|
Occultammina Sp
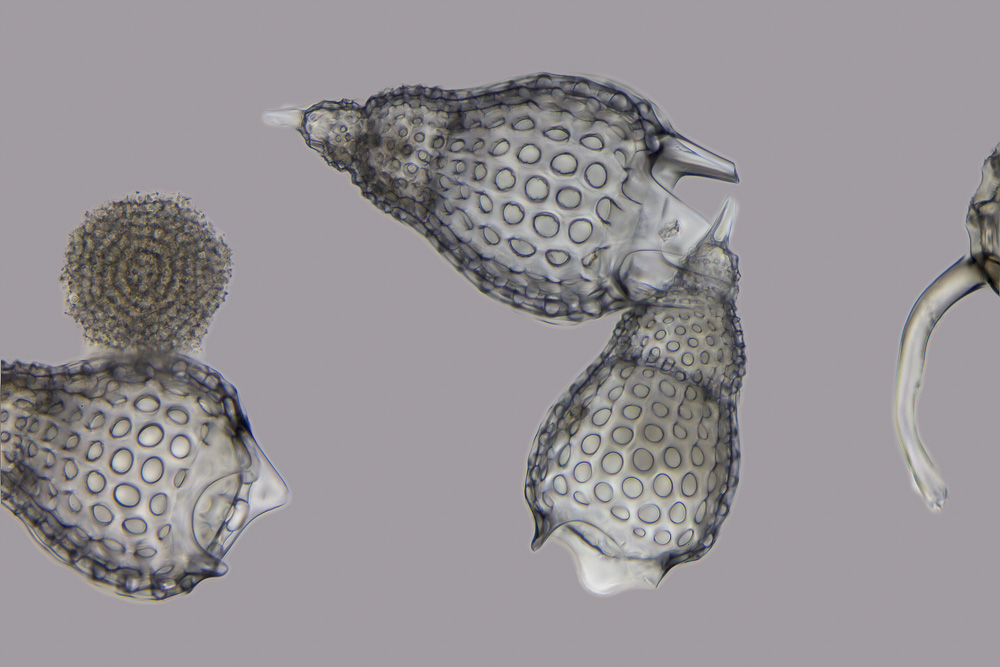
''Occultammina'' is a genus of xenophyophorean foraminifera known from the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It is notable for being the first known infaunal xenophyophore as well as for being a possible identity for the enigmatic trace fossil ''Paleodictyon''. Distribution and habitat Like all other known xenophyophores, ''Occultammina'' is found in the deep ocean; the first known specimen was first discovered in 1980 at a depth of in the Ogasawara Trench, off the coast of Japan and described in 1982 by a joint research team from the University of Copenhagen and the University of Tokyo. Further specimens referred to ''Occultammina'' sp. have been found at a depth of in the Porcupine Abyssal Plain, in the North Atlantic. Further studies have expanded its geographical and bathymetric range from in the Ogasawara Trench and from in the North Atlantic, and also recorded its presence at in the Japan trench. ''Occultammina'' sp. has also been recovered at a depth of about near the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera Genera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test, or shell, which can have either one or multiple chambers, some becoming quite elaborate in stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexactinellid
Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed siliceous spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually classified along with other sponges in the phylum Porifera, but some researchers consider them sufficiently distinct to deserve their own phylum, Symplasma. Some experts believe glass sponges are thlongest-lived animals on earth these scientists tentatively estimate a maximum age of up to 15,000 years. Biology Glass sponges are relatively uncommon and are mostly found at depths from below the sea level. Although the species '' Oopsacas minuta'' has been found in shallow water, others have been found much deeper. They are found in all oceans of the world, although they are particularly common in Antarctic and Northern Pacific waters. They are more-or-less cup-shaped animals, ranging from in height, with sturdy lattice-like internal skeletons made up of fused spicules of silica. The body is relatively symmetrical, with a large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North American from the Eurasian Plate and the African Plate, north and south of the Azores Triple Junction respectively. In the South Atlantic, it separates the African and South American plates. The ridge extends from a junction with the Gakkel Ridge (Mid-Arctic Ridge) northeast of Greenland southward to the Bouvet Triple Junction in the South Atlantic. Although the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is mostly an underwater feature, portions of it have enough elevation to extend above sea level, for example in Iceland. The ridge has an average spreading rate of about per year. Discovery A ridge under the northern Atlantic Ocean was first inferred by Matthew Fontaine Maury in 1853, based on soundings by the USS ''Dolphin''. The existence of the ridge an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleodictyon P
''Paleodictyon'' is a trace fossil, usually interpreted to be a burrow, which appears in the geologic marine record beginning in the Precambrian/Early Cambrian and in modern ocean environments.Swinbanks, D. D., 1982: ''Paleodictyon'': the traces of infaunal xenophyophores? Science, v. 218, 47-49. ''Paleodictyon'' were first described by Giuseppe Meneghini in 1850. The origin of the trace fossil is enigmatic and numerous candidates have been proposed. Description ''Paleodictyon'' consist of thin tunnels or ridges that usually form hexagonal or polygonal-shaped honeycomb-like network.KU Ichnology - Studying the Traces of Life IBGS Research Group Both irregular and regular nets are known throughout the stratigraphic range of ''Paleodictyon'', but it is the striking regular honeycomb patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radium-226
Radium (88Ra) has no stable or nearly stable isotopes, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. The longest lived, and most common, isotope of radium is 226Ra with a half-life of . 226Ra occurs in the decay chain of 238U (often referred to as the radium series). Radium has 33 known isotopes from 202Ra to 234Ra. In 2013 it was discovered that the nucleus of radium-224 is pear-shaped. This was the first discovery of an asymmetric nucleus. List of isotopes , - , 202Ra , , style="text-align:right" , 88 , style="text-align:right" , 114 , 202.00989(7) , 2.6(21) ms .7(+33−3) ms, , , 0+ , , - , rowspan=2, 203Ra , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 88 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 115 , rowspan=2, 203.00927(9) , rowspan=2, 4(3) ms , α , 199Rn , rowspan=2, (3/2−) , rowspan=2, , - , β+ (rare) , 203Fr , - , rowspan=2 style="text-indent:1em" , 203mRa , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 colspan="3" style="text-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polonium-210
Polonium-210 (210Po, Po-210, historically radium F) is an isotope of polonium. It undergoes alpha decay to stable 206Pb with a half-life of 138.376 days (about months), the longest half-life of all naturally occurring polonium isotopes. First identified in 1898, and also marking the discovery of the element polonium, 210Po is generated in the decay chain of uranium-238 and radium-226. 210Po is a prominent contaminant in the environment, mostly affecting seafood and tobacco. Its extreme toxicity is attributed to intense radioactivity, capable of severely harming humans. History In 1898, Marie and Pierre Curie discovered a strongly radioactive substance in pitchblende and determined that it was a new element; it was one of the first radioactive elements discovered. Having identified it as such, they named the element polonium after Marie's home country, Poland. Willy Marckwald discovered a similar radioactive activity in 1902 and named it radio-tellurium, and at roughly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead-210
Lead (82Pb) has four stable isotopes: 204Pb, 206Pb, 207Pb, 208Pb. Lead-204 is entirely a primordial nuclide and is not a radiogenic nuclide. The three isotopes lead-206, lead-207, and lead-208 represent the ends of three decay chains: the uranium series (or radium series), the actinium series, and the thorium series, respectively; a fourth decay chain, the neptunium series, terminates with the thallium isotope 205Tl. The three series terminating in lead represent the decay chain products of long-lived primordial 238U, 235U, and 232Th, respectively. However, each of them also occurs, to some extent, as primordial isotopes that were made in supernovae, rather than radiogenically as daughter products. The fixed ratio of lead-204 to the primordial amounts of the other lead isotopes may be used as the baseline to estimate the extra amounts of radiogenic lead present in rocks as a result of decay from uranium and thorium. (See lead–lead dating and uranium–lead dating). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiolaria
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards. Description Radiolarians have many needle-like pseudopods supported by bundles of microtubules, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus and most other organelles are in the endoplasm, while the ectoplasm is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
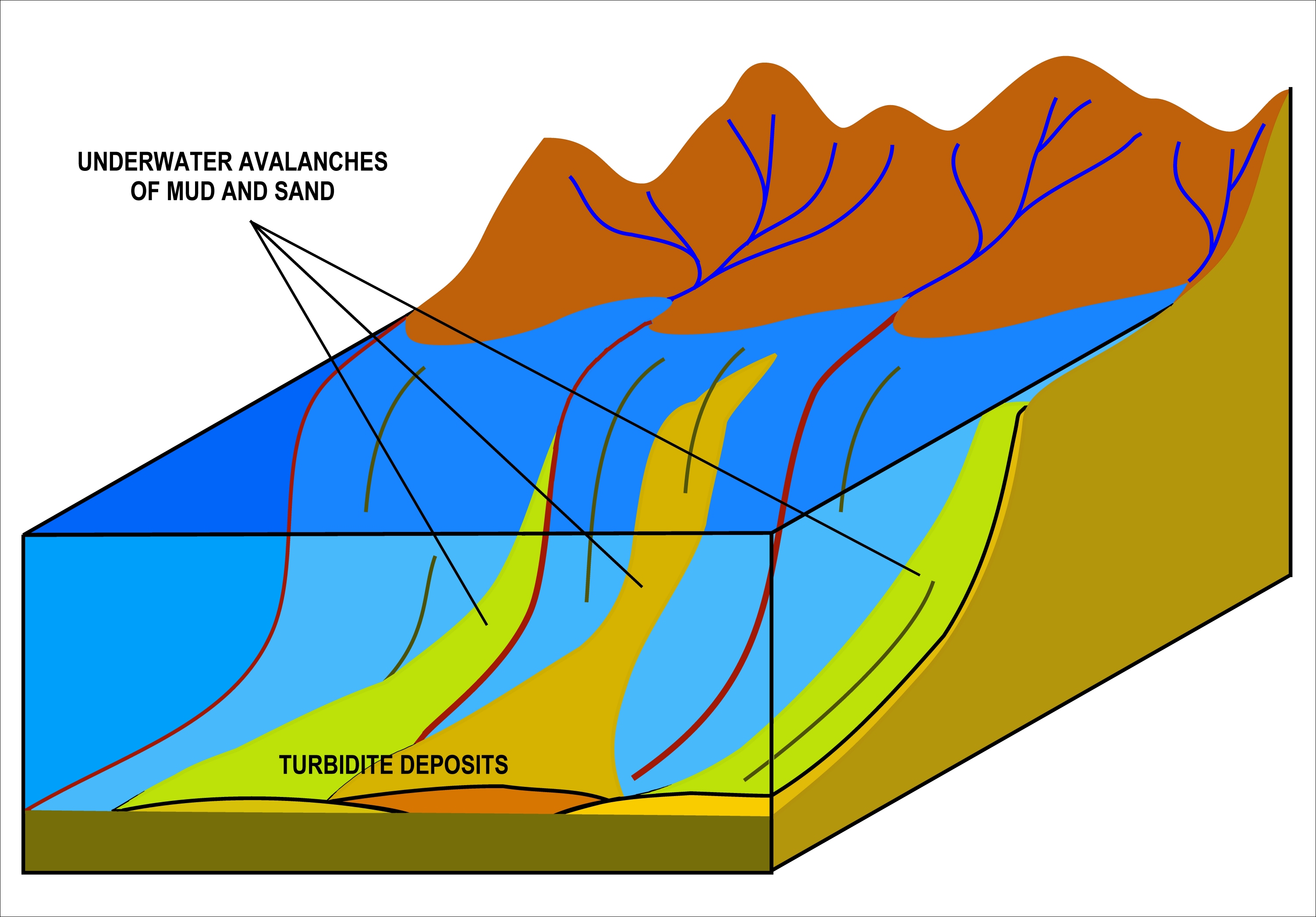
Turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophyophorea
Xenophyophorea is a clade of foraminiferans. Members of this class are multinucleate unicellular organisms found on the ocean floor throughout the world's oceans, at depths of . They are a kind of foraminiferan that extract minerals from their surroundings and use them to form an exoskeleton known as a test. They were first described by Henry Bowman Brady in 1883. They are abundant on abyssal plains, and in some regions are the dominant species. Fifteen genera and 75 species have been described, varying widely in size. The largest, '' Syringammina fragilissima'', is among the largest known coenocytes, reaching up to in diameter. Naming and classification The name Xenophyophora means "bearer of foreign bodies", from the Greek. This refers to the sediments, called xenophyae, which are cemented together to construct their tests. In 1883, Henry Bowman Brady classified them as primitive Foraminifera. Later they were placed within the sponges. In the beginning of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |