound enters the Citric Acid Cycle. The following diagram demonstrates the aforementioned reaction: Propionyl CoA + Bicarbonate → Methylmalonyl CoA → Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaric Acid
Margaric acid, or heptadecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid. Its molecular formula is . Classified as an odd-chain fatty acid, it occurs as a trace component of the fat and milkfat of ruminants. Salts and esters of margaric acid are called heptadecanoates. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek μάργαρος (''márgar(on)''), meaning "pearl(y)", due to its appearance. Semiochemistry For many species, margaric acid plays a role as a semiochemical. Specifically, it possesses pheromonic and allomonic properties. Margaric acid has been identified in the subcaudal gland secretions of the European badger (''Meles meles'') and in the occipital gland secretions of male Bactrian camels (''Camelus bactrianus'') where it is one of the many pheromonic chemicals responsible for aiding in the finding and selection of mates. Margaric acid is an attractant of the khapra beetle (''Trogoderma granarium'') and the yellow fever mosquito (''Aedes aegypti'') but is a repellent of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentadecanoic Acid
Pentadecylic acid, also known as pentadecanoic acid or C15:0, is an odd-chain saturated fatty acid. Its molecular formula is . It is a colorless solid. A laboratory preparation involves permanganate oxidation of 1-hexadecene (). It is one of the most common odd-chain fatty acids, which are rare in nature. Pentadecylic acid is found primarily in dairy fat, as well as in ruminant meat and some fish and plants. The butterfat in cow milk is its major dietary source, comprising 1.2% of cow milk fat. Rare genetic disorders causing unusually high concentrations of C15:0 and C17:0, including Refsum disease, Zellweger syndrome, and propionic acidemia, confirmed endogenous synthesis of these odd-chain FAs in humans, involving alpha oxidation. Research Pentadecanoic acid has been compared to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to evaluate the possibility that pentadecanoic acid is a previously unrecognized essential fatty acid. See also * List of saturated fatty acids Saturated fatty a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionic Acid Chemical Structure
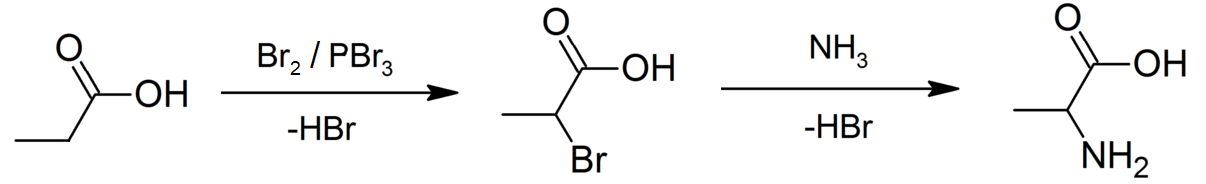
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek language, Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the Carboxylate salt, salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TCA Cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-CoA Redox, oxidation. The energy released is available in the form of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. The Hans Krebs (biochemist), Krebs cycle is used by organisms that generate energy via Cellular respiration, respiration, either anaerobic respiration, anaerobically or aerobic respiration, aerobically (organisms that Fermentation, ferment use different pathways). In addition, the cycle provides precursor (chemistry), precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADH, which are used in other reactions. Its central importance to many Metabolic pathway, biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest metabolism components. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It plays an essential role in the nervous system by supporting myelinogenesis, myelin synthesis and is critical for the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. While animals require B12, plants do not, relying instead on alternative enzymatic pathways. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and is synthesized exclusively by certain archaea and bacteria. Natural food sources include meat, shellfish, liver, fish, poultry, Egg as food, eggs, and dairy products. It is also added to many breakfast cereals through food fortification and is available in dietary supplement and pharmaceutical forms. Supplements are commonly taken orally but may be administered via intramuscular injection to treat defic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (, MCM), mitochondrial, also known as methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUT'' gene. This vitamin B12-dependent enzyme catalyzes the isomerization of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in humans. Mutations in ''MUT'' gene may lead to various types of methylmalonic aciduria. MCM was first identified in rat liver and sheep kidney in 1955. In its latent form, it is 750 amino acids in length. Upon entry to the mitochondria, the 32 amino acid mitochondrial leader sequence at the N-terminus of the protein is cleaved, forming the fully processed monomer. The monomers then associate into homodimers, and bind AdoCbl (one for each monomer active site) to form the final, active holoenzyme form. Structure Gene The ''MUT'' gene lies on the chromosome location of 6p12.3 and consists of 13 exons, spanning over 35kb. Protein The mature enzyme is a homodimer with the N-terminal CoA binding domain and the C- terminal cobala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |